Intro
Embark on an underwater adventure with our comprehensive guide on how to build a submarine. Learn the 7 crucial steps to construct a submersible vessel, from designing and planning to launching and testing. Discover the importance of materials, propulsion systems, and safety features, and master the art of submarine building with our expert insights and tips.
Building a submarine is a complex and challenging task that requires careful planning, precision engineering, and attention to detail. Whether you're a seasoned engineer or a curious enthusiast, constructing a submarine can be a fascinating project that pushes the boundaries of innovation and exploration. In this article, we'll delve into the 7 essential steps to build a submarine, highlighting the key considerations, materials, and techniques involved in this incredible endeavor.
The importance of submarines cannot be overstated. These underwater vessels have been used for centuries, from military operations to scientific research, and have played a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the ocean and its ecosystems. With the increasing need for sustainable and efficient transportation, as well as the exploration of the world's oceans, building a submarine has become an exciting and relevant pursuit.
From conceptualization to launch, building a submarine requires a multidisciplinary approach that combines expertise in engineering, materials science, and naval architecture. In this article, we'll guide you through the 7 essential steps to build a submarine, providing valuable insights and practical advice for those embarking on this extraordinary journey.

Step 1: Design and Planning
The first step in building a submarine is to design and plan the vessel's architecture, taking into account its intended purpose, size, and performance requirements. This involves creating detailed drawings and models of the submarine's hull, propulsion system, and internal layout.
Key considerations in this stage include:
- Determining the submarine's dimensions, shape, and material composition
- Selecting the propulsion system, including the type of engine, transmission, and propeller
- Designing the ballast tanks and buoyancy control system
- Planning the electrical and electronics systems, including power generation, distribution, and communication equipment

Materials and Tools Needed
- Computer-aided design (CAD) software
- Technical drawings and models
- Material selection and procurement
- Engineering expertise in naval architecture and mechanical engineering
Step 2: Hull Construction
Once the design and planning phase is complete, the next step is to construct the submarine's hull. This involves fabricating the steel plates, welding them together, and assembling the hull structure.
Key considerations in this stage include:
- Selecting the right materials for the hull, including steel, aluminum, or fiberglass
- Ensuring the hull's structural integrity and watertightness
- Installing the ballast tanks and buoyancy control system
- Integrating the propulsion system and electrical infrastructure

Materials and Tools Needed
- Steel plates or other hull materials
- Welding equipment and expertise
- Hull fabrication and assembly tools
- Quality control and inspection equipment
Step 3: Propulsion System Installation
The propulsion system is the heart of the submarine, providing the power and thrust needed to move through the water. This stage involves installing the engine, transmission, and propeller, as well as integrating the electrical and control systems.
Key considerations in this stage include:
- Selecting the right propulsion system for the submarine's size and performance requirements
- Ensuring the system's efficiency, reliability, and safety
- Integrating the propulsion system with the electrical and control infrastructure
- Testing and validating the propulsion system's performance

Materials and Tools Needed
- Engine and transmission components
- Propeller and shafting
- Electrical and control systems
- Testing and validation equipment
Step 4: Electrical and Electronics Installation
The electrical and electronics systems are critical to the submarine's operation, providing power, communication, and navigation capabilities. This stage involves installing the electrical infrastructure, including generators, batteries, and distribution systems, as well as integrating the electronics and communication equipment.
Key considerations in this stage include:
- Selecting the right electrical and electronics systems for the submarine's size and performance requirements
- Ensuring the system's efficiency, reliability, and safety
- Integrating the electrical and electronics systems with the propulsion and control infrastructure
- Testing and validating the electrical and electronics systems' performance

Materials and Tools Needed
- Electrical infrastructure components, including generators, batteries, and distribution systems
- Electronics and communication equipment
- Testing and validation equipment
- Electrical engineering expertise
Step 5: Interior Outfitting and Finishing
Once the hull, propulsion, and electrical systems are installed, the next step is to outfit the interior of the submarine. This involves installing the interior structures, including the crew quarters, galley, and control room, as well as finishing the interior surfaces and installing the necessary fixtures and equipment.
Key considerations in this stage include:
- Designing and installing the interior structures and surfaces
- Ensuring the interior's functionality, comfort, and safety
- Integrating the interior systems with the propulsion, electrical, and control infrastructure
- Testing and validating the interior systems' performance

Materials and Tools Needed
- Interior materials, including steel, aluminum, or fiberglass
- Interior fixtures and equipment, including furniture, appliances, and communication devices
- Interior design and installation expertise
- Testing and validation equipment
Step 6: Testing and Validation
Before the submarine can be launched and operated, it must undergo a series of tests and validation procedures to ensure its safety, performance, and reliability. This stage involves testing the submarine's systems, including the propulsion, electrical, and control systems, as well as conducting sea trials to validate its performance in various operating conditions.
Key considerations in this stage include:
- Developing a comprehensive testing and validation plan
- Conducting system-level testing and integration testing
- Performing sea trials to validate the submarine's performance
- Identifying and addressing any issues or defects

Materials and Tools Needed
- Testing and validation equipment, including sensors, data loggers, and analysis software
- Sea trial equipment, including navigation and communication systems
- Testing and validation expertise
- Issue tracking and resolution tools
Step 7: Launch and Commissioning
The final step in building a submarine is to launch and commission the vessel. This involves launching the submarine into the water, conducting final testing and validation, and preparing the vessel for operational service.
Key considerations in this stage include:
- Developing a comprehensive launch and commissioning plan
- Conducting final testing and validation procedures
- Preparing the submarine for operational service
- Training the crew and support personnel

Materials and Tools Needed
- Launch and commissioning equipment, including cranes, winches, and support vessels
- Testing and validation equipment
- Training and documentation materials
- Crew and support personnel
Submarine Image Gallery






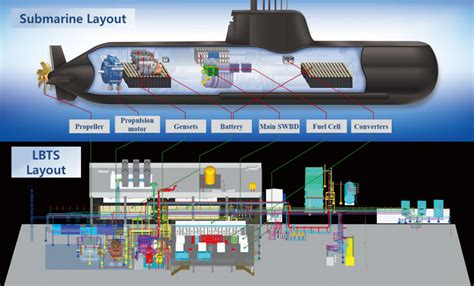

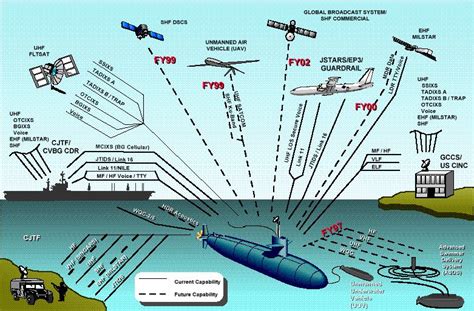

In conclusion, building a submarine is a complex and challenging task that requires careful planning, precision engineering, and attention to detail. By following these 7 essential steps, you can ensure that your submarine is safe, efficient, and effective, and that it meets the performance and operational requirements of its intended purpose. Whether you're a seasoned engineer or a curious enthusiast, building a submarine is an exciting and rewarding project that can push the boundaries of innovation and exploration.
