Self-employment can be a bit tricky when it comes to calculating income for food stamps. However, understanding the process can help you navigate the system and ensure you receive the benefits you're eligible for. In this article, we'll explore five ways to calculate self-employment income for food stamps, providing you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions.
What Counts as Self-Employment Income?
Before we dive into the calculation methods, it's essential to understand what counts as self-employment income. Self-employment income includes earnings from:
- Freelancing or consulting
- Running a small business
- Selling products online or in-person
- Renting out properties or equipment
- Farming or agricultural activities
Any income earned from these activities is considered self-employment income and must be reported when applying for food stamps.
Method 1: Net Profit Calculation
The first method of calculating self-employment income for food stamps is to determine your net profit. To do this, you'll need to:
- Calculate your total self-employment income
- Subtract business expenses, such as supplies, equipment, and rent
- Subtract depreciation and other deductions
The resulting amount is your net profit, which is then used to calculate your self-employment income.
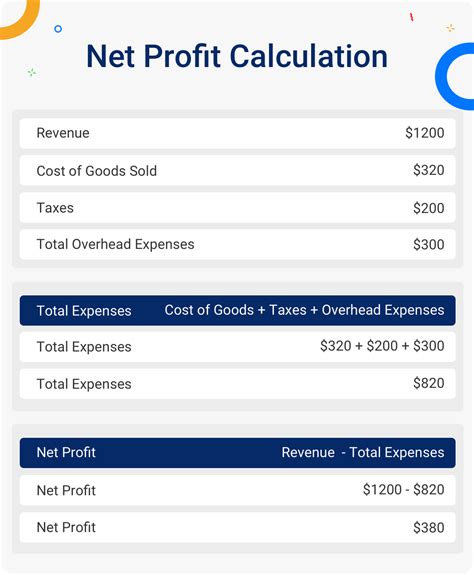
For example, let's say you earn $10,000 from freelancing and have $3,000 in business expenses. Your net profit would be $7,000.
Method 2: Average Monthly Income Calculation
The second method involves calculating your average monthly income from self-employment. To do this, you'll need to:
- Calculate your total self-employment income for the year
- Divide the total by 12 to get your average monthly income
This method is useful if you have a fluctuating income or if you're just starting out with your self-employment venture.
For example, if you earn $50,000 from self-employment in a year, your average monthly income would be $4,166.67.
Method 3: Quarterly Income Calculation
The third method involves calculating your self-employment income on a quarterly basis. To do this, you'll need to:
- Calculate your total self-employment income for the quarter
- Divide the total by 3 to get your average monthly income for the quarter
This method is useful if you have a seasonal business or if you experience fluctuations in income throughout the year.
For example, if you earn $20,000 from self-employment in a quarter, your average monthly income for that quarter would be $6,666.67.
Method 4: Projected Income Calculation
The fourth method involves projecting your self-employment income for the upcoming year. To do this, you'll need to:
- Estimate your total self-employment income for the upcoming year
- Divide the estimated total by 12 to get your projected average monthly income
This method is useful if you're just starting out with your self-employment venture or if you're experiencing significant changes in your business.
For example, if you estimate that you'll earn $60,000 from self-employment in the upcoming year, your projected average monthly income would be $5,000.
Method 5: Accounting Records Calculation
The fifth method involves using your accounting records to calculate your self-employment income. To do this, you'll need to:
- Review your accounting records for the past year
- Calculate your total self-employment income from the records
- Subtract business expenses and deductions to get your net profit
This method is useful if you have a well-established business and accurate accounting records.

For example, if your accounting records show that you earned $80,000 from self-employment and had $20,000 in business expenses, your net profit would be $60,000.
Gallery of Self-Employment Income Calculation Examples
Self-Employment Income Calculation Examples

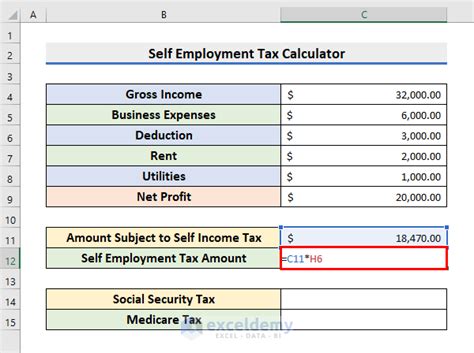

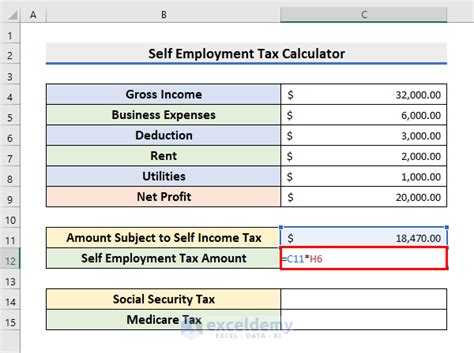
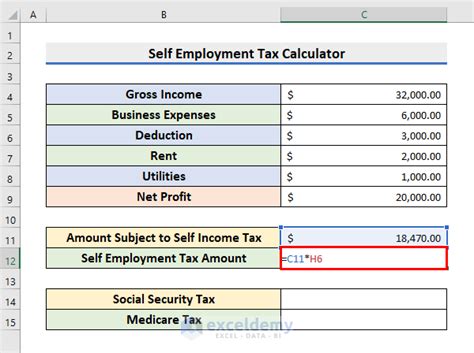
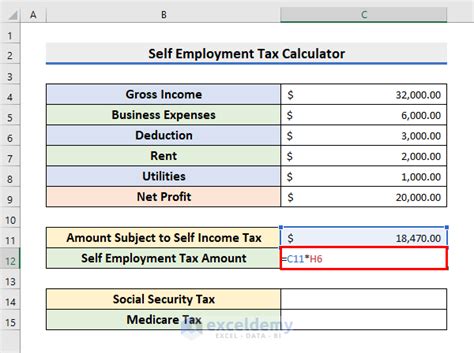

Take Action Today
Calculating self-employment income for food stamps can be complex, but understanding the different methods can help you make informed decisions. By using one or more of the methods outlined above, you can ensure that you're reporting your income accurately and receiving the benefits you're eligible for.
If you have any questions or concerns about calculating self-employment income for food stamps, we encourage you to leave a comment below or reach out to your local food stamp office for guidance.
