The p-value, a statistical measure that helps us determine the significance of our results. It's a crucial concept in data analysis, and fortunately, Excel makes it relatively easy to calculate. In this article, we'll explore three easy ways to find the p-value in Excel.
Whether you're a student, researcher, or data analyst, understanding p-values is essential to make informed decisions. The p-value represents the probability of observing a result as extreme or more extreme than the one you obtained, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. A small p-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that the result is statistically significant, while a large p-value suggests that the result is due to chance.
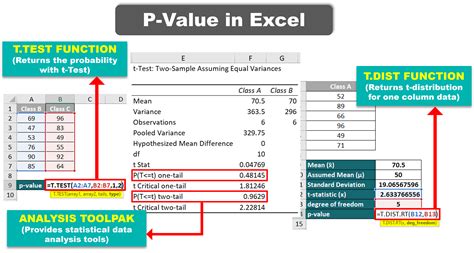
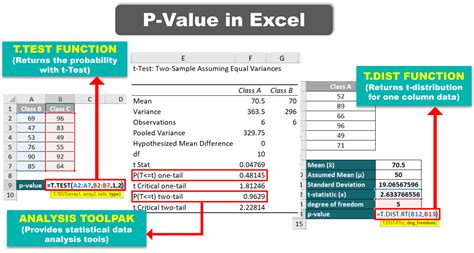
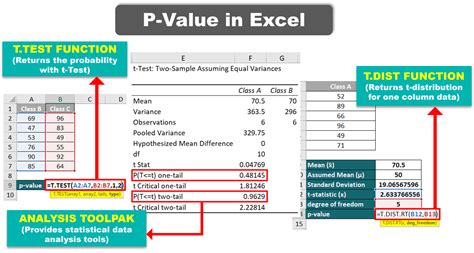
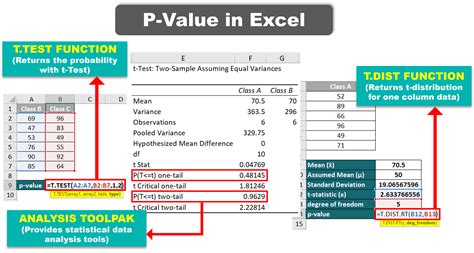
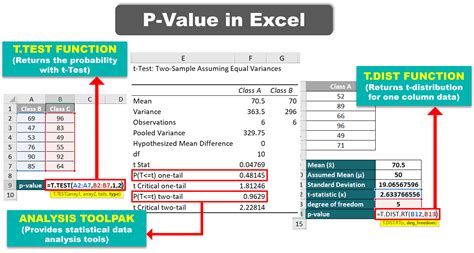
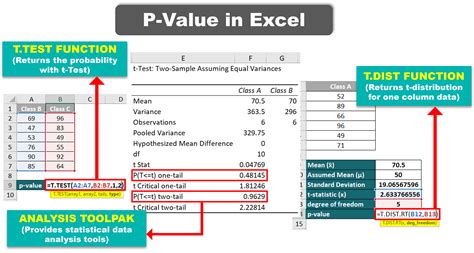
Method 1: Using the T.TEST Function
One of the simplest ways to calculate the p-value in Excel is by using the T.TEST function. This function is useful when you have two samples and want to determine if there's a significant difference between their means.
To use the T.TEST function, follow these steps:
- Enter your data into two columns, A and B.
- Click on the cell where you want to display the p-value.
- Type "=T.TEST(A1:A10,B1:B10,2,3)" and press Enter.
In this example, A1:A10 and B1:B10 represent the ranges of your data, 2 specifies a two-tailed test, and 3 indicates that the data is paired.
What to Do with the Result
The T.TEST function will return the p-value, which you can then use to determine the significance of your result. If the p-value is less than 0.05, you can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there's a statistically significant difference between the means of the two samples.
Method 2: Using the Z.TEST Function
Another way to calculate the p-value in Excel is by using the Z.TEST function. This function is useful when you have a large sample size (typically greater than 30) and want to determine if there's a significant difference between the sample mean and a known population mean.
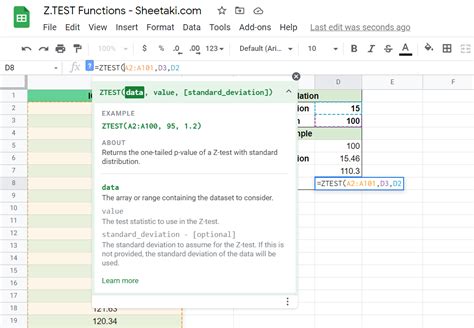
To use the Z.TEST function, follow these steps:
- Enter your data into a column, A.
- Click on the cell where you want to display the p-value.
- Type "=Z.TEST(A1:A100,10,2)" and press Enter.
In this example, A1:A100 represents the range of your data, 10 is the known population mean, and 2 specifies a two-tailed test.
What to Do with the Result
The Z.TEST function will return the p-value, which you can then use to determine the significance of your result. If the p-value is less than 0.05, you can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there's a statistically significant difference between the sample mean and the known population mean.
Method 3: Using the Analysis ToolPak
The Analysis ToolPak is an add-in in Excel that provides a range of statistical functions, including the ability to calculate p-values. To use the Analysis ToolPak, follow these steps:
- Go to the "Data" tab in Excel.
- Click on "Data Analysis" in the Analysis group.
- Select "t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances" or "z-Test: Two Sample for Means".
- Enter your data ranges and select the options you want.
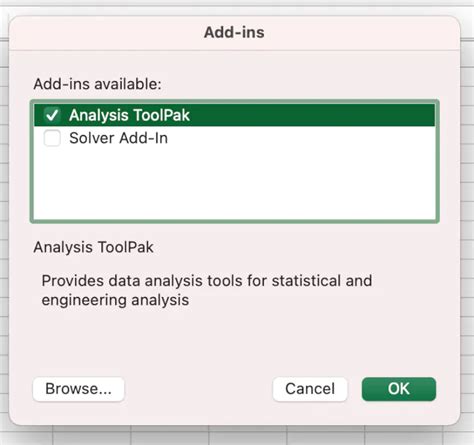
The Analysis ToolPak will return the p-value, which you can then use to determine the significance of your result.
Conclusion
Calculating the p-value in Excel is a straightforward process that can be accomplished using one of three methods: the T.TEST function, the Z.TEST function, or the Analysis ToolPak. By understanding p-values, you can make informed decisions about your data and determine the significance of your results.
P-Value in Excel Image Gallery
We hope this article has helped you understand how to calculate p-values in Excel. If you have any questions or need further clarification, please don't hesitate to ask. Share this article with your friends and colleagues who may find it useful.
