Intro
Heal skin tears with 7 expert tips, promoting wound care, skin repair, and tissue regeneration, to prevent infection and scarring, ensuring optimal healing and skin health.
Healing skin tears can be a challenging and delicate process, requiring careful attention to promote proper healing and minimize the risk of infection. Skin tears are a common injury, particularly among the elderly and those with fragile skin, and can be caused by a variety of factors including falls, scratches, and medical procedures. Understanding the best practices for healing skin tears is essential for maintaining skin integrity and overall health.
The importance of proper wound care cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in the healing process. Improper care can lead to complications, such as infection, delayed healing, and scarring. Moreover, skin tears can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and mobility issues. Therefore, it is essential to take a proactive approach to healing skin tears, using evidence-based practices and techniques to promote optimal healing.
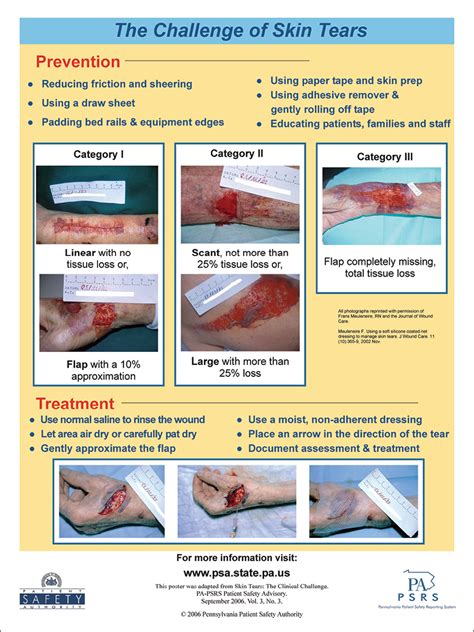
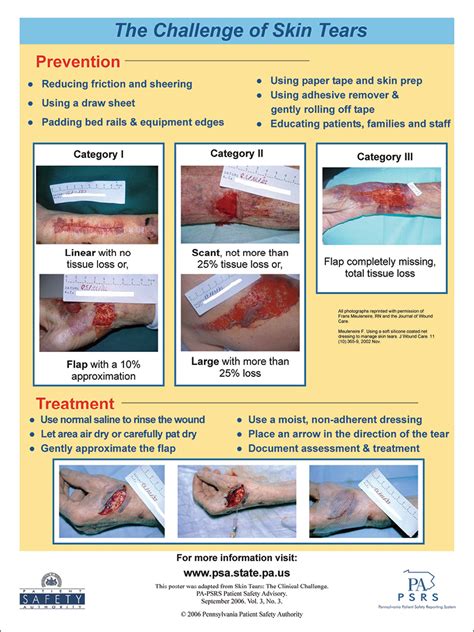
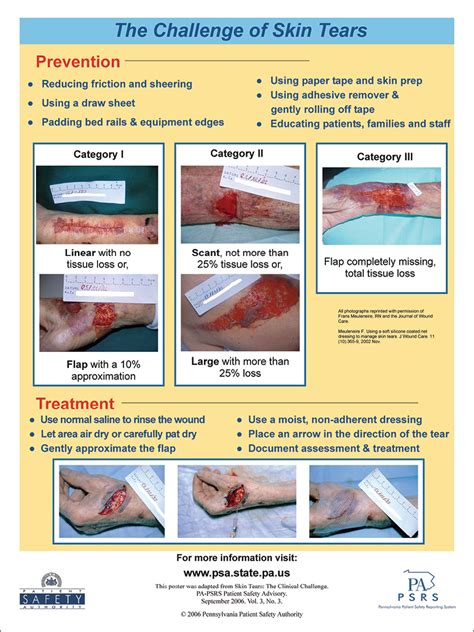
Skin tears can be classified into three categories: partial-thickness, full-thickness, and avulsion. Partial-thickness skin tears involve damage to the epidermis and dermis, while full-thickness skin tears extend through all layers of the skin. Avulsion skin tears occur when the skin is completely torn away from the underlying tissue. Each type of skin tear requires a unique approach to care, highlighting the need for individualized treatment plans.
Understanding Skin Tears
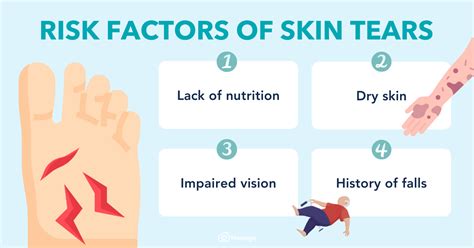
Causes of Skin Tears
Skin tears can be caused by a range of factors, including: * Mechanical stress: Skin tears can occur due to mechanical stress, such as friction, shear, or pressure. * Skin fragility: Fragile skin is more prone to tearing, particularly in older adults. * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and vascular disease, can increase the risk of skin tears. * Nutritional deficiencies: Poor nutrition can impair skin health, making it more susceptible to tears.Assessing Skin Tears
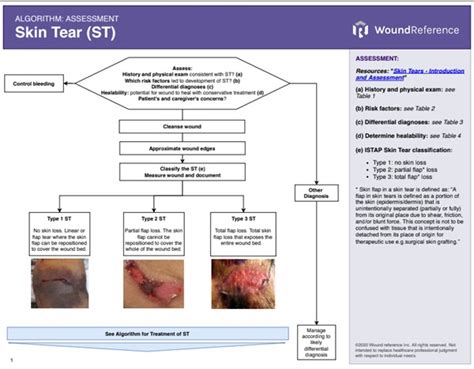
Assessment Techniques
Assessment techniques for skin tears include: * Visual inspection: Visual inspection of the tear to determine its size, depth, and location. * Palpation: Palpation of the surrounding tissue to assess for tenderness, swelling, or other signs of injury. * Medical history: Review of the individual's medical history to identify underlying conditions that may impact healing.Cleaning and Debridement
Cleaning and Debridement Techniques
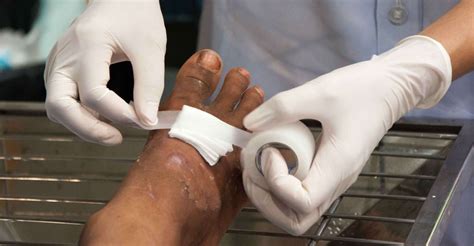
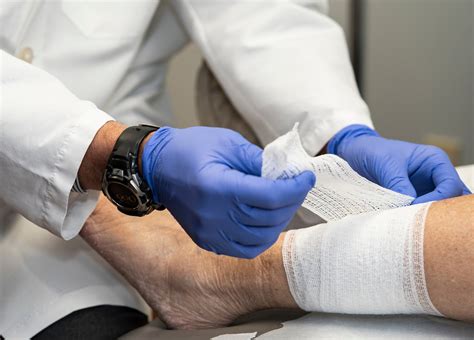
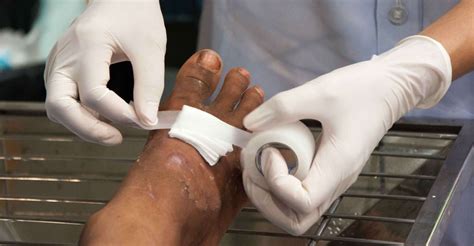
Cleaning and debridement techniques include: * Saline irrigation: Irrigation of the wound with sterile saline solution to remove bacteria and debris. * Debridement: Removal of dead tissue and debris from the wound, using sterile instruments and techniques.Dressing and Bandaging

Dressing and Bandaging Options
Dressing and bandaging options include: * Hydrocolloid dressings: Dressings that create a moist environment, promoting healing and tissue growth. * Foam dressings: Dressings that provide cushioning and protection, while promoting a dry environment. * Compression bandages: Bandages that provide compression, helping to reduce swelling and promote healing.Pain Management

Pain Management Techniques
Pain management techniques include: * Topical analgesics: Creams or ointments applied directly to the wound to reduce pain and discomfort. * Oral analgesics: Medications taken orally to reduce pain and discomfort. * Non-pharmacological interventions: Techniques such as relaxation, meditation, and deep breathing to reduce pain and promote relaxation.Nutrition and Hydration

Nutrition and Hydration Tips
Nutrition and hydration tips include: * Eating a balanced diet: Consuming a diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals to promote healing and tissue growth. * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water to maintain hydration and promote healing. * Avoiding nutritional deficiencies: Avoiding deficiencies in key nutrients, such as vitamin C and zinc, which are essential for healing.Wound Monitoring
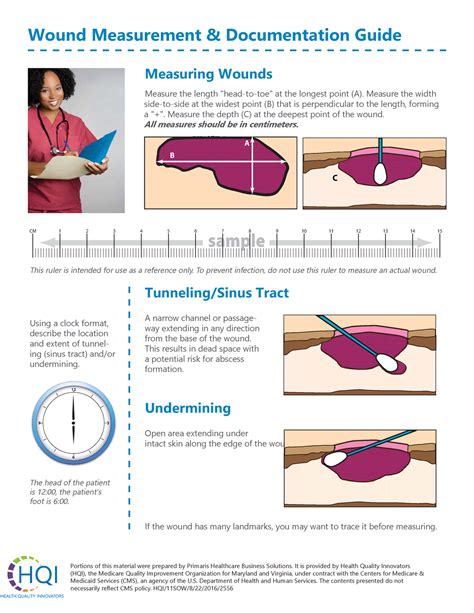
Wound Monitoring Techniques
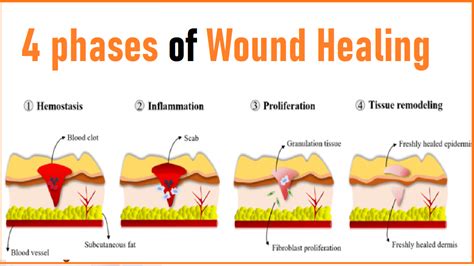
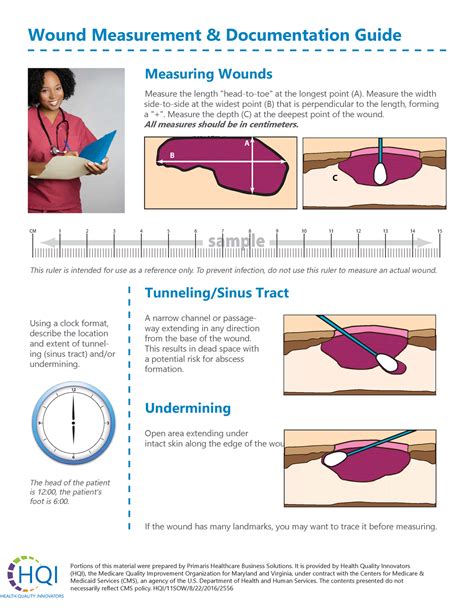
Wound monitoring techniques include: * Visual inspection: Regular visual inspection of the wound to assess for signs of healing or complications. * Measurement: Measurement of the wound to track changes in size and depth. * Photography: Photography of the wound to document progress and identify potential complications.Healing Skin Tears Image Gallery


In conclusion, healing skin tears requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the individual's unique needs and circumstances. By following the 7 tips outlined in this article, healthcare professionals can promote optimal healing, minimize the risk of complications, and improve overall health outcomes. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on healing skin tears, and to explore the resources and information provided in this article to learn more about this important topic. Whether you are a healthcare professional or an individual seeking to promote skin health, we hope that this article has provided you with valuable insights and practical tips to achieve your goals.
