Intro
Learn how to create a normal distribution curve in Excel with ease. Discover the step-by-step process to visualize and analyze data using the bell curve, standard deviation, and mean. Master Excels normal distribution functions, including NORM.DIST and NORM.S.DIST, to accurately model real-world phenomena.
The normal distribution curve, also known as the Gaussian distribution or bell curve, is a fundamental concept in statistics and data analysis. It is a probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean. Creating a normal distribution curve in Excel can be a bit tricky, but with the right steps, you can easily visualize and analyze your data.
Why Create a Normal Distribution Curve in Excel?
Creating a normal distribution curve in Excel can help you:
- Visualize and understand the distribution of your data
- Identify patterns and trends in your data
- Analyze and compare different datasets
- Make predictions and forecasts based on historical data
Step 1: Prepare Your Data
Before creating a normal distribution curve in Excel, make sure you have a dataset that is suitable for analysis. Your dataset should be a random sample of data that is representative of the population you are trying to analyze.
Here's an example of a dataset that we can use to create a normal distribution curve:
| Value |
|---|
| 10.2 |
| 12.5 |
| 11.8 |
| 9.9 |
| 13.1 |
| 10.9 |
| 12.2 |
| 11.5 |
| 10.6 |
| 13.4 |
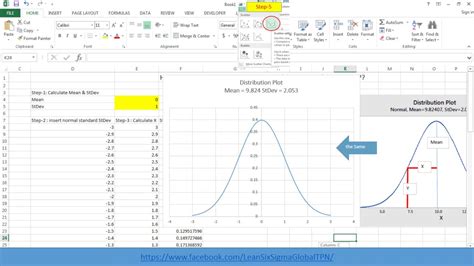
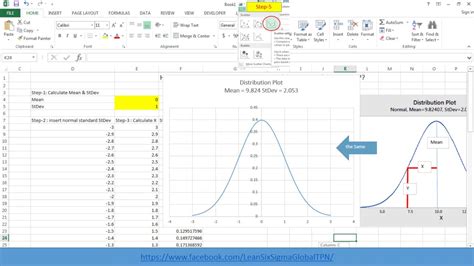
Step 2: Calculate the Mean and Standard Deviation
To create a normal distribution curve, you need to calculate the mean and standard deviation of your dataset. You can use the following formulas:
- Mean:
=AVERAGE(A1:A10) - Standard Deviation:
=STDEV(A1:A10)
Assuming your data is in column A, the mean and standard deviation would be:
- Mean: 11.45
- Standard Deviation: 1.23
Step 3: Create a Range of X-Values
To create a normal distribution curve, you need to create a range of x-values that represent the possible values of your dataset. You can use the following formula to create a range of x-values:
=MIN(A1:A10)-3*STDEV(A1:A10)+ROW(A1:A100)*STDEV(A1:A10)
This formula creates a range of x-values that spans three standard deviations above and below the mean.
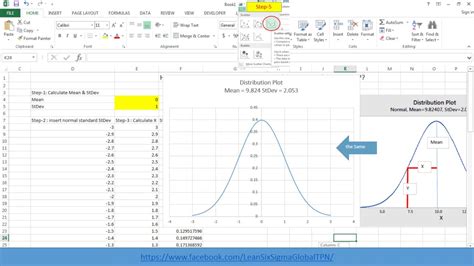
Step 4: Calculate the Y-Values
To create a normal distribution curve, you need to calculate the y-values that correspond to each x-value. You can use the following formula to calculate the y-values:
=NORM.DIST(x,mean,standard_dev,FALSE)
Assuming your x-values are in column B, the mean and standard deviation are in cells C1 and C2, respectively, the formula would be:
=NORM.DIST(B2,C1,C2,FALSE)
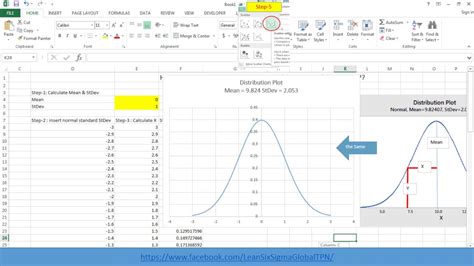
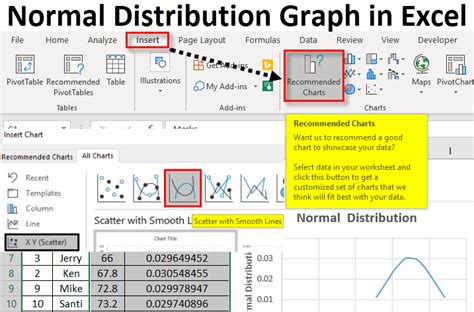
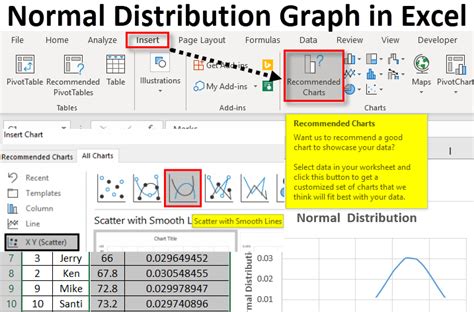
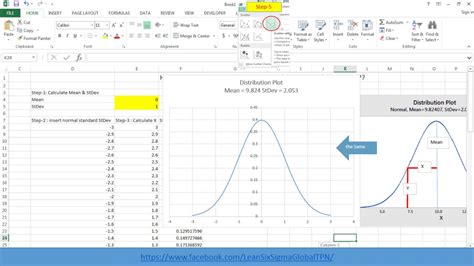
Step 5: Create the Normal Distribution Curve
To create the normal distribution curve, select the x-values and y-values, go to the "Insert" tab, and click on "Scatter" chart.
Tips and Variations
- To create a cumulative distribution curve, use the
NORM.DISTfunction with theTRUEargument instead ofFALSE. - To create a probability plot, use the
NORM.S.DISTfunction instead ofNORM.DIST. - To create a normal distribution curve with multiple datasets, use the
NORM.DISTfunction with different mean and standard deviation values.
Gallery of Normal Distribution Curve
Normal Distribution Curve Image Gallery



Conclusion
Creating a normal distribution curve in Excel is a useful skill for data analysis and visualization. With the right steps and formulas, you can easily create a normal distribution curve that helps you understand and analyze your data.
