Stopping VBA code execution while it's running can be a useful skill to have, especially when you're debugging or testing your code. In this article, we'll explore the different methods to stop VBA code execution, including using the Visual Basic Editor, keyboard shortcuts, and code modifications.
Why Stop VBA Code Execution?
Before we dive into the methods, let's quickly discuss why you might need to stop VBA code execution. Here are a few scenarios:
- Debugging: You're testing your code and want to pause execution to inspect variables, check the call stack, or step through the code line by line.
- Error handling: Your code encounters an error, and you want to stop execution to prevent further errors or data corruption.
- Performance issues: Your code is running slowly, and you want to pause execution to investigate performance bottlenecks.
Method 1: Using the Visual Basic Editor
The Visual Basic Editor (VBE) provides a built-in way to stop code execution. Here's how:
- Open the VBE by pressing
Alt + F11or navigating to Developer > Visual Basic in the ribbon. - In the VBE, click on the "Run" button or press
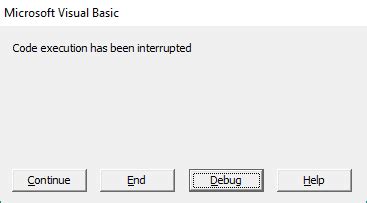
F5to start code execution. - To stop code execution, click on the "Break" button or press
Ctrl + Break.
Method 2: Using Keyboard Shortcuts
You can also use keyboard shortcuts to stop VBA code execution. Here are a few options:
Ctrl + Break: Stops code execution immediately.Shift + F8: Steps through the code line by line, allowing you to pause execution at any point.F8: Continues code execution until the next breakpoint or the end of the code.
Method 3: Modifying Your Code
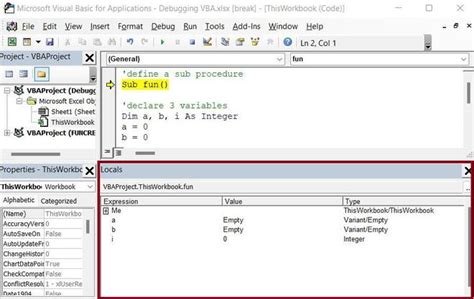
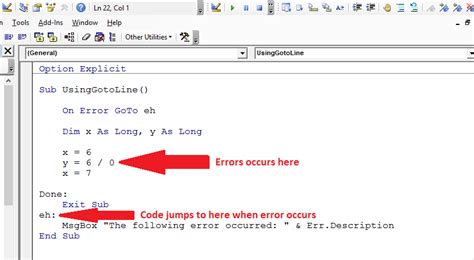
In some cases, you might want to stop code execution programmatically. You can use the Stop statement or the Debug.Assert statement to achieve this.
Stop: Stops code execution immediately.Debug.Assert: Stops code execution if the assertion fails.
Here's an example:
Sub MySub()
' Code execution will stop here
Stop
' Code below this line will not be executed
MsgBox "Hello World!"
End Sub

Gallery of VBA Debugging Techniques
VBA Debugging Techniques



We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide on how to stop VBA code execution while it's running. Whether you're debugging, testing, or optimizing your code, these methods will come in handy. Happy coding!
