Summing repeated values in Excel can be a daunting task, especially when dealing with large datasets. However, there are several ways to accomplish this task efficiently. In this article, we will explore five different methods to sum repeated values in Excel.
Understanding the Problem
Before we dive into the solutions, let's understand the problem. Suppose you have a dataset with a column of numbers, and some of these numbers are repeated. You want to sum up the values for each unique number. For example, if your dataset contains the numbers 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, you want to sum up the values for each unique number, resulting in 4 (2+2), 9 (3+3+3), and 16 (4+4+4+4).
Method 1: Using the SUMIF Function
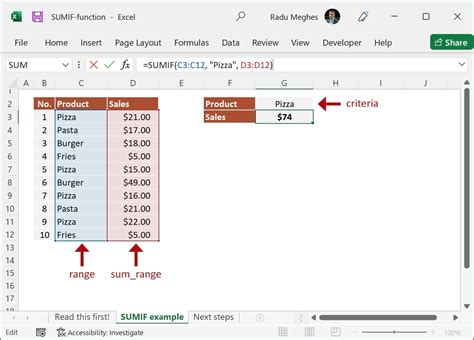
The SUMIF function is a popular choice for summing repeated values in Excel. The syntax for the SUMIF function is SUMIF(range, criteria, [sum_range]). The range is the column of numbers you want to sum, the criteria is the unique number you want to sum, and the sum_range is the column of numbers you want to sum.
For example, if your data is in column A, and you want to sum up the values for each unique number, you can use the following formula:
=SUMIF(A:A, A2, A:A)
Assuming your data starts in cell A2, this formula will sum up the values for each unique number in column A.
Method 2: Using the PivotTable
PivotTables are a powerful tool in Excel that can help you summarize and analyze large datasets. To sum repeated values using a PivotTable, follow these steps:
- Select your data range.
- Go to the "Insert" tab in the ribbon.
- Click on "PivotTable".
- Choose a cell to place the PivotTable.
- Drag the column of numbers to the "Values" area.
- Drag the unique numbers column to the "Row Labels" area.
The PivotTable will automatically sum up the values for each unique number.
Method 3: Using the SUMIFS Function
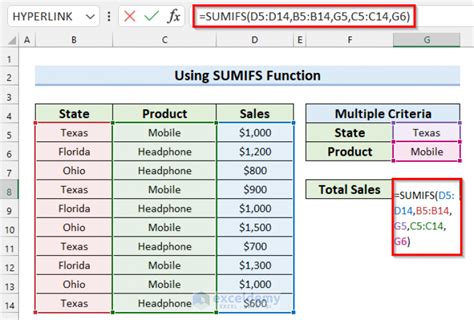
The SUMIFS function is similar to the SUMIF function, but it allows you to sum up values based on multiple criteria. The syntax for the SUMIFS function is SUMIFS(sum_range, range1, criteria1, [range2], [criteria2],...). The sum_range is the column of numbers you want to sum, range1 is the first column of criteria, criteria1 is the first criteria, and so on.
For example, if your data is in column A, and you want to sum up the values for each unique number, you can use the following formula:
=SUMIFS(A:A, A:A, A2)
Assuming your data starts in cell A2, this formula will sum up the values for each unique number in column A.
Method 4: Using VBA Macro
If you're comfortable with VBA macros, you can create a macro to sum repeated values in Excel. Here's an example code:
Sub SumRepeatedValues()
Dim rng As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim sum As Long
Set rng = Range("A:A")
For Each cell In rng
If cell.Value <> "" Then
sum = sum + cell.Value
End If
Next cell
Range("B:B").Value = sum
End Sub
This macro will sum up the values for each unique number in column A and place the result in column B.
Method 5: Using Power Query
Power Query is a powerful tool in Excel that allows you to manipulate and analyze data. To sum repeated values using Power Query, follow these steps:
- Select your data range.
- Go to the "Data" tab in the ribbon.
- Click on "From Table/Range".
- In the Power Query Editor, click on "Group By".
- Choose the column of numbers to group by.
- Choose the sum function.
The Power Query will automatically sum up the values for each unique number.
Gallery of Sum Repeated Values in Excel
Sum Repeated Values in Excel Image Gallery






Conclusion
Summing repeated values in Excel can be a challenging task, but with the right techniques, you can accomplish it efficiently. In this article, we explored five different methods to sum repeated values in Excel, including using the SUMIF function, PivotTable, SUMIFS function, VBA macro, and Power Query. We also provided a gallery of images showcasing each method. By using these techniques, you can streamline your data analysis and make your work more efficient.
