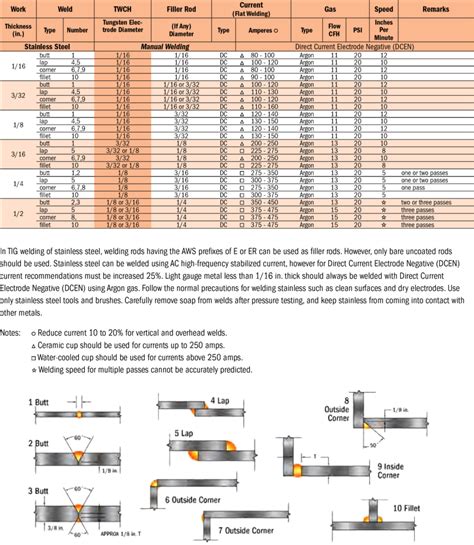
Intro
Improve your welding skills with our expert guide to Mastering Mig Welding. Discover 7 essential tips and techniques to enhance your MIG welding performance, covering wire selection, shielding gas, and joint preparation. Learn to minimize porosity, increase penetration, and achieve smooth welds with our comprehensive tutorial.
Mig welding, also known as gas metal arc welding (GMAW), is a popular welding process that uses a continuous wire electrode and an inert gas to shield the arc. It is widely used in various industries, including automotive, construction, and manufacturing. However, mastering mig welding requires practice, patience, and a deep understanding of the process. In this article, we will share 7 essential tips to help you improve your mig welding skills.
Understanding the Basics of Mig Welding

Before we dive into the tips, it's essential to understand the basics of mig welding. Mig welding uses a continuous wire electrode that is fed through a gun, which is connected to a power source and a gas cylinder. The wire electrode is shielded by an inert gas, such as argon or helium, which protects the arc from atmospheric gases. The process produces a smooth, consistent weld with minimal spatter.
Tips for Improving Your Mig Welding Skills
Tip 1: Choose the Right Equipment
Choosing the right equipment is crucial for successful mig welding. You'll need a mig welder, a wire feeder, and a shielding gas cylinder. Make sure the welder is suitable for your project, and the wire feeder is compatible with the welder. Additionally, choose a shielding gas that is suitable for the type of metal you're working with.
Types of Mig Welders
- DC (direct current) welders: Suitable for most mig welding applications
- AC (alternating current) welders: Suitable for welding aluminum and other non-ferrous metals
- Inverter welders: Suitable for high-precision welding and welding thin materials

Tip 2: Prepare Your Workpiece
Preparing your workpiece is essential for successful mig welding. Clean the metal surface to remove any dirt, oil, or grease. Remove any rust or scale, and grind the surface to create a smooth finish. This will help ensure a strong, consistent weld.
Methods for Preparing Your Workpiece
- Cleaning with a wire brush or sandpaper
- Grinding with a grinder or sanding disc
- Using a degreaser or solvent to remove oil and grease

Tip 3: Set the Right Welding Parameters
Setting the right welding parameters is crucial for successful mig welding. The parameters you'll need to set include the voltage, wire feed speed, and shielding gas flow rate. Consult the manufacturer's instructions or a welding chart to determine the correct settings for your project.
Factors Affecting Welding Parameters
- Metal thickness and type
- Welding position (flat, horizontal, vertical, or overhead)
- Shielding gas type and flow rate
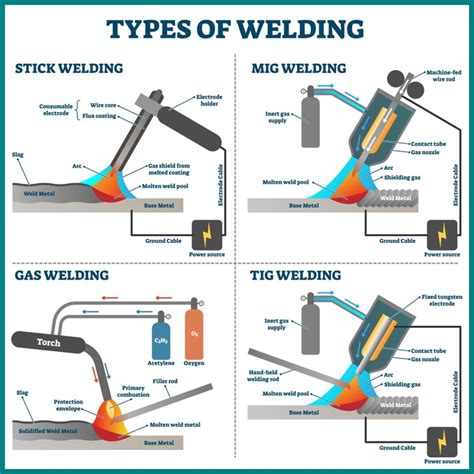
Tip 4: Use the Right Welding Technique
Using the right welding technique is essential for successful mig welding. The technique you use will depend on the type of metal you're working with and the welding position. Practice different techniques, such as the "push" or "pull" method, to develop your skills.
Common Mig Welding Techniques
- Push method: Suitable for most mig welding applications
- Pull method: Suitable for welding thin materials or in tight spaces
- Weave method: Suitable for welding large, flat surfaces
Tip 5: Monitor Your Weld Pool
Monitoring your weld pool is essential for successful mig welding. Keep an eye on the weld pool to ensure it's the correct size and shape. Adjust your welding technique or parameters as needed to maintain a consistent weld.
Factors Affecting Weld Pool Size and Shape
- Welding voltage and current
- Wire feed speed and shielding gas flow rate
- Welding technique and angle
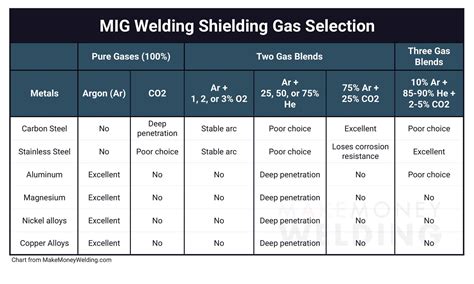
Tip 6: Use Shielding Gas Correctly
Using shielding gas correctly is essential for successful mig welding. The shielding gas protects the arc from atmospheric gases, which can cause porosity or other defects. Use the correct shielding gas type and flow rate for your project.
Types of Shielding Gases
- Argon: Suitable for most mig welding applications
- Helium: Suitable for welding aluminum and other non-ferrous metals
- Argon-helium mixtures: Suitable for welding thin materials or in tight spaces
Tip 7: Practice, Practice, Practice
Practice is essential for mastering mig welding. The more you practice, the more comfortable you'll become with the process. Start with simple projects, such as welding a small plate or pipe, and gradually move on to more complex projects.
Tips for Practicing Mig Welding
- Start with thin materials and gradually move on to thicker materials
- Practice different welding techniques, such as the "push" or "pull" method
- Use a welding simulator or practice welding on scrap metal before working on actual projects

Gallery of Mig Welding Images
Mig Welding Image Gallery










By following these 7 essential tips, you'll be well on your way to mastering mig welding. Remember to practice regularly, and don't be afraid to experiment with different techniques and parameters. With time and patience, you'll become a skilled mig welder, capable of producing high-quality welds with ease.
