Intro
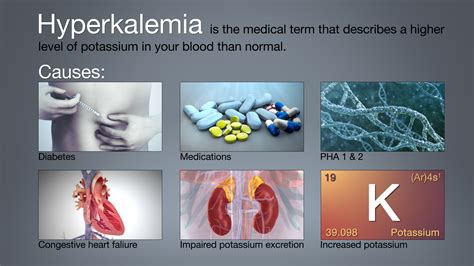
Hyperkalemia is a medical condition where the potassium levels in the blood become elevated, posing a significant threat to the heart and overall health. When left untreated, hyperkalemia can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, muscle weakness, and even death. Managing hyperkalemia requires a comprehensive approach, combining lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical interventions. Here are five ways to manage hyperkalemia system disorder.
Understanding Hyperkalemia
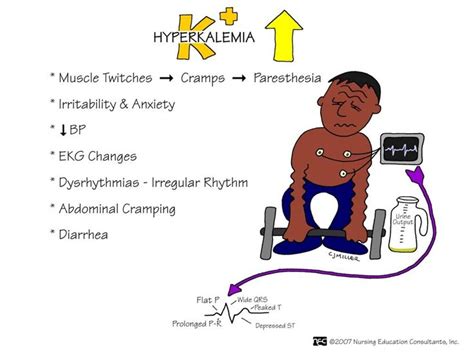
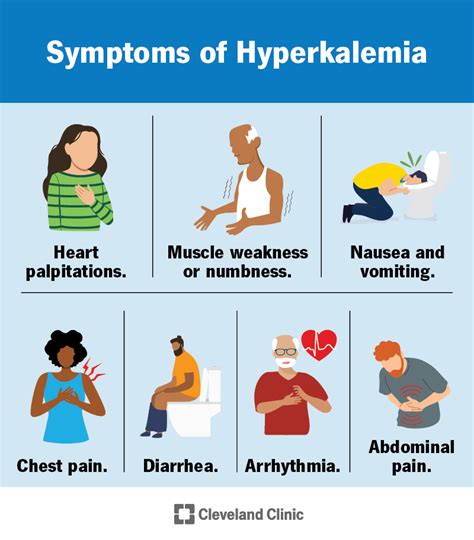
Hyperkalemia is a complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body fails to regulate potassium levels, often due to kidney problems, hormonal imbalances, or excessive potassium intake. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia is crucial for early intervention and effective management.
1. Dietary Changes
A well-planned diet plays a vital role in managing hyperkalemia. Individuals with hyperkalemia should focus on reducing potassium-rich foods, such as:
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale
- Fresh fruits like bananas and avocados
- Legumes like beans and lentils
- Nuts and seeds like almonds and pumpkin seeds
Instead, opt for low-potassium foods, including:
- Fresh vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower
- Fresh fruits like apples and berries
- Lean proteins like chicken and fish
- Whole grains like rice and quinoa

2. Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to dietary changes, several lifestyle modifications can help manage hyperkalemia:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess potassium from the body.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help improve kidney function and reduce potassium levels.
- Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate hyperkalemia; engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga can help mitigate this effect.
- Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and can help regulate potassium levels.
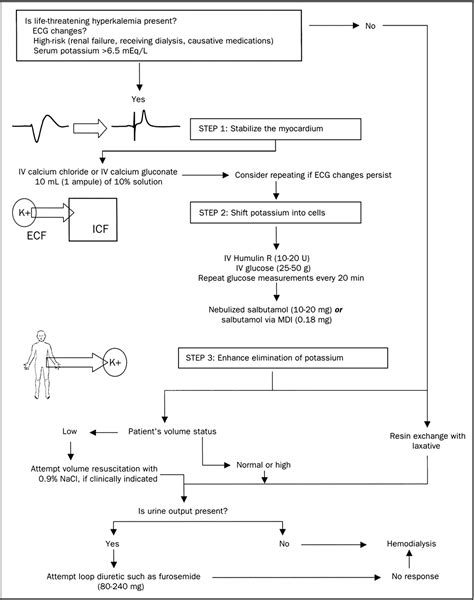
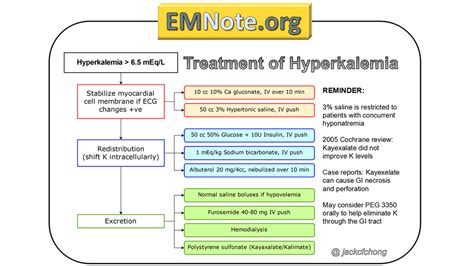
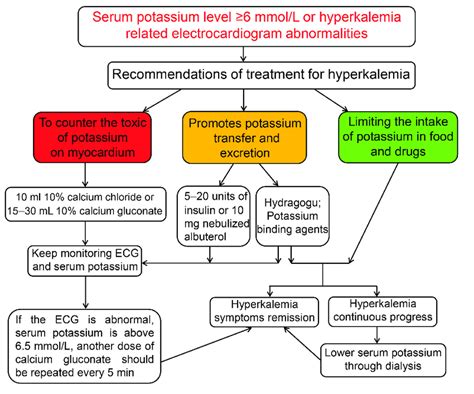
3. Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to manage hyperkalemia:
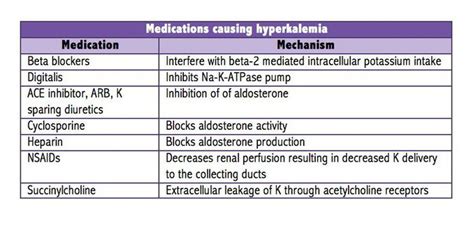
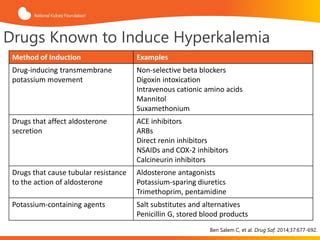
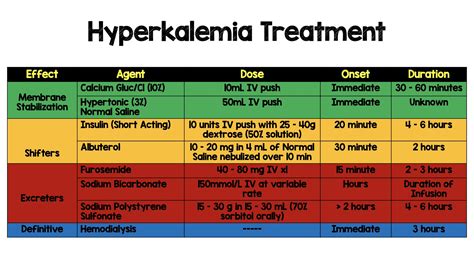
- Medications: Diuretics, potassium-binding resins, and beta-blockers may be prescribed to help reduce potassium levels.
- Dialysis: In severe cases, dialysis may be necessary to remove excess potassium from the blood.
4. Monitor Potassium Levels
Regular monitoring of potassium levels is crucial for managing hyperkalemia:
- Blood tests: Regular blood tests can help track potassium levels and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
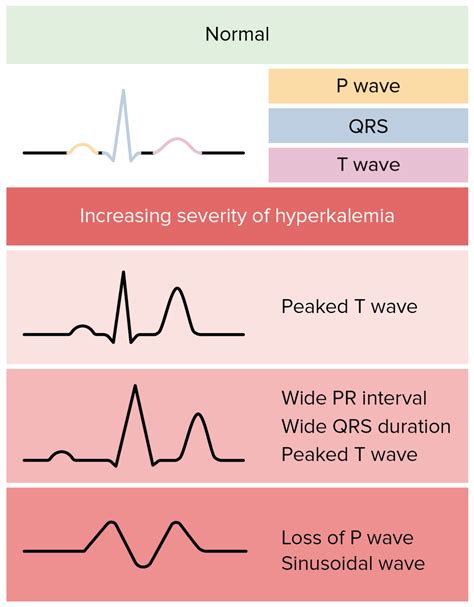
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG can help detect cardiac arrhythmias and other complications associated with hyperkalemia.
5. Alternative Therapies
Certain alternative therapies may also help manage hyperkalemia:
- Herbal supplements: Certain herbs like licorice root and ginseng may help reduce potassium levels.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help improve kidney function and reduce potassium levels.
Gallery of Hyperkalemia Management
Hyperkalemia Management Image Gallery

Final Thoughts
Managing hyperkalemia requires a comprehensive approach that combines dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and alternative therapies. By understanding the causes and symptoms of hyperkalemia and taking proactive steps to manage the condition, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health. Share your thoughts and experiences with hyperkalemia management in the comments below!
