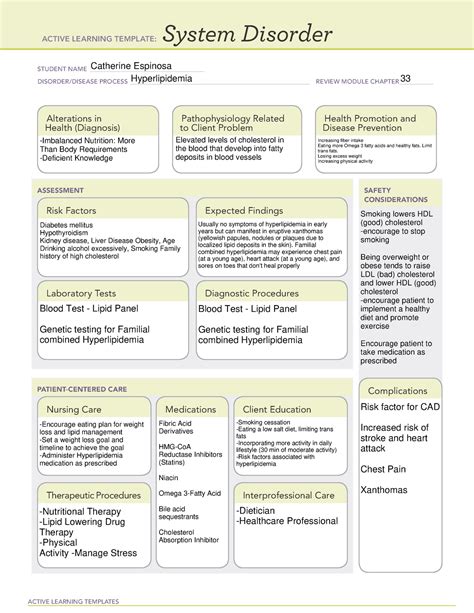
Intro
Living with hyperlipidemia, a condition characterized by elevated levels of lipids in the blood, can be challenging. However, with the right management strategies, it is possible to control the condition and reduce the risk of complications. Hyperlipidemia is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death worldwide. In this article, we will discuss seven ways to manage hyperlipidemia and maintain overall health.
Understanding Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia is a condition where the levels of lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, in the blood are elevated. This can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. Hyperlipidemia can be caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, including a high-fat diet, lack of exercise, and obesity.
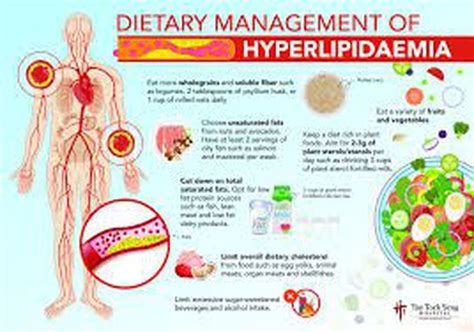
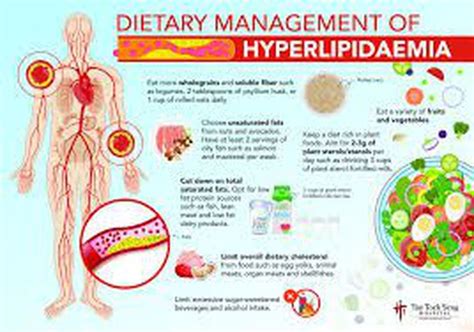
1. Dietary Changes
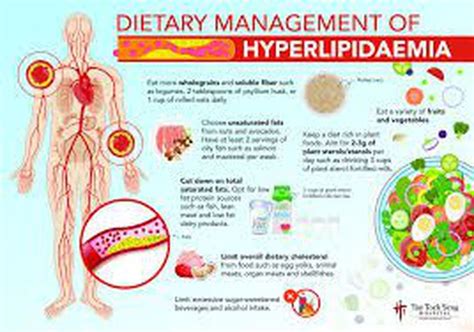
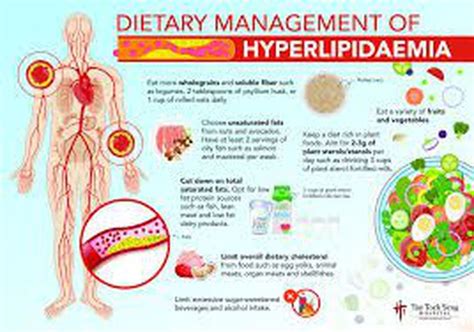
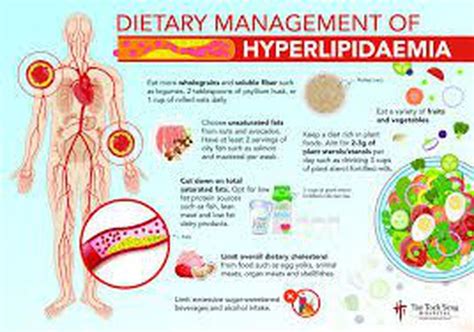
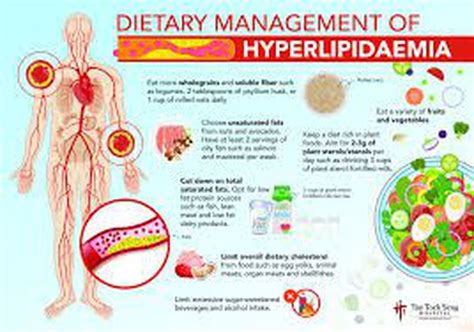
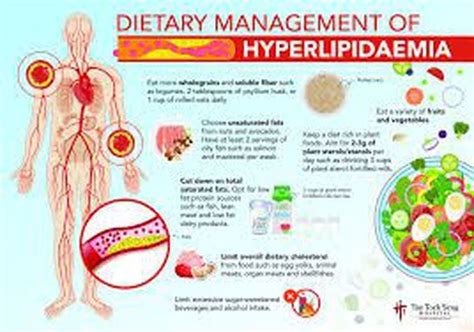
Making dietary changes is a crucial step in managing hyperlipidemia. A healthy diet can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Here are some dietary changes that can help:
- Increase soluble fiber intake: Soluble fiber, found in foods such as oats, barley, and fruits, can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Choose healthy fats: Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can help lower triglycerides and improve overall heart health.
- Limit saturated and trans fats: Saturated and trans fats, found in foods such as red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed snacks, can increase cholesterol levels.
- Incorporate plant-based protein: Plant-based protein sources, such as beans, lentils, and tofu, can help lower cholesterol levels and improve overall heart health.
2. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise is essential for managing hyperlipidemia. Exercise can help:
- Improve insulin sensitivity: Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Lower triglycerides: Exercise can help lower triglycerides and improve overall heart health.
- Increase HDL cholesterol: Regular exercise can help increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels.

3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing hyperlipidemia. Excess weight, particularly around the waistline, can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Lose weight if necessary: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help lower cholesterol levels and improve overall heart health.
- Maintain weight loss: Once you have lost weight, it is essential to maintain weight loss through a healthy diet and regular exercise.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Here are some ways to manage stress:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help reduce stress and anxiety.
- Get enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is essential for managing stress and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Engage in physical activity: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress and improve overall mental health.

5. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and improve overall health.
- Get professional help: If you are struggling to quit smoking, consider getting professional help from a healthcare provider or a counselor.
- Use nicotine replacement therapy: Nicotine replacement therapy, such as gum or patches, can help reduce withdrawal symptoms and increase the chances of quitting smoking.
6. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Limit daily intake: Limiting daily alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Avoid binge drinking: Binge drinking can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and other health problems.

7. Monitor and Manage Other Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: If you have diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Manage hypertension: Managing hypertension through lifestyle changes and medication can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.

Hyperlipidemia Management Image Gallery


In conclusion, managing hyperlipidemia requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary changes, regular exercise, weight management, stress management, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and monitoring and managing other health conditions. By following these seven ways to manage hyperlipidemia, individuals can reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular disease and maintain overall health.
