Insulin glargine is a long-acting insulin analog that is used to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It is designed to provide a steady, basal level of insulin activity over a 24-hour period, with a relatively flat peak-to-trough ratio. This makes it an ideal choice for patients who require a consistent and reliable insulin supply throughout the day.
Insulin glargine is typically administered once daily, at the same time each day, via subcutaneous injection. It is usually taken in the evening, around bedtime, to help control blood sugar levels throughout the night and into the next day. However, the exact timing and dosage of insulin glargine may vary depending on individual patient needs and medical conditions.
Benefits of Insulin Glargine
Insulin glargine has several benefits that make it a popular choice for patients with diabetes. Some of these benefits include:
- Improved glycemic control: Insulin glargine provides a consistent and reliable source of insulin, which helps to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Reduced risk of hypoglycemia: The flat peak-to-trough ratio of insulin glargine reduces the risk of hypoglycemia, especially at night.
- Increased flexibility: Insulin glargine can be administered at any time of day, as long as it is taken at the same time each day.
- Simplified dosing regimen: Insulin glargine is typically administered once daily, which can simplify the dosing regimen and improve patient adherence.
Side Effects of Insulin Glargine
While insulin glargine is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects. Common side effects include:
- Injection site reactions: Redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site.
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar, which can occur if the dose is too high or if the patient skips a meal.
- Weight gain: Insulin glargine can cause weight gain, especially if the patient is not following a healthy diet and exercise plan.
- Allergic reactions: Rarely, patients may experience an allergic reaction to insulin glargine, which can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.
Contraindications and Precautions
Insulin glargine is contraindicated in patients with:
- Hypersensitivity to insulin glargine: Patients who are allergic to insulin glargine or any of its components should not use this medication.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: Insulin glargine is not indicated for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Precautions should be taken when using insulin glargine in patients with:
- Kidney or liver disease: Insulin glargine may need to be adjusted in patients with kidney or liver disease.
- Heart failure: Insulin glargine may worsen heart failure in some patients.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Insulin glargine may be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but the dose may need to be adjusted.
Dosage and Administration
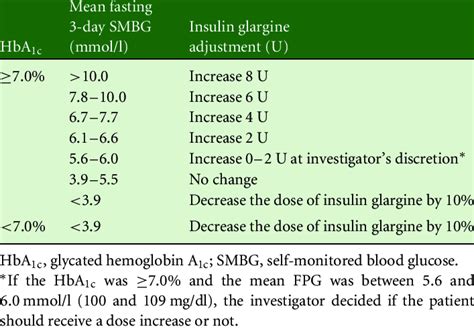
The dosage of insulin glargine varies depending on individual patient needs and medical conditions. The usual starting dose is 10 units once daily, but the dose may need to be adjusted based on blood glucose monitoring and patient response.
Insulin glargine is administered via subcutaneous injection, typically in the abdominal wall, thigh, or upper arm. The injection site should be rotated to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy.
Template for Insulin Glargine Medication Guide
Here is a template for an insulin glargine medication guide:
Medication Name: Insulin Glargine
Dosage: 10 units once daily
Administration: Subcutaneous injection in the abdominal wall, thigh, or upper arm
Injection Site: Rotate injection site to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy
Time: Administer at the same time each day, preferably in the evening
Monitoring: Monitor blood glucose levels regularly to adjust the dose as needed
Side Effects: Report any side effects, such as injection site reactions, hypoglycemia, or allergic reactions, to the healthcare provider immediately.
Contraindications: Do not use insulin glargine if you are allergic to insulin glargine or any of its components.
Precautions: Use with caution in patients with kidney or liver disease, heart failure, pregnancy, and breastfeeding.
Storage: Store insulin glargine in the refrigerator at a temperature between 39°F and 46°F (4°C and 8°C).
Expiration Date: Check the expiration date on the label and discard any expired medication.
Patient Education: Educate patients on the proper use of insulin glargine, including dosage, administration, and monitoring. Emphasize the importance of rotating the injection site and reporting any side effects to the healthcare provider.
Insulin Glargine Image Gallery


We hope this article has provided a comprehensive guide to insulin glargine medication. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from it.
