Intro
Learn about Chondrosis vs Osteoarthritis, understanding joint pain, cartilage degeneration, and arthritis symptoms to manage chronic inflammation and improve joint health.
Chondrosis and osteoarthritis are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different conditions. Understanding the differences between these two conditions can help individuals better manage their symptoms and seek proper treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of chondrosis and osteoarthritis, exploring their definitions, causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Chondrosis is a condition characterized by the degeneration of cartilage in the joints. Cartilage is the connective tissue that cushions the joints, allowing for smooth movement and reducing friction between bones. When cartilage degenerates, it can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Chondrosis can affect any joint, but it is most commonly seen in the hands, knees, hips, and spine. The condition is often associated with aging, as the cartilage naturally wears down over time. However, it can also be caused by injury, overuse, or certain medical conditions.
Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is a type of arthritis that affects the joints. It is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage and the formation of bone spurs, which can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. It can affect any joint, but it is most commonly seen in the hands, knees, hips, and spine. The condition is often associated with aging, as the joints naturally wear down over time. However, it can also be caused by injury, overuse, or certain medical conditions.
Understanding Chondrosis

Chondrosis is a condition that affects the cartilage in the joints. Cartilage is the connective tissue that cushions the joints, allowing for smooth movement and reducing friction between bones. When cartilage degenerates, it can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Chondrosis can affect any joint, but it is most commonly seen in the hands, knees, hips, and spine. The condition is often associated with aging, as the cartilage naturally wears down over time. However, it can also be caused by injury, overuse, or certain medical conditions.
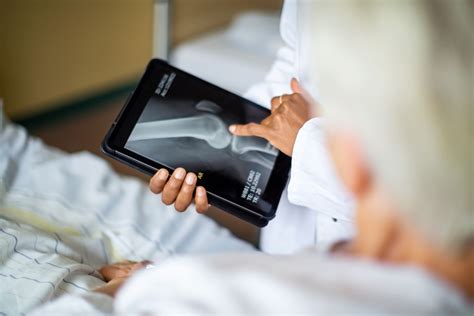
The symptoms of chondrosis can vary depending on the affected joint and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. In some cases, the condition can also cause swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint. Chondrosis can be diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI.
Causes of Chondrosis
The causes of chondrosis can be divided into two categories: primary and secondary. Primary chondrosis is caused by the natural wear and tear of the cartilage over time. This type of chondrosis is often associated with aging and can affect anyone. Secondary chondrosis, on the other hand, is caused by injury, overuse, or certain medical conditions. This type of chondrosis can affect anyone, regardless of age.
Some of the common causes of secondary chondrosis include:
- Injury: A sudden injury, such as a fall or a blow to the joint, can cause chondrosis.
- Overuse: Repetitive movements or activities that put stress on the joint can cause chondrosis.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, can increase the risk of developing chondrosis.
Understanding Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects the joints. It is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage and the formation of bone spurs, which can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. It can affect any joint, but it is most commonly seen in the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary depending on the affected joint and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. In some cases, the condition can also cause swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint. Osteoarthritis can be diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI.
Causes of Osteoarthritis
The causes of osteoarthritis can be divided into two categories: primary and secondary. Primary osteoarthritis is caused by the natural wear and tear of the cartilage over time. This type of osteoarthritis is often associated with aging and can affect anyone. Secondary osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is caused by injury, overuse, or certain medical conditions. This type of osteoarthritis can affect anyone, regardless of age.
Some of the common causes of secondary osteoarthritis include:
- Injury: A sudden injury, such as a fall or a blow to the joint, can cause osteoarthritis.
- Overuse: Repetitive movements or activities that put stress on the joint can cause osteoarthritis.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Key Differences Between Chondrosis and Osteoarthritis

While both chondrosis and osteoarthritis affect the joints, there are some key differences between the two conditions. Chondrosis is a condition that affects the cartilage in the joints, while osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects the joints. Chondrosis is often associated with the degeneration of cartilage, while osteoarthritis is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage and the formation of bone spurs.
In terms of symptoms, both conditions can cause joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. However, osteoarthritis is often associated with more severe symptoms, such as swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint. Chondrosis, on the other hand, is often associated with milder symptoms, such as joint pain and stiffness.
Treatment Options for Chondrosis and Osteoarthritis
The treatment options for chondrosis and osteoarthritis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the affected joint. In general, treatment options for both conditions include:
- Pain relief medications: Over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate joint pain and stiffness.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss or exercise, can help reduce stress on the joints and alleviate symptoms.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the affected joint. This is often the case for osteoarthritis, which can cause severe joint damage and disability.
Managing Chondrosis and Osteoarthritis
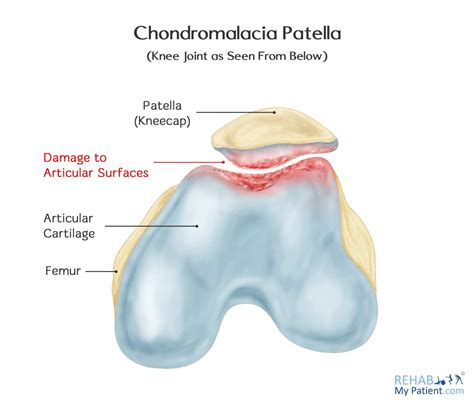
Managing chondrosis and osteoarthritis requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, pain relief medications, and physical therapy. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the affected joint.
Some tips for managing chondrosis and osteoarthritis include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put stress on the joints, exacerbating symptoms.
- Engaging in regular exercise: Regular exercise can help improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Avoiding repetitive movements: Repetitive movements or activities that put stress on the joint can exacerbate symptoms.
- Getting enough rest: Getting enough rest can help reduce stress on the joints and alleviate symptoms.
Preventing Chondrosis and Osteoarthritis
Preventing chondrosis and osteoarthritis requires a proactive approach that includes lifestyle modifications and regular exercise. Some tips for preventing chondrosis and osteoarthritis include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put stress on the joints, increasing the risk of developing chondrosis or osteoarthritis.
- Engaging in regular exercise: Regular exercise can help improve joint mobility and reduce the risk of developing chondrosis or osteoarthritis.
- Avoiding repetitive movements: Repetitive movements or activities that put stress on the joint can increase the risk of developing chondrosis or osteoarthritis.
- Getting enough rest: Getting enough rest can help reduce stress on the joints and prevent chondrosis or osteoarthritis.
Gallery of Chondrosis and Osteoarthritis
Chondrosis and Osteoarthritis Image Gallery
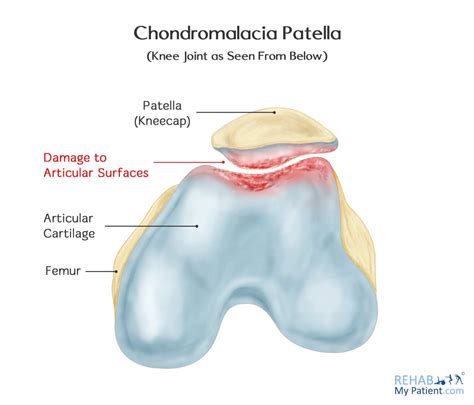
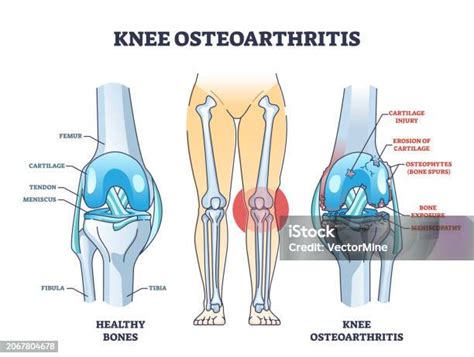




Final Thoughts

In conclusion, chondrosis and osteoarthritis are two conditions that affect the joints, but they have distinct differences in terms of causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, pain relief medications, and physical therapy, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into chondrosis and osteoarthritis. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with your friends and family who may be affected by these conditions. Together, we can raise awareness and promote better understanding of chondrosis and osteoarthritis.
