Intro
Implementing a quality management system is essential for any organization seeking to enhance customer satisfaction, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency. One crucial aspect of this system is the creation of a quality plan, as outlined in the ISO 10005 standard. This international standard provides guidelines for developing and implementing quality plans, ensuring that organizations can effectively manage and control their processes to achieve desired quality levels.
In this article, we will delve into the seven steps necessary to create an ISO 10005 quality plan template, providing a comprehensive guide to help organizations establish a robust quality management system.
Understanding ISO 10005 and Its Importance
ISO 10005 is an international standard that outlines the guidelines for developing and implementing quality plans. It provides a framework for organizations to establish a quality management system, ensuring that their processes are designed to achieve specific quality objectives.
The importance of ISO 10005 lies in its ability to help organizations manage and control their processes, reducing errors and improving overall efficiency. By implementing a quality plan, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction, increase productivity, and reduce costs.
Step 1: Define Quality Objectives and Policies
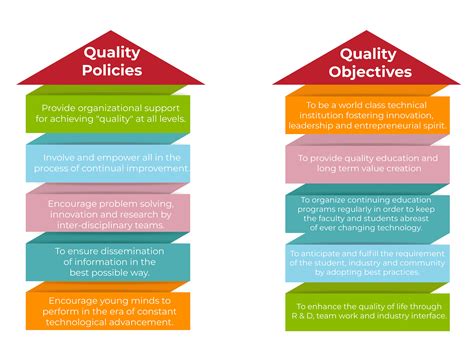
The first step in creating an ISO 10005 quality plan template is to define quality objectives and policies. This involves identifying the organization's quality goals and establishing policies that will guide the implementation of the quality plan.
Quality objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), while quality policies should outline the organization's commitment to quality and its approach to achieving quality objectives.
Example of Quality Objectives:"
- Reduce product defects by 20% within the next 12 months
- Increase customer satisfaction ratings by 15% within the next 6 months
- Improve process efficiency by 10% within the next 9 months
Example of Quality Policies:
- Our organization is committed to delivering high-quality products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- We will continuously monitor and evaluate our processes to identify areas for improvement.
- We will provide ongoing training and development opportunities to ensure that our employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to achieve quality objectives.
Step 2: Identify Processes and Activities

The second step is to identify the processes and activities that will be included in the quality plan. This involves mapping out the organization's workflows and identifying the key processes that impact quality.
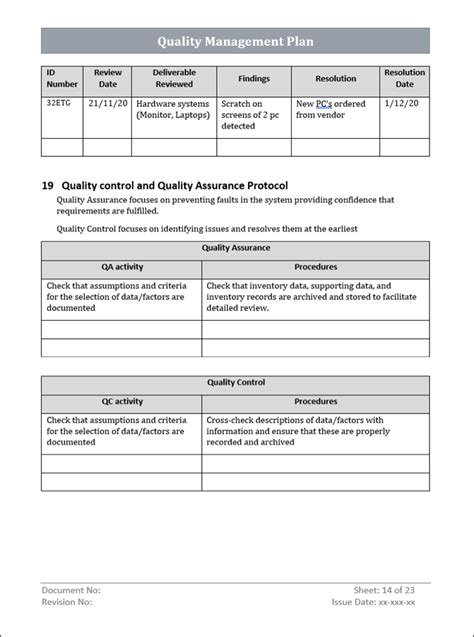
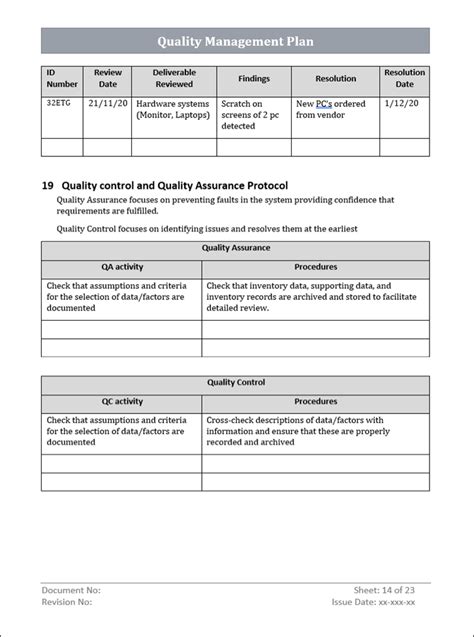
Processes and activities should be documented and described in detail, including inputs, outputs, and process boundaries.
Example of Processes and Activities:
- Product design and development
- Material procurement and supply chain management
- Manufacturing and production
- Quality control and testing
- Customer service and support
Step 3: Establish Quality Requirements

The third step is to establish quality requirements for each process and activity. This involves identifying the specific quality standards and regulations that apply to each process, as well as any customer or regulatory requirements.
Quality requirements should be documented and communicated to relevant personnel, including employees, suppliers, and contractors.
Example of Quality Requirements:
- Product design and development: Compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as ISO 9001 and FDA regulations.
- Material procurement and supply chain management: Compliance with supplier quality agreements and industry standards, such as ISO 14001.
- Manufacturing and production: Compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as OSHA and EPA regulations.
Step 4: Assign Responsibilities and Authorities

The fourth step is to assign responsibilities and authorities for each process and activity. This involves identifying the personnel responsible for implementing and maintaining the quality plan, as well as their roles and responsibilities.
Responsibilities and authorities should be documented and communicated to relevant personnel, including employees, suppliers, and contractors.
Example of Responsibilities and Authorities:
- Quality manager: Responsible for developing and implementing the quality plan, as well as monitoring and evaluating its effectiveness.
- Department managers: Responsible for implementing and maintaining quality processes and activities within their respective departments.
- Employees: Responsible for following quality procedures and reporting any quality issues or concerns.
Step 5: Identify and Provide Resources

The fifth step is to identify and provide resources necessary for implementing and maintaining the quality plan. This includes personnel, equipment, materials, and infrastructure.
Resources should be allocated and provided to support the implementation of quality processes and activities.
Example of Resources:
- Personnel: Quality manager, department managers, and employees.
- Equipment: Manufacturing equipment, testing equipment, and quality control equipment.
- Materials: Raw materials, supplies, and packaging materials.
- Infrastructure: Manufacturing facilities, offices, and IT systems.
Step 6: Monitor and Evaluate the Quality Plan

The sixth step is to monitor and evaluate the quality plan to ensure its effectiveness. This involves tracking and measuring quality performance, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments.
Monitoring and evaluation should be ongoing, with regular review and assessment of the quality plan.
Example of Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Track and measure quality performance metrics, such as defect rates and customer satisfaction ratings.
- Conduct regular audits and assessments to identify areas for improvement.
- Review and revise the quality plan as necessary to ensure its continued effectiveness.
Step 7: Continuously Improve the Quality Plan

The seventh and final step is to continuously improve the quality plan. This involves identifying areas for improvement, implementing changes, and evaluating the effectiveness of those changes.
Continuous improvement should be an ongoing process, with a focus on continually enhancing the quality plan to achieve better results.
Example of Continuous Improvement:
- Identify areas for improvement through monitoring and evaluation.
- Implement changes to the quality plan, such as new processes or procedures.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of changes and make further adjustments as necessary.
Gallery of ISO 10005 Quality Plan Templates
ISO 10005 Quality Plan Templates

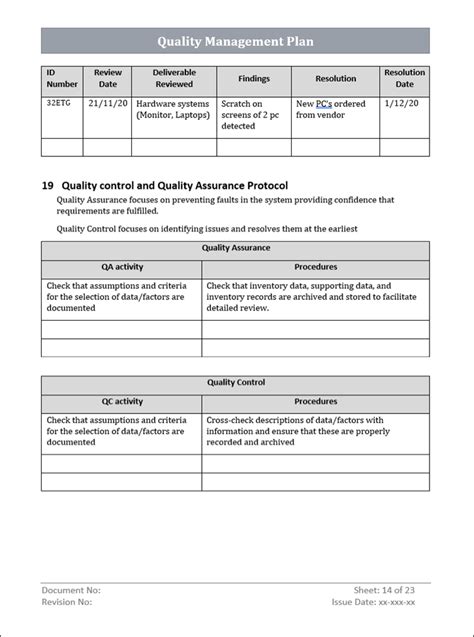
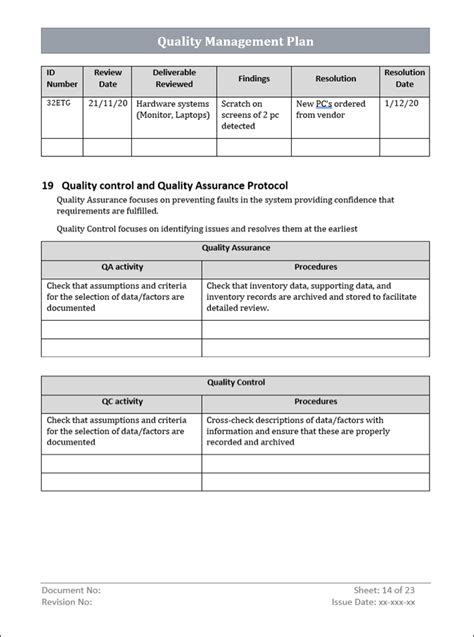
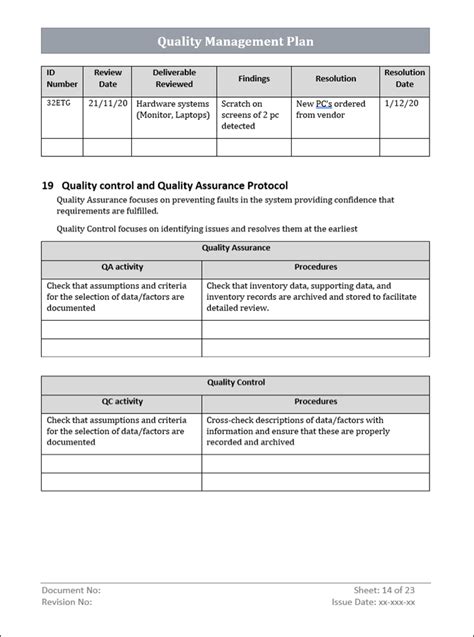
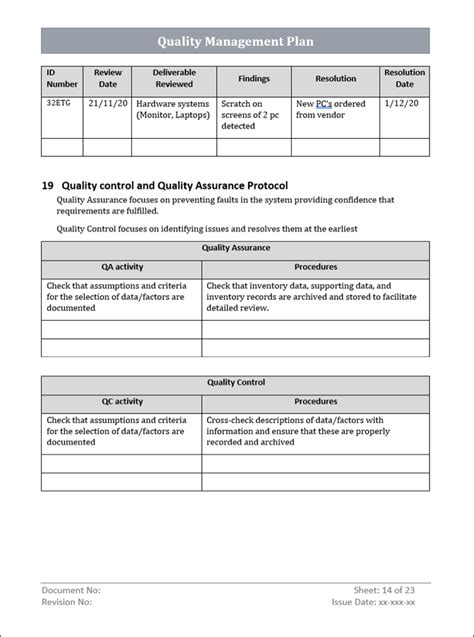
By following these seven steps, organizations can create an effective ISO 10005 quality plan template that will help them achieve their quality objectives and improve overall performance. Remember to continuously monitor and evaluate the quality plan to ensure its effectiveness and make necessary adjustments to achieve better results.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to creating an ISO 10005 quality plan template. If you have any questions or need further clarification, please don't hesitate to comment below.
