Uncover the inner workings of a jet engine with this in-depth guide to its cross-section. Explore the 7 key components, including compressors, turbines, combustion chambers, and nozzles, and discover how they work together to generate thrust. Learn about fan blades, engine mounts, and more to understand the intricacies of modern jet engine design and functionality.
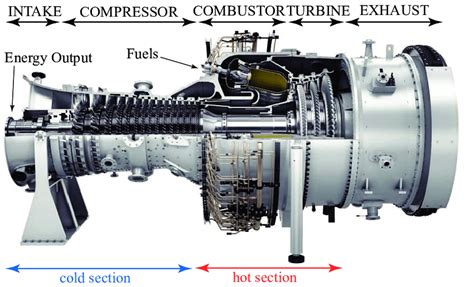
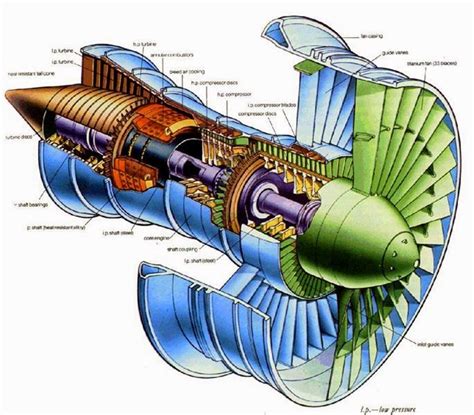
Jet engines are complex machines that have revolutionized the aviation industry, enabling aircraft to fly faster, higher, and more efficiently. At the heart of every jet engine is a remarkable combination of components that work together to generate the thrust needed to propel an aircraft through the skies. In this article, we will delve into the 7 key components of a jet engine cross section, exploring their functions, characteristics, and importance in the overall operation of the engine.
Component 1: Fan

The fan is the first component of a jet engine and is responsible for drawing in a large volume of air. As the fan spins, it accelerates the air rearward, creating a low-pressure area behind it. This low-pressure area pulls more air into the engine, which is then compressed and mixed with fuel for combustion. The fan is typically made up of a series of blades attached to a central hub and is designed to produce a high volume of airflow while minimizing energy consumption.
Types of Fans
There are several types of fans used in jet engines, including:
- Low Bypass Fan: This type of fan is designed to produce a high-pressure ratio and is typically used in high-bypass turbofans.
- High Bypass Fan: This type of fan is designed to produce a lower pressure ratio and is typically used in low-bypass turbofans.
Component 2: Compressor

The compressor is responsible for compressing the air drawn in by the fan to a high pressure, typically between 10 and 30 times atmospheric pressure. The compressor is made up of a series of stages, each consisting of a rotor and stator. The rotor is attached to the engine shaft and spins at high speed, accelerating the air rearward. The stator is fixed in place and helps to slow down the air, increasing its pressure. The compressed air is then mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustion chamber.
Types of Compressors
There are several types of compressors used in jet engines, including:
- Axial Compressor: This type of compressor uses a series of stages to compress the air and is typically used in high-bypass turbofans.
- Centrifugal Compressor: This type of compressor uses a single stage to compress the air and is typically used in low-bypass turbofans.
Component 3: Combustion Chamber
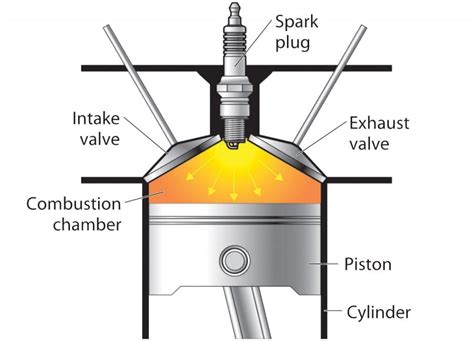
The combustion chamber is where the compressed air is mixed with fuel and ignited, producing a high-temperature and high-pressure gas. The combustion chamber is typically annular in shape and is lined with a heat-resistant material to protect the engine from the high temperatures. The fuel is injected into the combustion chamber through a series of nozzles and is ignited by a spark or flame.
Types of Combustion Chambers
There are several types of combustion chambers used in jet engines, including:
- Annular Combustion Chamber: This type of combustion chamber is annular in shape and is typically used in high-bypass turbofans.
- Can-Annular Combustion Chamber: This type of combustion chamber uses a series of cans to mix the air and fuel and is typically used in low-bypass turbofans.
Component 4: Turbine
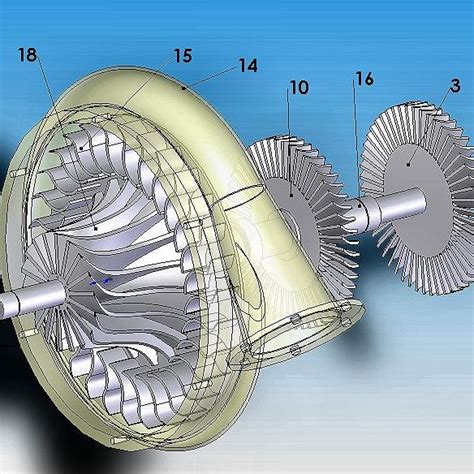
The turbine is responsible for extracting energy from the high-temperature and high-pressure gas produced in the combustion chamber. The turbine is made up of a series of stages, each consisting of a rotor and stator. The rotor is attached to the engine shaft and spins at high speed, extracting energy from the gas. The stator is fixed in place and helps to slow down the gas, increasing its pressure. The energy extracted by the turbine is used to drive the compressor and fan.
Types of Turbines
There are several types of turbines used in jet engines, including:
- Axial Turbine: This type of turbine uses a series of stages to extract energy from the gas and is typically used in high-bypass turbofans.
- Centrifugal Turbine: This type of turbine uses a single stage to extract energy from the gas and is typically used in low-bypass turbofans.
Component 5: Nozzle
The nozzle is responsible for accelerating the gas produced in the turbine to a high velocity, producing a high-velocity exhaust. The nozzle is typically convergent in shape and is designed to produce a high-velocity exhaust while minimizing energy consumption. The nozzle is also responsible for producing the thrust needed to propel the aircraft.
Types of Nozzles
There are several types of nozzles used in jet engines, including:
- Convergent Nozzle: This type of nozzle is convergent in shape and is typically used in high-bypass turbofans.
- Divergent Nozzle: This type of nozzle is divergent in shape and is typically used in low-bypass turbofans.
Component 6: Exhaust

The exhaust is responsible for producing the thrust needed to propel the aircraft. The exhaust is typically made up of a series of stages, each consisting of a nozzle and a convergent section. The nozzle accelerates the gas to a high velocity, producing a high-velocity exhaust. The convergent section then accelerates the exhaust to an even higher velocity, producing the thrust needed to propel the aircraft.
Types of Exhausts
There are several types of exhausts used in jet engines, including:
- Axial Exhaust: This type of exhaust uses a series of stages to produce the thrust and is typically used in high-bypass turbofans.
- Centrifugal Exhaust: This type of exhaust uses a single stage to produce the thrust and is typically used in low-bypass turbofans.
Component 7: Accessory Gearbox

The accessory gearbox is responsible for providing power to the engine's accessories, such as the fuel pumps, oil pumps, and generators. The accessory gearbox is typically driven by the engine shaft and is designed to provide a high level of reliability and durability. The accessory gearbox is also responsible for providing a high level of flexibility, allowing the engine to operate efficiently over a wide range of speeds and altitudes.
Types of Accessory Gearboxes
There are several types of accessory gearboxes used in jet engines, including:
- Planetary Gearbox: This type of gearbox uses a series of planet gears to provide a high level of flexibility and is typically used in high-bypass turbofans.
- Spur Gearbox: This type of gearbox uses a series of spur gears to provide a high level of reliability and is typically used in low-bypass turbofans.
Jet Engine Component Image Gallery



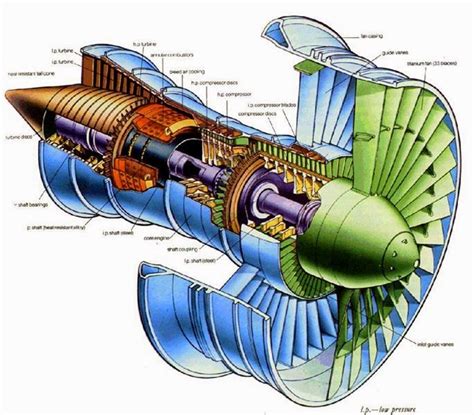
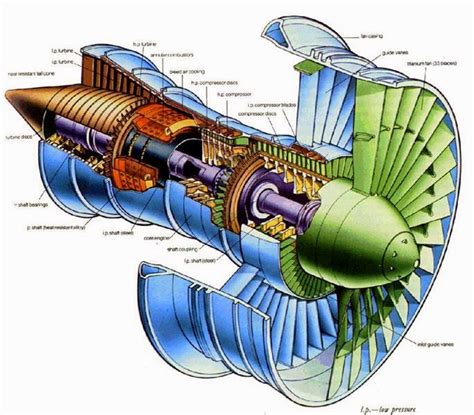
In conclusion, the 7 key components of a jet engine cross section are critical to the operation of a jet engine. Each component plays a vital role in producing the thrust needed to propel an aircraft through the skies. By understanding the functions and characteristics of each component, we can better appreciate the complexity and sophistication of jet engines. Whether you're an aviation enthusiast or a seasoned engineer, the world of jet engines is a fascinating and complex field that continues to evolve and improve with each passing day.
