Intro
Discover the average life expectancy of welders and the health risks associated with the profession. Learn how welding fumes, radiation, and physical demands impact a welders lifespan. Get insights into the occupational hazards and safety measures that can help increase life expectancy for welders, ensuring a safer and healthier career.
Welding is a highly skilled and physically demanding profession that requires precision, attention to detail, and a strong work ethic. While it can be a rewarding and lucrative career, many people are concerned about the potential health risks associated with welding. One of the most significant concerns is the impact of welding on life expectancy. In this article, we will explore the average life expectancy of welders and discuss the factors that contribute to their mortality rates.
Welding is a hazardous occupation that exposes workers to a range of toxic substances, including metals, gases, and particulate matter. Prolonged exposure to these substances can lead to serious health problems, including respiratory diseases, cancer, and neurological disorders. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), welding is one of the most hazardous occupations in the United States, with welders experiencing a higher rate of work-related injuries and illnesses than many other professions.
Despite the risks, many people are drawn to the welding profession because of its job security, good pay, and sense of satisfaction that comes from creating something with one's own hands. However, it is essential for welders to understand the potential health risks associated with their profession and take steps to mitigate them.
What is the Average Life Expectancy of Welders?

According to various studies, the average life expectancy of welders is lower than that of the general population. A study published in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine found that the average life expectancy of welders is around 60-65 years, which is 5-10 years lower than the average life expectancy of the general population.
Another study published in the American Journal of Industrial Medicine found that welders experience a higher rate of mortality than the general population, with a standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of 1.34. This means that welders are 34% more likely to die prematurely than the general population.
Factors Contributing to Mortality Rates in Welders
There are several factors that contribute to the lower life expectancy of welders, including:
- Exposure to toxic substances: Welders are exposed to a range of toxic substances, including metals, gases, and particulate matter, which can cause serious health problems.
- Respiratory diseases: Welders are at risk of developing respiratory diseases, including lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma.
- Cancer: Welders are at risk of developing various types of cancer, including lung, liver, and kidney cancer.
- Neurological disorders: Welders are at risk of developing neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases.
- Cardiovascular disease: Welders are at risk of developing cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure.
Occupational Hazards in Welding

Welding is a hazardous occupation that exposes workers to a range of occupational hazards, including:
- Physical hazards: Welders are at risk of physical injuries, including burns, cuts, and musculoskeletal disorders.
- Chemical hazards: Welders are exposed to toxic substances, including metals, gases, and particulate matter.
- Biological hazards: Welders are at risk of developing biological hazards, including infections and diseases.
- Psychological hazards: Welders are at risk of developing psychological hazards, including stress, anxiety, and depression.
Prevention and Control Measures
There are several prevention and control measures that can be taken to reduce the risks associated with welding, including:
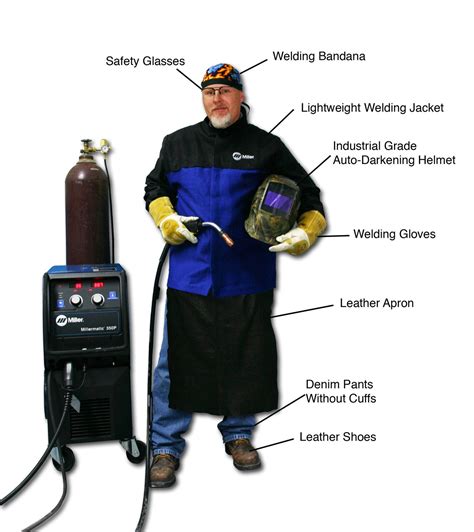
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Welders should wear PPE, including gloves, safety glasses, and respirators, to protect themselves from physical and chemical hazards.
- Ventilation: Good ventilation is essential to reduce exposure to toxic substances.
- Training: Welders should receive training on safe welding practices, including proper equipment use and maintenance.
- Health monitoring: Welders should undergo regular health monitoring to detect any health problems early.
Reducing Mortality Rates in Welders
There are several ways to reduce mortality rates in welders, including:
- Improving working conditions: Improving working conditions, including reducing exposure to toxic substances and providing good ventilation, can help reduce mortality rates.
- Providing training: Providing training on safe welding practices and proper equipment use and maintenance can help reduce mortality rates.
- Encouraging health monitoring: Encouraging welders to undergo regular health monitoring can help detect any health problems early.
- Promoting healthy lifestyles: Promoting healthy lifestyles, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can help reduce mortality rates.
Conclusion
Welding is a hazardous occupation that exposes workers to a range of physical and chemical hazards. While the average life expectancy of welders is lower than that of the general population, there are several ways to reduce mortality rates, including improving working conditions, providing training, encouraging health monitoring, and promoting healthy lifestyles. By taking these steps, welders can reduce their risk of developing serious health problems and increase their life expectancy.
Welding Safety Image Gallery









We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the average life expectancy of welders and the factors that contribute to their mortality rates. By taking the necessary precautions and promoting healthy lifestyles, welders can reduce their risk of developing serious health problems and increase their life expectancy.
