Intro
Discover the 7 Autoimmune Diseases, including lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Hashimotos, and learn about their symptoms, causes, and treatments, to understand immune system disorders and chronic inflammation conditions.
Autoimmune diseases have become a significant concern in the medical community, affecting millions of people worldwide. These diseases occur when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, tissues, and organs, leading to a wide range of symptoms and health complications. Understanding autoimmune diseases is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and improving the quality of life for those affected. In this article, we will delve into the world of autoimmune diseases, exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, with a focus on seven specific diseases.
The importance of understanding autoimmune diseases cannot be overstated. These diseases can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity, and can have a significant impact on daily life. From mild symptoms to life-threatening conditions, autoimmune diseases require prompt medical attention and ongoing management. By learning more about these diseases, individuals can take the first step towards seeking help, managing their symptoms, and improving their overall health.
Autoimmune diseases are a complex and multifaceted group of conditions, and researchers are still working to understand the underlying causes. However, it is believed that a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors contribute to the development of these diseases. In some cases, autoimmune diseases may be triggered by infections, stress, or other factors that disrupt the balance of the immune system. As our understanding of autoimmune diseases grows, so does our ability to develop effective treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Introduction to Autoimmune Diseases
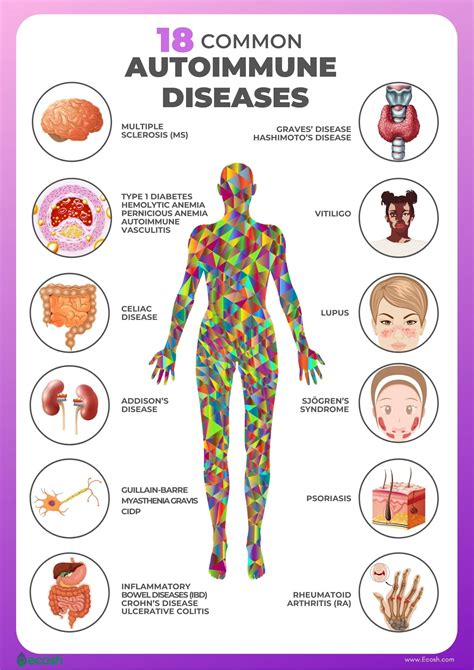
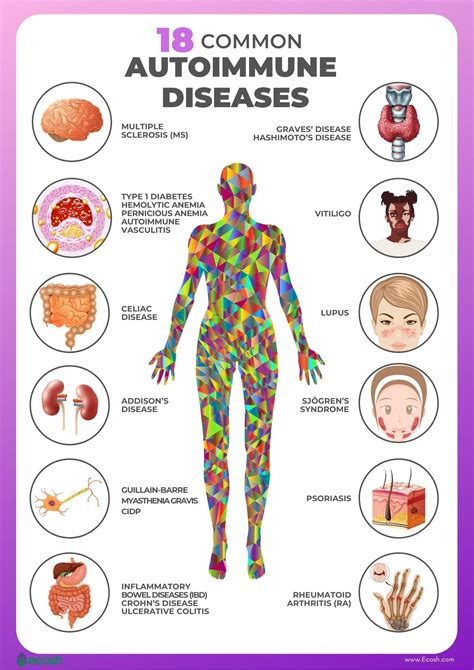
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by an abnormal immune response, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, tissues, and organs. This can lead to inflammation, tissue damage, and a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. The seven autoimmune diseases we will explore in this article are rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, psoriasis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and Crohn's disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of autoimmune diseases are complex and multifaceted. While the exact triggers are still not fully understood, research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors contribute to the development of these diseases. Some common risk factors include: * Family history: Individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases are more likely to develop one themselves. * Genetic predisposition: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing an autoimmune disease. * Environmental factors: Exposure to certain toxins, infections, and other environmental factors may trigger an autoimmune response. * Hormonal imbalances: Hormonal changes, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases.Rheumatoid Arthritis
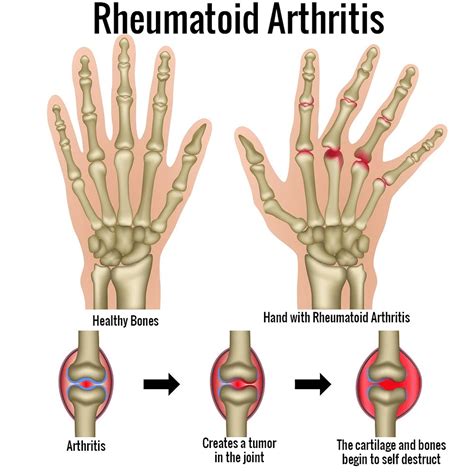
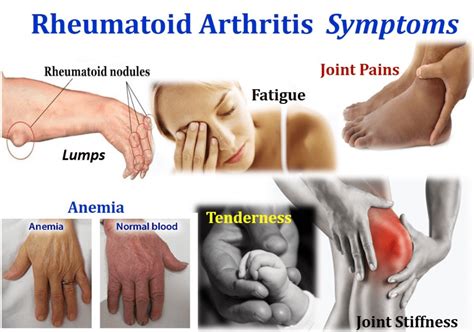
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. The symptoms of RA can vary from person to person but often include:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Swelling and redness in the affected joints
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Fever and flu-like symptoms
Treatment Options
The treatment of RA typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies. Some common treatment options include: * Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These medications can help slow the progression of the disease and reduce symptoms. * Biologics: These medications can help reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage. * Physical therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches can help improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. * Alternative therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and other alternative therapies can help manage pain and improve overall well-being.Lupus
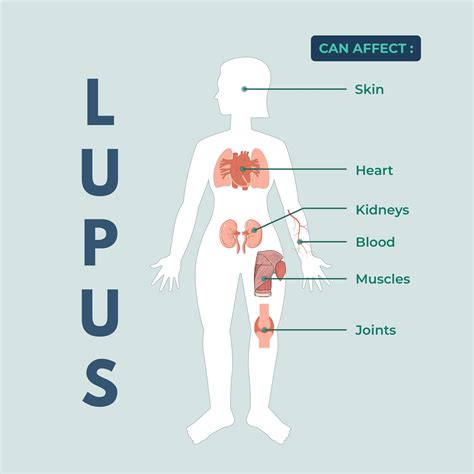
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and other organs. The symptoms of lupus can vary widely but often include:
- Skin rashes and lesions
- Joint pain and swelling
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever and flu-like symptoms
- Kidney damage and other organ problems
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of lupus can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other diseases. A combination of blood tests, imaging studies, and physical examinations can help confirm the diagnosis. Treatment options for lupus typically include: * Corticosteroids: These medications can help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. * Immunosuppressive medications: These medications can help reduce the risk of organ damage and other complications. * Anti-inflammatory medications: These medications can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. * Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as getting regular exercise and eating a balanced diet, can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.Multiple Sclerosis

Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, causing damage to the brain and spinal cord. The symptoms of MS can vary widely but often include:
- Vision problems, such as blurred vision or double vision
- Muscle weakness and spasms
- Balance and coordination problems
- Fatigue and weakness
- Cognitive difficulties, such as memory loss and difficulty concentrating
Treatment Options
The treatment of MS typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies. Some common treatment options include: * Disease-modifying therapies: These medications can help slow the progression of the disease and reduce symptoms. * Steroids: These medications can help reduce inflammation and manage relapses. * Physical therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches can help improve mobility and reduce stiffness. * Alternative therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and other alternative therapies can help manage pain and improve overall well-being.Type 1 Diabetes
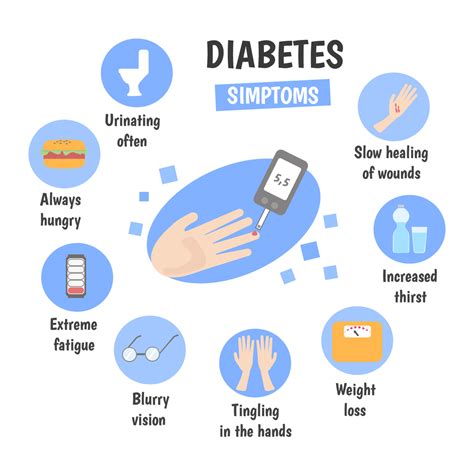
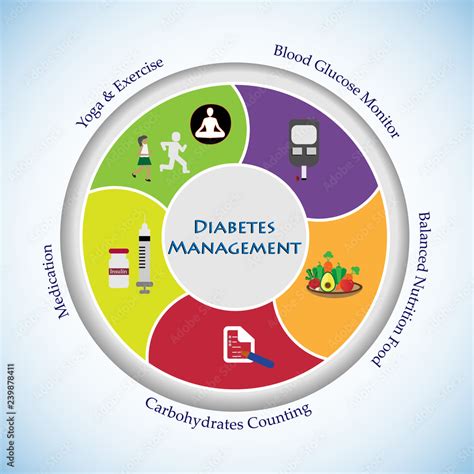
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the pancreas, causing the body to produce little or no insulin. The symptoms of type 1 diabetes can develop rapidly and may include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Cuts or wounds that are slow to heal
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet
Management and Treatment
The management of type 1 diabetes typically involves a combination of insulin therapy, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Some common treatment options include: * Insulin therapy: Insulin injections or an insulin pump can help regulate blood sugar levels. * Healthy eating: Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates can help manage blood sugar levels. * Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of complications. * Monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring can help identify any changes in blood sugar levels and prevent complications.Psoriasis

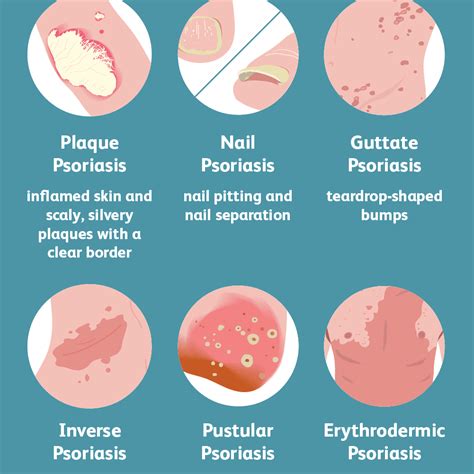
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches to develop. The symptoms of psoriasis can vary widely but often include:
- Red, scaly patches on the skin
- Itching and burning sensations
- Dry, cracked skin
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Nail changes, such as thickening or pitting
Treatment Options
The treatment of psoriasis typically involves a combination of topical medications, light therapy, and systemic medications. Some common treatment options include: * Topical corticosteroids: These medications can help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. * Topical retinoids: These medications can help reduce the growth of skin cells and improve skin texture. * Light therapy: Exposure to ultraviolet light can help reduce inflammation and improve skin symptoms. * Systemic medications: Medications such as biologics and oral retinoids can help reduce inflammation and improve skin symptoms.Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
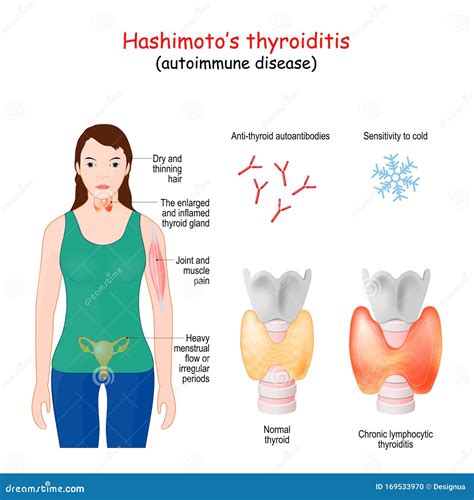
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid gland, causing hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). The symptoms of Hashimoto's thyroiditis can develop slowly and may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin and hair
- Hair loss
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis typically involves a combination of blood tests and physical examinations. Treatment options for Hashimoto's thyroiditis typically include: * Thyroid hormone replacement: Medications can help replace the missing thyroid hormones and improve symptoms. * Anti-inflammatory medications: Medications can help reduce inflammation and improve thyroid function. * Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as getting regular exercise and eating a balanced diet, can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.Crohn's Disease
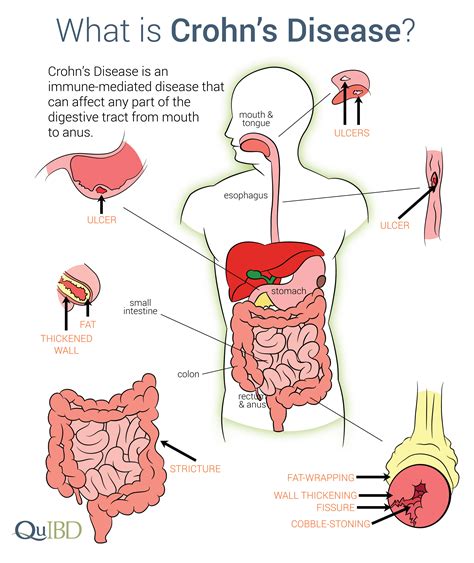
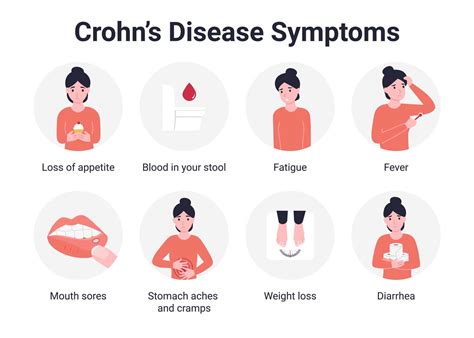
Crohn's disease is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the digestive tract, causing inflammation and damage to the lining of the gut. The symptoms of Crohn's disease can vary widely but often include:
- Diarrhea and abdominal pain
- Weight loss and fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rectal bleeding
Treatment Options
The treatment of Crohn's disease typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and surgery. Some common treatment options include: * Aminosalicylates: These medications can help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms. * Corticosteroids: These medications can help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. * Immunomodulators: These medications can help reduce the risk of complications and improve symptoms. * Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged portions of the gut or to repair fistulas.Autoimmune Diseases Image Gallery




In conclusion, autoimmune diseases are a complex and multifaceted group of conditions that require prompt medical attention and ongoing management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these diseases, individuals can take the first step towards seeking help and improving their overall health. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be affected by autoimmune diseases, and to explore the many resources and support groups available for those living with these conditions. Together, we can raise awareness and promote education about autoimmune diseases, and work towards a future where these conditions are better understood and more effectively managed.
