Intro
Master Lorazepam with our Active Learning Template Guide. Learn about this benzodiazepine medication, its uses, side effects, and interactions. Understand its pharmacology, dosing, and patient education. Ideal for healthcare professionals and students, this guide covers everything you need to know about Lorazepam, including anxiety treatment and insomnia management.
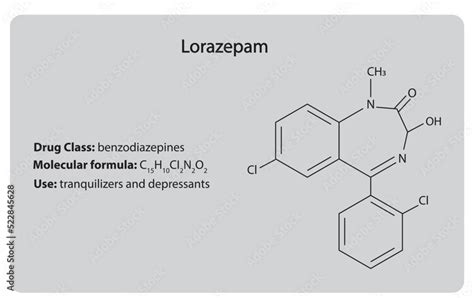
The use of lorazepam, a benzodiazepine medication, is a crucial aspect of medical treatment for various conditions, including anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. As a healthcare professional, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of lorazepam's mechanism of action, benefits, and potential risks to provide effective patient care.
Lorazepam, commonly known by the brand name Ativan, is a fast-acting benzodiazepine that enhances the effects of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. This enhancement leads to a calming effect on the nervous system, making lorazepam an effective treatment for anxiety-related disorders.
Mechanism of Action
Lorazepam's mechanism of action involves the facilitation of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter that reduces the activity of neurons. By enhancing the effects of GABA, lorazepam decreases the excitability of neurons, leading to a calming effect on the nervous system. This mechanism of action makes lorazepam an effective treatment for anxiety-related disorders, insomnia, and seizures.
Benefits of Lorazepam
Lorazepam has several benefits that make it a popular choice for treating anxiety-related disorders. Some of the benefits of lorazepam include:
- Fast-acting: Lorazepam has a rapid onset of action, making it an effective treatment for acute anxiety attacks.
- Effective: Lorazepam is highly effective in reducing anxiety symptoms, making it a popular choice for treating anxiety-related disorders.
- Versatile: Lorazepam can be used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures.
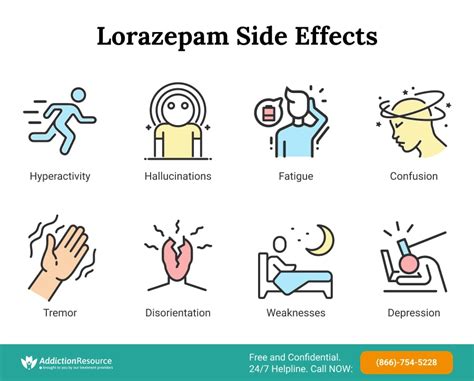
Potential Risks and Side Effects
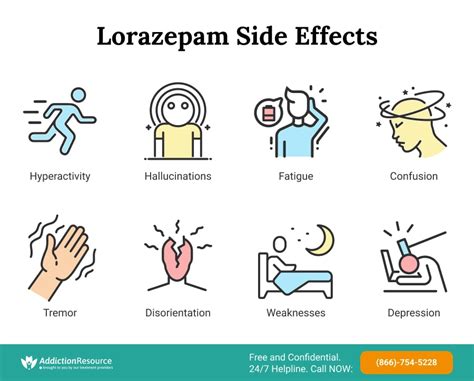
While lorazepam is an effective treatment for anxiety-related disorders, it also has potential risks and side effects. Some of the potential risks and side effects of lorazepam include:
- Dependence and withdrawal: Lorazepam can be habit-forming, and long-term use can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
- Cognitive impairment: Lorazepam can impair cognitive function, including memory and concentration.
- Interactions: Lorazepam can interact with other medications, including opioids and other benzodiazepines.
Contraindications and Precautions
Lorazepam has several contraindications and precautions that must be considered before prescribing. Some of the contraindications and precautions of lorazepam include:
- Pregnancy and lactation: Lorazepam should be used with caution during pregnancy and lactation, as it can pass into breast milk.
- Respiratory disease: Lorazepam should be used with caution in patients with respiratory disease, as it can exacerbate respiratory depression.
- Hepatic impairment: Lorazepam should be used with caution in patients with hepatic impairment, as it can increase the risk of toxicity.
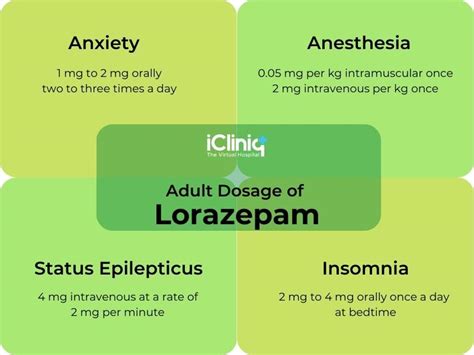
Dosage and Administration
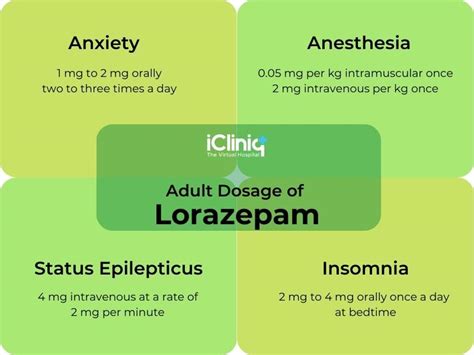
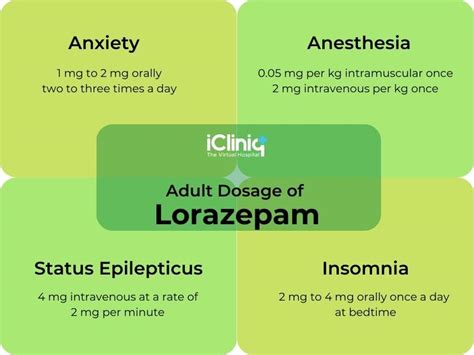
The dosage and administration of lorazepam vary depending on the condition being treated and the patient's age and weight. Some general guidelines for the dosage and administration of lorazepam include:
- Anxiety: The usual dosage of lorazepam for anxiety is 2-3 mg per day, divided into two or three doses.
- Insomnia: The usual dosage of lorazepam for insomnia is 2-4 mg per day, taken 15-30 minutes before bedtime.
- Seizures: The usual dosage of lorazepam for seizures is 2-4 mg per day, divided into two or three doses.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring and evaluation are crucial aspects of lorazepam treatment. Some of the parameters to monitor and evaluate during lorazepam treatment include:
- Vital signs: Monitor vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate.
- Cognitive function: Monitor cognitive function, including memory and concentration.
- Side effects: Monitor for side effects, including drowsiness, dizziness, and nausea.
Patient Education
Patient education is an essential aspect of lorazepam treatment. Some of the key points to educate patients about lorazepam include:
- Dosage and administration: Educate patients on the correct dosage and administration of lorazepam.
- Potential risks and side effects: Educate patients on the potential risks and side effects of lorazepam.
- Contraindications and precautions: Educate patients on the contraindications and precautions of lorazepam.
Gallery of Lorazepam
Lorazepam Image Gallery




Conclusion
Lorazepam is a benzodiazepine medication that is widely used to treat anxiety-related disorders, insomnia, and seizures. While lorazepam is effective in reducing anxiety symptoms, it also has potential risks and side effects that must be considered. Monitoring and evaluation are crucial aspects of lorazepam treatment, and patient education is essential to ensure safe and effective treatment. By understanding the benefits and risks of lorazepam, healthcare professionals can provide effective patient care and improve treatment outcomes.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable information about lorazepam. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We'd be happy to help.
