Intro
Unlock peak performance with track and field macro nutrition strategies. Discover how balanced macronutrient intake, protein timing, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats fuel athletes for optimal speed, endurance, and recovery. Boost your performance with tailored nutrition advice for infinite success on the track and field.
The world of track and field is a demanding one, requiring athletes to push their bodies to the limit in pursuit of excellence. To achieve success, track and field athletes must combine rigorous training with a well-planned nutrition strategy. Macro nutrition, in particular, plays a critical role in supporting the energy demands of track and field events. In this article, we'll explore the importance of macro nutrition for track and field athletes, discussing the key components of a performance-enhancing diet.
The Energy Demands of Track and Field
Track and field events are diverse, ranging from short sprints to long-distance runs, jumps, and throws. Each event has unique energy demands, requiring athletes to adapt their nutrition strategy to meet specific needs. For example, sprinters require rapid energy production to fuel their short, intense efforts, while distance runners need sustained energy release to support their prolonged activities.

The Role of Macro Nutrition in Track and Field Performance
Macro nutrition refers to the three primary macronutrients: carbohydrates, protein, and fat. Each macronutrient plays a vital role in supporting track and field performance.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy. Track and field athletes require adequate carbohydrate intake to support high-intensity, short-duration activities, as well as sustained energy release for longer events.
- Protein: Protein is essential for muscle growth, repair, and maintenance. Adequate protein intake helps track and field athletes recover from intense training sessions and competitions.
- Fat: Fat is a critical energy source for low-to-moderate intensity activities, such as distance running. It also plays a role in hormone production and absorption of essential vitamins.
Carbohydrate Intake for Track and Field Athletes
Carbohydrates are the most important macronutrient for track and field athletes, providing energy for high-intensity activities. The International Society of Sports Nutrition recommends that track and field athletes consume 1.6-3.0 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight per day. For example, a 70 kg (154 lbs) athlete would require 112-210 grams of carbohydrates per day.

Protein Intake for Track and Field Athletes
Protein is essential for muscle growth, repair, and maintenance. The International Society of Sports Nutrition recommends that track and field athletes consume 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. For example, a 70 kg (154 lbs) athlete would require 112-154 grams of protein per day.
Fat Intake for Track and Field Athletes
Fat is a critical energy source for low-to-moderate intensity activities, such as distance running. The International Society of Sports Nutrition recommends that track and field athletes consume 0.5-1.0 grams of fat per kilogram of body weight per day. For example, a 70 kg (154 lbs) athlete would require 35-70 grams of fat per day.
Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Proper hydration and electrolyte balance are crucial for track and field athletes. Inadequate hydration can lead to decreased performance, while electrolyte imbalances can cause muscle cramping and other complications.
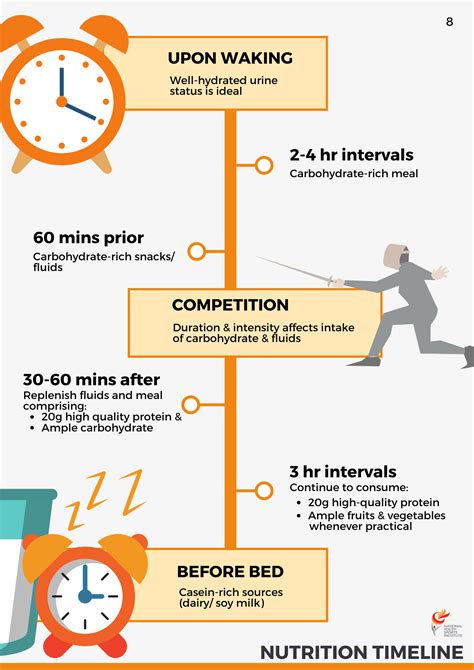
Practical Applications for Track and Field Athletes
So, how can track and field athletes apply these macro nutrition principles to enhance their performance?
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Periodize nutrition: Adjust macronutrient intake based on training phase and competition schedule.
- Monitor hydration and electrolyte balance: Drink plenty of water and consume electrolyte-rich foods or supplements as needed.
- Seek professional guidance: Consult with a sports dietitian or other qualified healthcare professional to develop a personalized nutrition plan.
Track and Field Macro Nutrition Image Gallery







Conclusion
Macro nutrition plays a critical role in supporting the energy demands of track and field athletes. By understanding the importance of carbohydrates, protein, and fat, and applying practical nutrition principles, track and field athletes can optimize their performance and achieve success. Whether you're a sprinter, distance runner, or thrower, a well-planned nutrition strategy can help you reach your full potential.
Share Your Thoughts
We'd love to hear from you! Share your thoughts on track and field macro nutrition in the comments below. What are your favorite nutrition tips for optimal performance?
