Discover key Malignant Fibrous Tumor facts, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this rare cancer, also known as Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma.
Malignant fibrous tumors, also known as malignant fibrous histiocytomas, are a type of cancer that originates in the soft tissues of the body. These tumors are formed from a mixture of fibroblasts and histiocytes, which are two types of cells that are found in connective tissue. Malignant fibrous tumors can occur in various parts of the body, including the limbs, trunk, and internal organs. They are relatively rare, accounting for only about 2-3% of all soft tissue tumors.
The importance of understanding malignant fibrous tumors lies in their potential to cause significant harm if left untreated. These tumors can grow rapidly and invade surrounding tissues, leading to pain, swelling, and limited mobility. In some cases, they can also spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, and bones, through a process called metastasis. Early detection and treatment of malignant fibrous tumors are crucial to prevent these complications and improve patient outcomes.
Malignant fibrous tumors can affect anyone, regardless of age or sex. However, they are more common in older adults, with the majority of cases occurring in people over the age of 50. The exact causes of these tumors are still not fully understood, but they are thought to be related to genetic mutations, exposure to radiation, and certain medical conditions, such as chronic inflammation or scarring. In some cases, malignant fibrous tumors may also be associated with other types of cancer, such as sarcomas or carcinomas.
Types of Malignant Fibrous Tumors
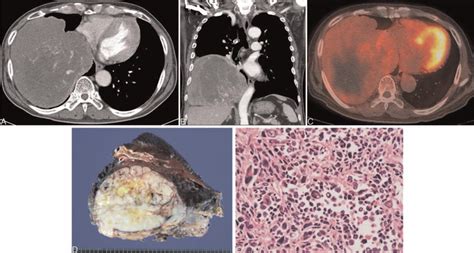
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of malignant fibrous tumors are still not fully understood. However, several risk factors have been identified, including: * Genetic mutations: Certain genetic mutations, such as those that affect the p53 tumor suppressor gene, have been linked to an increased risk of developing malignant fibrous tumors. * Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, either through medical treatment or environmental exposure, has been linked to an increased risk of developing malignant fibrous tumors. * Chronic inflammation: Chronic inflammation, such as that seen in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, has been linked to an increased risk of developing malignant fibrous tumors. * Scarring: Scarring, either from trauma or surgery, has been linked to an increased risk of developing malignant fibrous tumors.Symptoms and Diagnosis
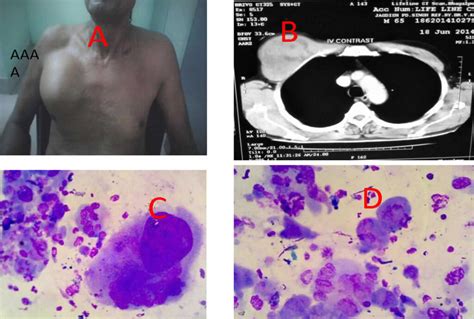
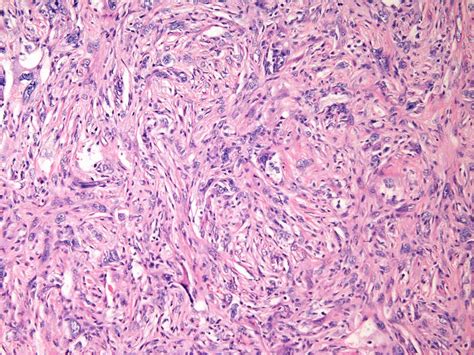
Diagnosis of malignant fibrous tumors typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, and biopsy. The biopsy involves removing a sample of tissue from the tumor and examining it under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
Treatment Options
Treatment of malignant fibrous tumors typically involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The goal of treatment is to remove the tumor and prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body. * Surgery: Surgery is usually the first line of treatment for malignant fibrous tumors. The goal of surgery is to remove the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue around it. * Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy may be used to treat malignant fibrous tumors that are too large to be removed surgically or that have spread to other parts of the body. * Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be used to treat malignant fibrous tumors that have spread to other parts of the body or that are not responding to other treatments.Prognosis and Outlook
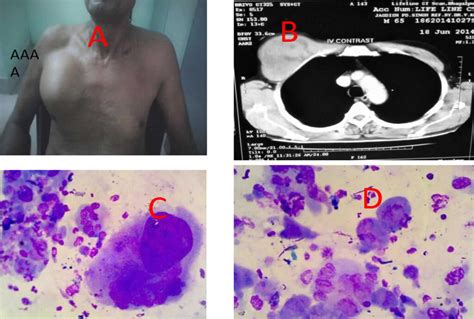
Prevention and Screening
There is no known way to prevent malignant fibrous tumors. However, early detection and treatment can improve patient outcomes. Screening for malignant fibrous tumors typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans. * Physical examination: A physical examination can help identify any unusual growths or masses that may be indicative of a malignant fibrous tumor. * Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, can help identify any tumors that may be present in the body.Current Research and Developments
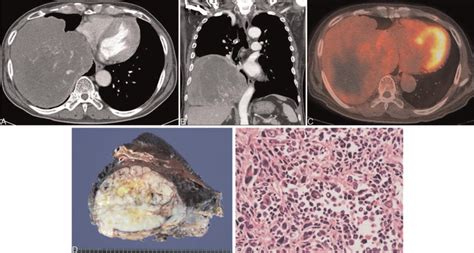
Support and Resources
There are several support and resources available for patients with malignant fibrous tumors, including: * Support groups: Support groups can provide emotional support and connect patients with others who are going through similar experiences. * Online resources: Online resources, such as websites and forums, can provide information and support for patients with malignant fibrous tumors. * Medical professionals: Medical professionals, such as doctors and nurses, can provide medical care and support for patients with malignant fibrous tumors.Malignant Fibrous Tumor Image Gallery
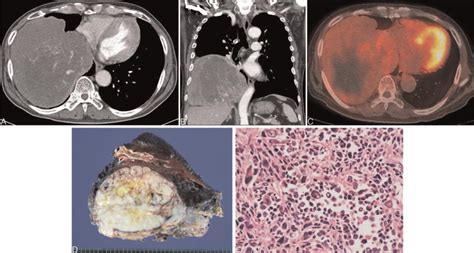
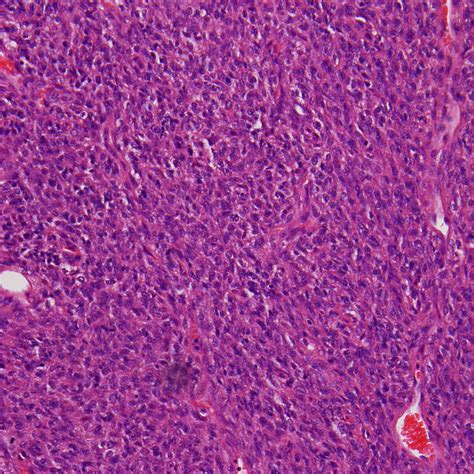
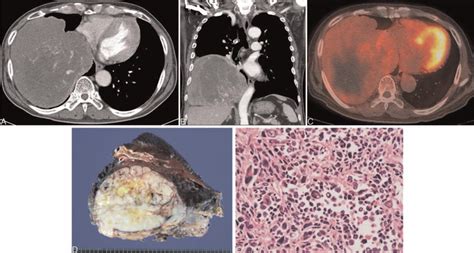
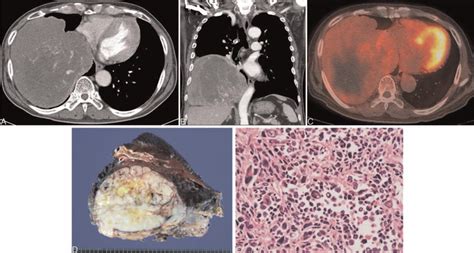
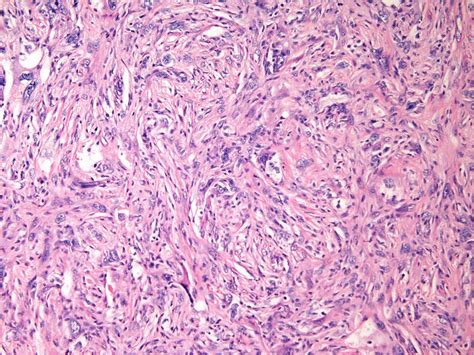
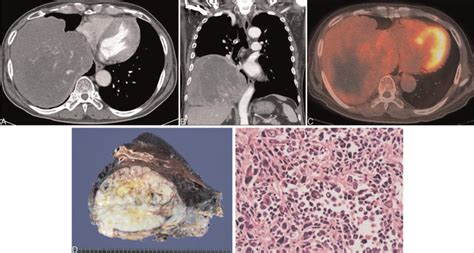
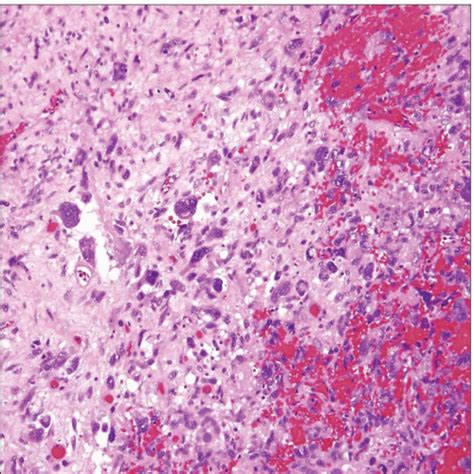
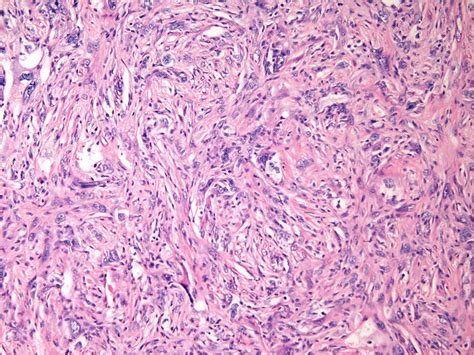

In final thoughts, malignant fibrous tumors are a type of cancer that can have significant consequences if left untreated. Early detection and treatment are crucial to improving patient outcomes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for malignant fibrous tumors, patients and medical professionals can work together to provide the best possible care. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with malignant fibrous tumors in the comments below, and to share this article with anyone who may be affected by this condition.
