Intro
Explore the latest trends and insights on US Marine Corps retention rates. Discover the factors influencing re-enlistment decisions, including deployment tempo, career advancement, and education benefits. Analyze the demographics and statistics shaping Marine Corps retention, and understand the implications for military readiness and national security.
The United States Marine Corps is one of the most prestigious and elite fighting forces in the world. With a rich history of honor, courage, and commitment, the Corps has long been a source of pride for the nation. However, in recent years, the Marine Corps has faced challenges in retaining its personnel, with retention rates fluctuating significantly. In this article, we will delve into the trends and insights of US Marine Corps retention rates, exploring the factors that influence retention, the consequences of low retention rates, and potential solutions to improve retention.
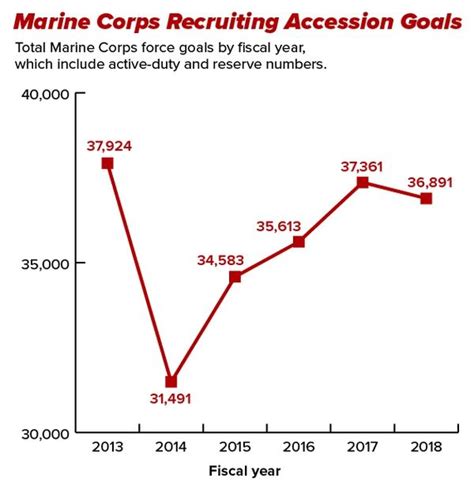
Understanding Retention Rates in the US Marine Corps
Retention rates in the US Marine Corps refer to the percentage of Marines who choose to re-enlist or extend their service beyond their initial contract. The Corps has traditionally relied on a mix of experienced veterans and new recruits to maintain its strength and effectiveness. However, with the changing landscape of modern warfare, the Corps faces increasing competition from civilian employers and other branches of the military.
Factors Influencing Retention Rates
Several factors contribute to the fluctuating retention rates in the US Marine Corps. Some of the key factors include:
- Career advancement opportunities: Marines who perceive limited opportunities for career advancement are more likely to leave the Corps.
- Quality of life: Factors such as base housing, family support, and access to healthcare influence a Marine's decision to stay or leave.
- Deployment frequency and duration: Frequent and prolonged deployments can lead to burnout and decreased retention rates.
- Civilian job market: A strong civilian job market can lure Marines away from the Corps with promises of higher pay and better benefits.
- Leadership and mentorship: Strong leadership and mentorship can significantly impact a Marine's decision to stay or leave.
Trends in US Marine Corps Retention Rates
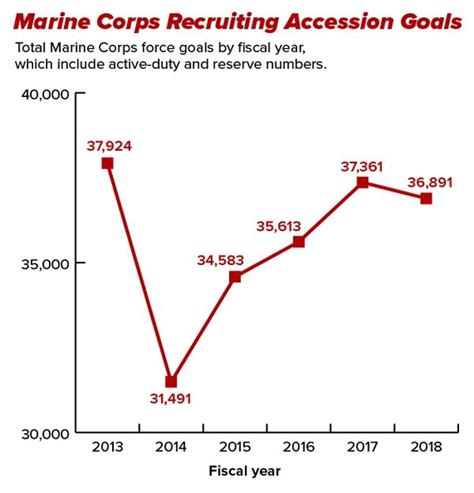
According to recent data, the US Marine Corps has experienced fluctuations in retention rates over the past decade. In 2019, the Corps reported a retention rate of 69.4%, a significant decrease from the 75.4% rate in 2015. The decline in retention rates can be attributed to various factors, including the changing nature of modern warfare, increased competition from civilian employers, and concerns about quality of life.
Consequences of Low Retention Rates
Low retention rates can have severe consequences for the US Marine Corps, including:
- Loss of experienced personnel: The Corps risks losing experienced Marines who possess critical skills and knowledge.
- Increased training costs: The Corps must invest significant resources in training new recruits to replace departing Marines.
- Decreased operational effectiveness: Low retention rates can compromise the Corps' ability to conduct operations effectively.
Strategies to Improve Retention Rates

To improve retention rates, the US Marine Corps can implement several strategies, including:
- Enhancing career advancement opportunities: The Corps can provide more opportunities for Marines to develop new skills and advance in their careers.
- Improving quality of life: The Corps can invest in base housing, family support, and access to healthcare to improve the overall quality of life for Marines.
- Reducing deployment frequency and duration: The Corps can explore alternatives to frequent and prolonged deployments to reduce burnout and increase retention rates.
- Offering competitive pay and benefits: The Corps can offer competitive pay and benefits to match those offered by civilian employers.
- Fostering strong leadership and mentorship: The Corps can emphasize the importance of strong leadership and mentorship in retaining Marines.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, the US Marine Corps faces significant challenges in retaining its personnel. To improve retention rates, the Corps must address the factors that influence retention, including career advancement opportunities, quality of life, deployment frequency and duration, civilian job market, and leadership and mentorship. By implementing strategies to enhance these factors, the Corps can increase retention rates, reduce training costs, and maintain its operational effectiveness.
Gallery of US Marine Corps Images
US Marine Corps Image Gallery








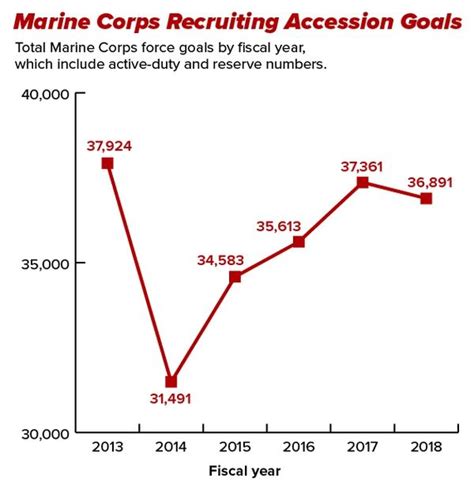

FAQs
Q: What is the current retention rate of the US Marine Corps? A: The current retention rate of the US Marine Corps is approximately 69.4%.
Q: What are the main factors that influence retention rates in the US Marine Corps? A: The main factors that influence retention rates in the US Marine Corps include career advancement opportunities, quality of life, deployment frequency and duration, civilian job market, and leadership and mentorship.
Q: How can the US Marine Corps improve retention rates? A: The US Marine Corps can improve retention rates by enhancing career advancement opportunities, improving quality of life, reducing deployment frequency and duration, offering competitive pay and benefits, and fostering strong leadership and mentorship.
Q: What are the consequences of low retention rates in the US Marine Corps? A: The consequences of low retention rates in the US Marine Corps include loss of experienced personnel, increased training costs, and decreased operational effectiveness.
Share Your Thoughts
We encourage you to share your thoughts and insights on the topic of US Marine Corps retention rates. Have you or a loved one served in the Marine Corps? What factors do you think contribute to retention rates? Share your comments below!
