Intro
Explore the Marine Reserves pay chart and salary information to understand compensation for part-time military service. Discover the latest pay scales, allowances, and benefits for Marine Reserves personnel, including drill pay, special duty pay, and retirement plans. Get informed about your financial future in the Marine Reserves.
Marine reserves play a vital role in supporting the active-duty Marine Corps by providing a pool of trained personnel who can be mobilized in times of war or national emergency. If you're considering joining the Marine reserves, it's essential to understand the pay and salary structure to make informed decisions about your future. In this article, we'll delve into the Marine reserves pay chart and provide detailed information about salaries, allowances, and benefits.
The Marine reserves pay chart is based on a combination of factors, including rank, time in service, and level of training. To start, let's take a look at the basic pay chart for Marine reserves.
Marine Reserves Pay Chart
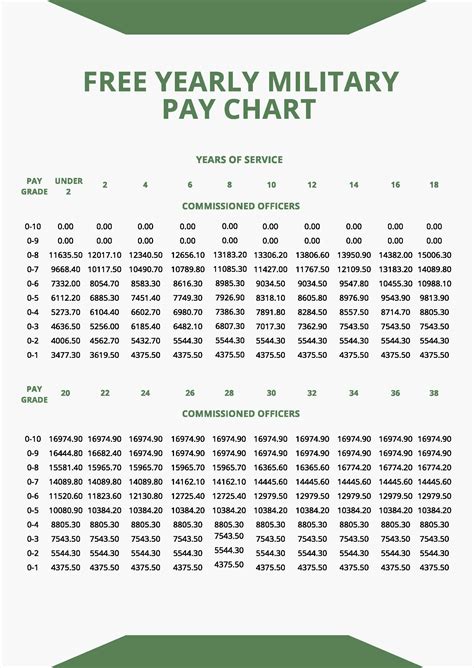
The pay chart above shows the basic monthly salary for Marine reserves based on rank and time in service. As you can see, the pay increases with both rank and time in service. However, this is just the basic pay, and there are other forms of compensation and benefits that can significantly impact your total salary.
Drill Pay
As a Marine reserve, you'll typically drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training session. During these periods, you'll receive drill pay, which is a supplement to your basic pay. Drill pay is based on your rank and the number of drills you attend.
Special Duty Pay
In addition to basic pay and drill pay, Marine reserves may also receive special duty pay for performing specific tasks or duties. This can include things like hazardous duty pay, diving duty pay, or parachute duty pay.
Allowances
Marine reserves may also receive various allowances to help cover the cost of living, food, and other expenses. These allowances can include:
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): This allowance helps cover the cost of food and is typically paid to Marine reserves who are not receiving free meals.
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): This allowance helps cover the cost of housing and is typically paid to Marine reserves who are not living in government-provided housing.
- Cost of Living Allowance (COLA): This allowance helps cover the cost of living in areas with a high cost of living.
Salary Information
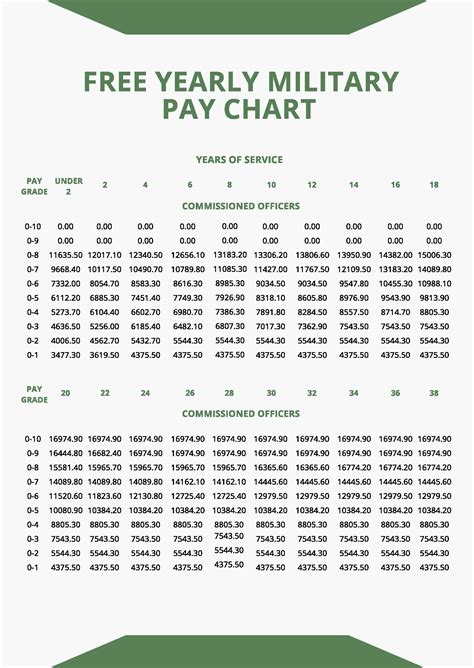
To give you a better idea of the total salary for Marine reserves, here are some approximate annual salary ranges based on rank and time in service:
- Private (E-1): $24,000 - $30,000
- Lance Corporal (E-3): $28,000 - $35,000
- Corporal (E-4): $32,000 - $40,000
- Sergeant (E-5): $36,000 - $45,000
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): $40,000 - $50,000
- Gunnery Sergeant (E-7): $45,000 - $55,000
- Master Sergeant (E-8): $50,000 - $60,000
- First Sergeant (E-8): $55,000 - $65,000
Keep in mind that these are approximate salary ranges and can vary depending on individual circumstances.
Benefits
In addition to salary, Marine reserves also receive a range of benefits, including:
- Education benefits: Marine reserves may be eligible for education benefits, such as the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Federal Tuition Assistance (FTA) program.
- Health benefits: Marine reserves and their families may be eligible for health benefits through the TRICARE program.
- Retirement benefits: Marine reserves may be eligible for retirement benefits after 20 years of service.
- Veterans' benefits: Marine reserves may be eligible for a range of veterans' benefits, including home loan guarantees, employment assistance, and healthcare benefits.
Conclusion
Joining the Marine reserves can be a rewarding and challenging experience that provides a range of benefits, including education assistance, healthcare benefits, and retirement benefits. By understanding the Marine reserves pay chart and salary structure, you can make informed decisions about your future and take the first step towards a rewarding career in the Marine reserves.
Next Steps
If you're considering joining the Marine reserves, here are some next steps you can take:
- Research the different types of roles and specialties available in the Marine reserves.
- Speak with a recruiter to learn more about the enlistment process and the benefits of joining the Marine reserves.
- Take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test to determine your eligibility for different roles.
- Complete the enlistment process and begin your training as a Marine reserve.
FAQs
- Q: How much do Marine reserves get paid? A: Marine reserves receive basic pay, drill pay, and special duty pay, as well as allowances for food, housing, and other expenses.
- Q: What are the benefits of joining the Marine reserves? A: Marine reserves receive a range of benefits, including education assistance, healthcare benefits, and retirement benefits.
- Q: How do I join the Marine reserves? A: To join the Marine reserves, you'll need to research the different types of roles and specialties available, speak with a recruiter, take the ASVAB test, and complete the enlistment process.
Gallery of Marine Reserves
Marine Reserves Image Gallery









We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the Marine reserves pay chart and salary information. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about joining the Marine reserves, please don't hesitate to comment below.

