Intro
Master asepsis in nursing with our comprehensive ATI template and study guide. Learn the principles of asepsis, infection control, and medical asepsis techniques to prevent hospital-acquired infections. Discover the importance of sterile technique, patient safety, and evidence-based practice in asepsis nursing care. Get ready to ace your nursing exams and deliver high-quality patient care.
Asepsis is a crucial concept in nursing that plays a vital role in preventing the spread of infections and maintaining a safe environment for patients. As a nurse, it is essential to understand the principles of asepsis and how to apply them in various clinical settings. In this article, we will explore the concept of asepsis in nursing, including its definition, importance, and guidelines for practice.
Asepsis in Nursing: Definition and Importance
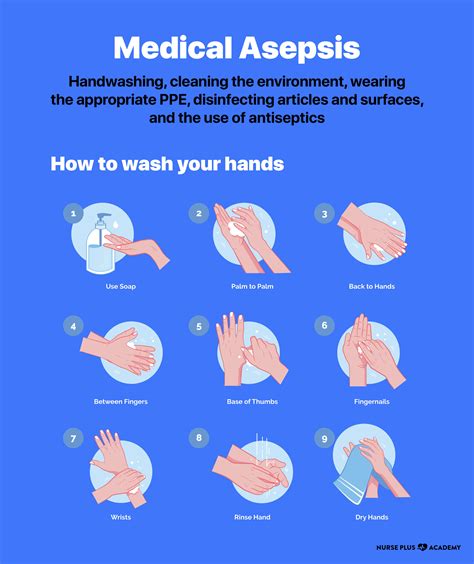
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing microorganisms. In nursing, asepsis is achieved through various techniques and practices that reduce the risk of infection transmission. Asepsis is essential in nursing because it helps to prevent the spread of infections, which can be life-threatening for patients with compromised immune systems.
Types of Asepsis
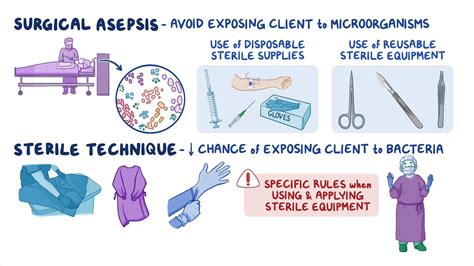
There are two types of asepsis: medical asepsis and surgical asepsis.
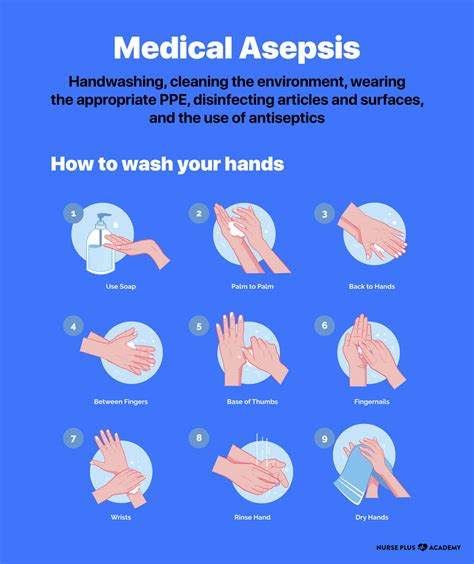
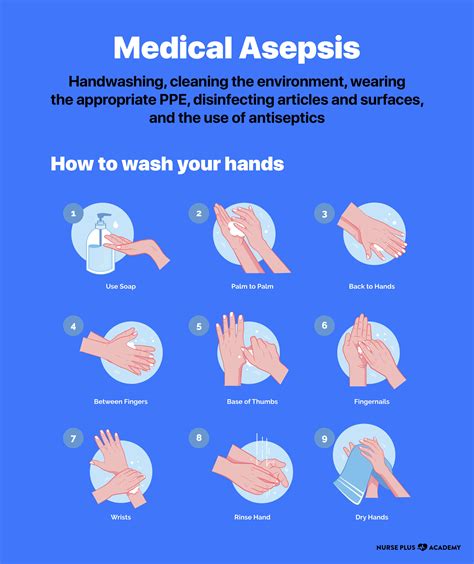
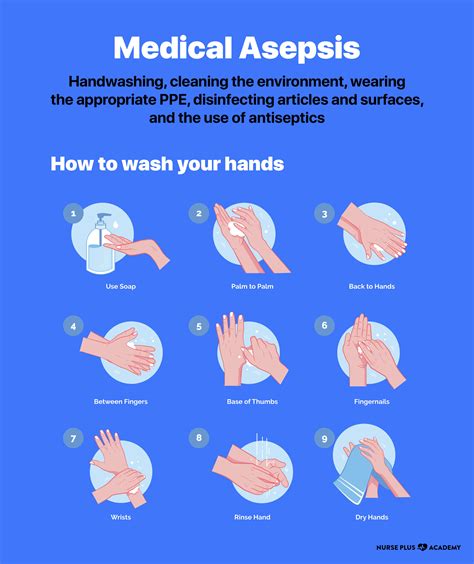
- Medical Asepsis: Medical asepsis is the removal or reduction of pathogens from the skin and mucous membranes. This type of asepsis is used for routine patient care activities, such as wound dressing and medication administration.
- Surgical Asepsis: Surgical asepsis is the complete removal of pathogens from the skin and mucous membranes. This type of asepsis is used for invasive procedures, such as surgery and insertion of medical devices.
Asepsis in Nursing Practice
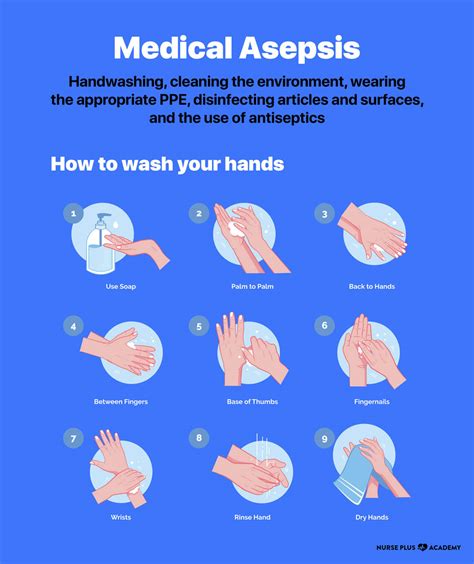
Asepsis is an essential component of nursing practice. Here are some guidelines for asepsis in nursing:
- Hand Hygiene: Hand hygiene is the most critical component of asepsis in nursing. Nurses should wash their hands with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer before and after patient contact.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): PPE, such as gloves and masks, should be worn when interacting with patients who have infectious diseases.
- Sterilization and Disinfection: Medical equipment and surfaces should be sterilized or disinfected regularly to prevent the spread of infections.
- Wound Care: Wounds should be cleaned and dressed regularly to prevent infection.
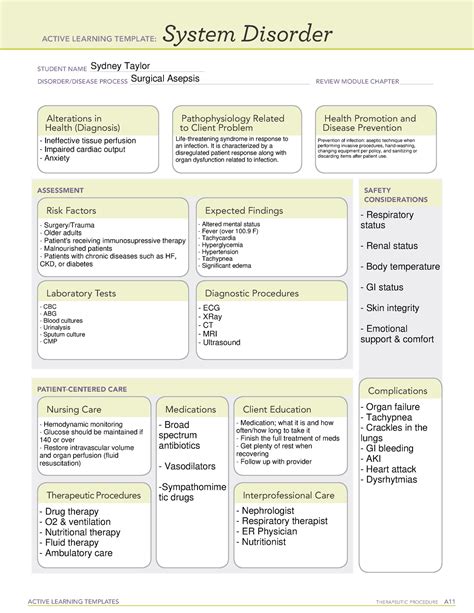
Asepsis in Nursing ATI Template
The ATI template is a framework for nursing practice that includes the following components:
- Assessment: Assess the patient's risk for infection and identify any potential sources of infection.
- Diagnosis: Diagnose any infections or potential infections based on the patient's symptoms and laboratory results.
- Planning: Develop a plan of care that includes strategies for preventing infection and promoting asepsis.
- Implementation: Implement the plan of care, including administering medications, performing wound care, and using PPE.
- Evaluation: Evaluate the effectiveness of the plan of care and make any necessary adjustments.
Asepsis in Nursing Study Guide

Here are some study guide questions to help you assess your knowledge of asepsis in nursing:
- What is the definition of asepsis in nursing?
- What are the two types of asepsis in nursing?
- What is the importance of hand hygiene in asepsis?
- What is the difference between sterilization and disinfection?
- What are the components of the ATI template?
Gallery of Asepsis in Nursing Images
Asepsis in Nursing Image Gallery
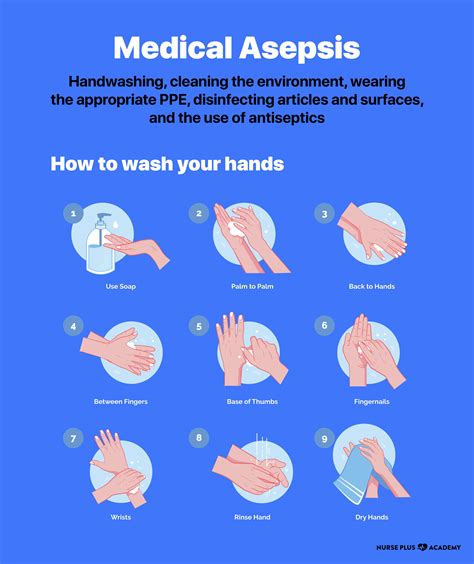
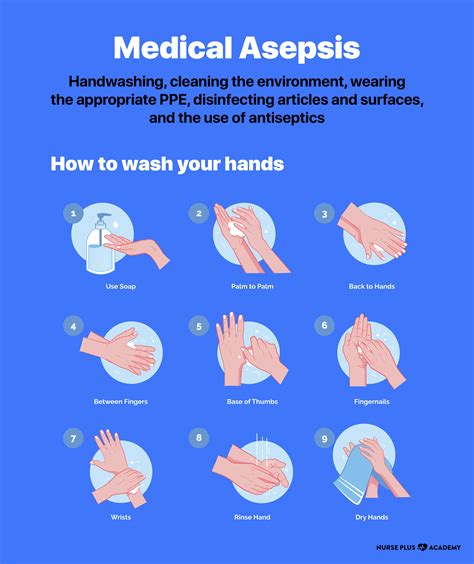



We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of asepsis in nursing. Remember to always practice asepsis when interacting with patients to prevent the spread of infections. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
