Uncover the dark secrets of Medieval Torturers Exposed, revealing brutal methods and instruments of torture, inquisition techniques, and cruel punishments used during the Middle Ages, shining light on historical torture devices and practices.
The medieval period, often referred to as the Middle Ages, was a time of significant historical, cultural, and social change in Europe. Lasting from the 5th to the 15th century, this era was marked by the rise and fall of empires, the growth of trade and commerce, and the development of art, literature, and architecture. However, it was also a time of great brutality and violence, particularly in the realm of punishment and torture. The use of torture as a means of extracting confessions, punishing criminals, and maintaining social control was widespread during this period, and those responsible for carrying out these gruesome acts were often shrouded in mystery and feared by the general population.
The medieval torturers, often referred to as "torture masters" or "executioners," were responsible for designing, constructing, and operating the various devices and techniques used to inflict pain and suffering on their victims. These individuals were typically skilled craftsmen, familiar with the use of tools and machinery, and were often trained in the art of torture from a young age. Despite their importance in the medieval justice system, relatively little is known about the lives and experiences of these torturers, and their role in shaping the course of history is often overlooked. However, by examining the various torture devices and techniques used during this period, as well as the social and cultural context in which they operated, it is possible to gain a deeper understanding of the medieval torturers and their significance in the medieval world.
The use of torture as a means of punishment and social control was not unique to the medieval period, but it was during this time that it became a widespread and institutionalized practice. The medieval justice system was based on the principle of "trial by ordeal," in which the accused was subjected to various forms of physical punishment in order to determine their guilt or innocence. If the accused survived the ordeal, they were deemed innocent, while those who did not were considered guilty. This system relied heavily on the use of torture, and the various devices and techniques used to inflict pain and suffering on the accused were designed to extract confessions, punish criminals, and maintain social control.
Introduction to Medieval Torture Devices

The medieval torturers used a wide range of devices and techniques to inflict pain and suffering on their victims. These devices, often designed and constructed by the torturers themselves, were typically made of wood, metal, or stone, and were used to inflict physical pain, disfigurement, and even death. Some of the most common medieval torture devices include the rack, the iron maiden, the thumbscrew, and the breaking wheel. The rack, for example, was a wooden frame used to stretch and dislocate the limbs of the accused, while the iron maiden was a metal device lined with spikes that was used to pierce and mutilate the victim's body. The thumbscrew, on the other hand, was a small device used to crush the thumbs and fingers of the accused, while the breaking wheel was a large, wooden wheel used to break the bones of the victim.
Types of Medieval Torture Devices
Some of the other medieval torture devices used during this period include: * The garrote: a metal device used to strangle the victim * The gibbet: a metal cage used to display the bodies of executed criminals * The stocks: a wooden device used to restrain and humiliate the accused * The pillory: a wooden device used to restrain and punish the accused * The branding iron: a metal device used to brand the victim with a hot ironThe Role of Medieval Torturers in Society

The medieval torturers played a significant role in the medieval justice system, and their services were in high demand by the authorities. These individuals were responsible for designing, constructing, and operating the various devices and techniques used to inflict pain and suffering on the accused, and were often skilled craftsmen and technicians. Despite their importance in the medieval justice system, however, the medieval torturers were often shunned and feared by the general population. They were seen as brutal and merciless, and their occupation was often viewed as unclean and dishonorable.
Social Status of Medieval Torturers
The social status of medieval torturers varied depending on the region and the time period. In some areas, they were viewed as skilled craftsmen and technicians, and were respected for their expertise and knowledge. In other areas, however, they were seen as brutal and merciless, and were shunned and feared by the general population. Despite their varied social status, however, the medieval torturers played a significant role in shaping the course of history, and their legacy continues to be felt today.Notable Medieval Torturers

There were several notable medieval torturers who made significant contributions to the development of torture devices and techniques. One of the most famous medieval torturers was Giovanni Tortelli, an Italian torturer who lived during the 15th century. Tortelli was known for his expertise in designing and constructing torture devices, and was responsible for creating several innovative devices, including the "torture wheel" and the "iron maiden." Another notable medieval torturer was Franz Schmidt, a German torturer who lived during the 16th century. Schmidt was known for his brutality and mercilessness, and was responsible for executing hundreds of people during his lifetime.
Legacy of Medieval Torturers
The legacy of medieval torturers continues to be felt today, and their impact on the development of modern torture devices and techniques is still evident. The use of torture as a means of punishment and social control has been widely criticized, and many countries have banned the practice altogether. However, the legacy of medieval torturers serves as a reminder of the importance of protecting human rights and preventing the use of torture and other forms of cruel, inhuman, and degrading treatment.Medieval Torture Techniques

The medieval torturers used a wide range of techniques to inflict pain and suffering on their victims. These techniques, often designed to extract confessions, punish criminals, and maintain social control, were typically brutal and merciless. Some of the most common medieval torture techniques include:
- Waterboarding: a technique in which the victim is subjected to near-drowning
- Burning: a technique in which the victim is subjected to burns, often using hot irons or other objects
- Disembowelment: a technique in which the victim is subjected to disembowelment, often using a sharp object
- Flaying: a technique in which the victim is subjected to flaying, often using a sharp object
Psychological Effects of Medieval Torture
The psychological effects of medieval torture were often severe and long-lasting. Many victims of medieval torture suffered from anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and some were even driven to madness or suicide. The use of torture as a means of punishment and social control was widely criticized, and many people argued that it was ineffective and inhumane.Gallery of Medieval Torture Devices
Medieval Torture Devices Image Gallery
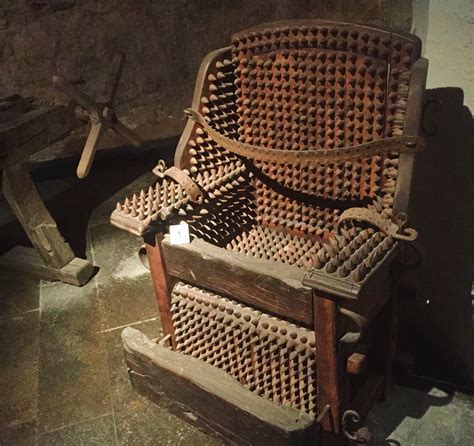
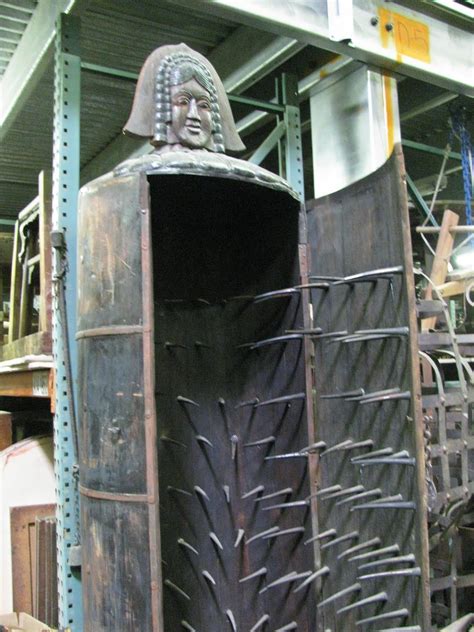
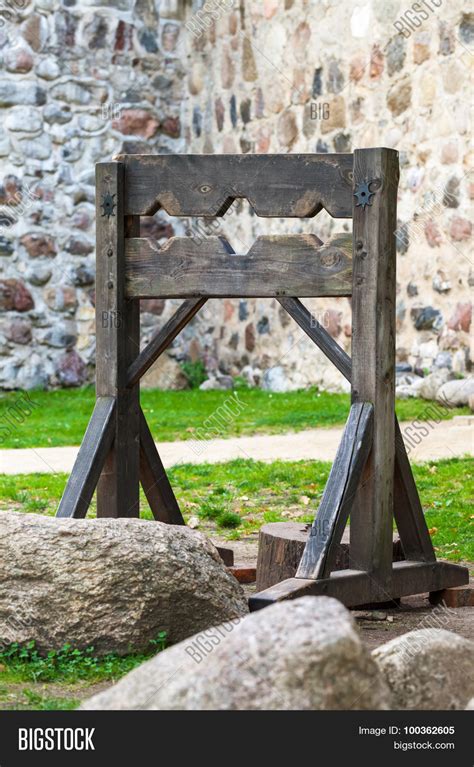
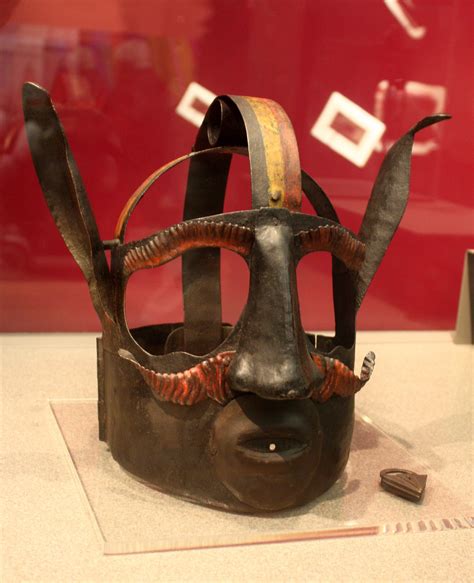


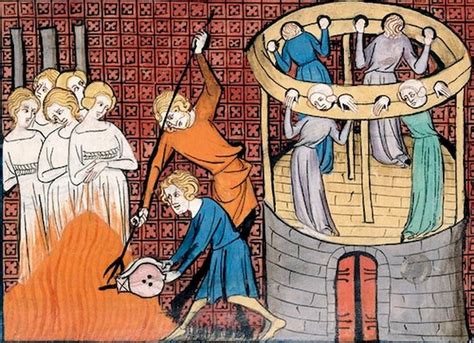



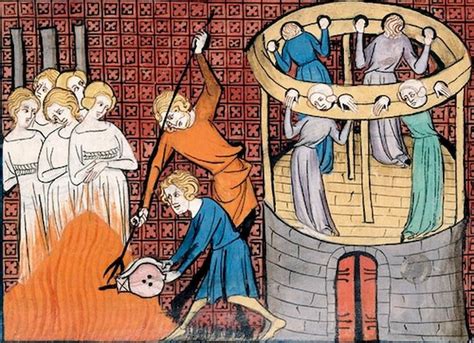



In conclusion, the medieval torturers played a significant role in shaping the course of history, and their legacy continues to be felt today. The use of torture as a means of punishment and social control was widely criticized, and many countries have banned the practice altogether. However, the study of medieval torture devices and techniques serves as a reminder of the importance of protecting human rights and preventing the use of torture and other forms of cruel, inhuman, and degrading treatment. We invite you to share your thoughts and opinions on this topic, and to explore the many resources available for learning more about the medieval period and the history of torture. By working together, we can promote a greater understanding of the past and build a more just and compassionate future for all.
