Intro
Discover the 5 key differences in military pay that impact your compensation. Learn about Basic Pay, Allowances, Bonuses, and Special Pays that vary by branch, rank, and time in service. Understand how military pay charts, benefits, and incentives differ between Active Duty, Reserve, and National Guard personnel.
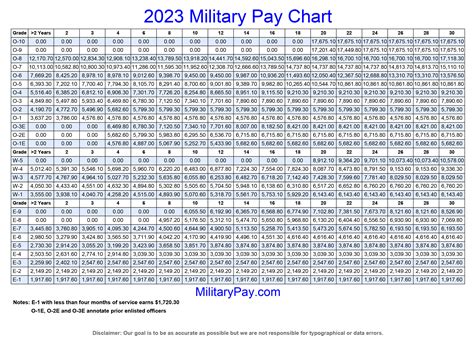
The military pay system can be complex and varies depending on several factors, including the branch of service, rank, time in service, and type of pay. Understanding the differences in military pay is essential for service members to make informed decisions about their careers and financial planning. In this article, we will explore five key differences in military pay.
Base Pay vs. Allowances

One of the primary differences in military pay is between base pay and allowances. Base pay is the basic salary paid to service members, which varies depending on their rank and time in service. Allowances, on the other hand, are additional forms of compensation that are paid to service members to help them cover specific expenses, such as housing, food, and clothing.
Base pay is the largest component of military pay and is paid to all service members. Allowances, however, are only paid to service members who meet specific eligibility criteria. For example, service members who are married or have dependents may be eligible for a Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) or a Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS).
Types of Allowances
There are several types of allowances that service members may be eligible for, including:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): paid to service members who are eligible for housing assistance
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): paid to service members who are eligible for food assistance
- Clothing Allowance: paid to service members to help them purchase and maintain their uniforms
- Hazardous Duty Pay: paid to service members who perform hazardous duties, such as flying or diving
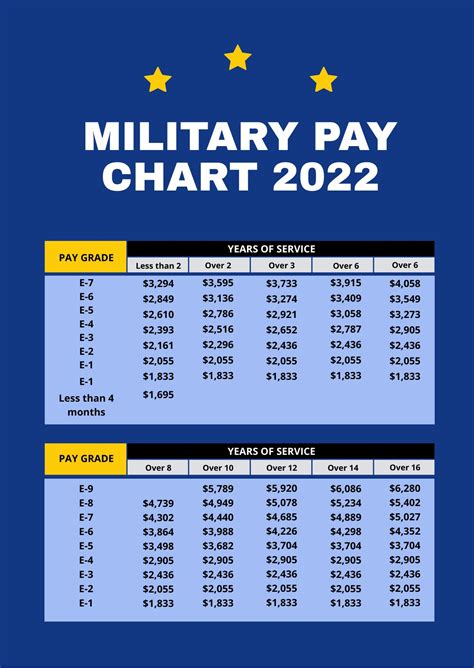
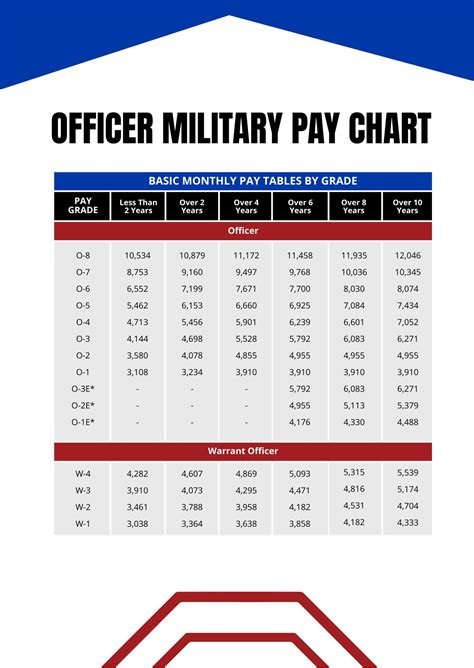
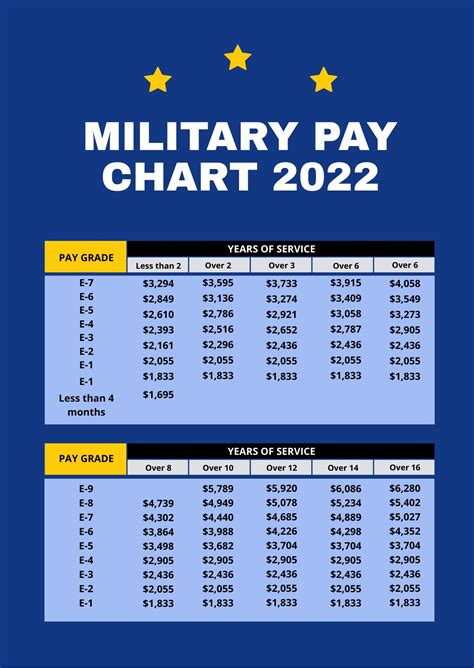
Enlisted vs. Officer Pay

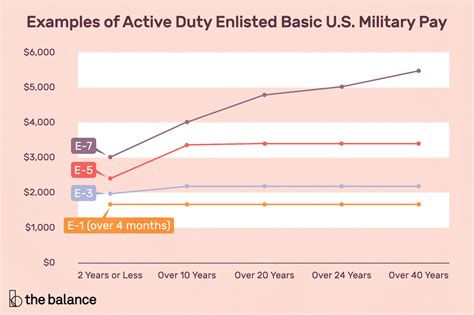
Another key difference in military pay is between enlisted and officer pay. Enlisted service members are paid according to their rank and time in service, while officers are paid according to their rank, time in service, and level of education.
Enlisted service members typically start at a lower pay grade than officers and may require more time and experience to reach higher pay grades. Officers, on the other hand, typically start at a higher pay grade than enlisted service members and may have more opportunities for advancement and higher pay.
Officer Pay vs. Enlisted Pay
Here is a comparison of officer and enlisted pay for the same rank and time in service:
- Enlisted E-4 (Corporal) with 4 years of service: $2,500 per month
- Officer O-3 (Captain) with 4 years of service: $5,000 per month
As you can see, officers tend to earn more than enlisted service members, even at the same rank and time in service.
Reserve vs. Active Duty Pay

Another key difference in military pay is between reserve and active duty pay. Reserve service members are paid according to their rank, time in service, and type of duty, while active duty service members are paid according to their rank and time in service.
Reserve service members typically serve one weekend a month and two weeks a year, while active duty service members serve full-time. As a result, active duty service members tend to earn more than reserve service members, even at the same rank and time in service.
Reserve Pay vs. Active Duty Pay
Here is a comparison of reserve and active duty pay for the same rank and time in service:
- Reserve E-4 (Corporal) with 4 years of service: $1,500 per month
- Active Duty E-4 (Corporal) with 4 years of service: $2,500 per month
As you can see, active duty service members tend to earn more than reserve service members, even at the same rank and time in service.
Special Pay vs. Bonus Pay

Finally, another key difference in military pay is between special pay and bonus pay. Special pay is paid to service members who perform specific duties or have specific skills, such as flying or diving. Bonus pay, on the other hand, is paid to service members who enlist for a specific period of time or who agree to serve in a specific role.
Special pay is typically paid on a regular basis, while bonus pay is typically paid in a lump sum. For example, service members who enlist for 6 years may receive a bonus of $10,000, while service members who perform hazardous duties may receive special pay of $500 per month.
Types of Special Pay
There are several types of special pay that service members may be eligible for, including:
- Hazardous Duty Pay: paid to service members who perform hazardous duties, such as flying or diving
- Jump Pay: paid to service members who are qualified parachutists
- Dive Pay: paid to service members who are qualified divers
Types of Bonus Pay
There are several types of bonus pay that service members may be eligible for, including:
- Enlistment Bonus: paid to service members who enlist for a specific period of time
- Reenlistment Bonus: paid to service members who reenlist for a specific period of time
- Officer Bonus: paid to officers who agree to serve in a specific role or for a specific period of time
Military Pay Image Gallery





We hope this article has helped you understand the five key differences in military pay. Whether you're a service member, a veteran, or simply interested in learning more about the military pay system, we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.
