Intro
Discover the top 5 differences between military officers and enlisted personnel. Learn about the distinct roles, responsibilities, and requirements of each, including leadership, training, and career advancement opportunities. Understand the key distinctions between commissioned and non-commissioned personnel in the armed forces.
The military is a hierarchical organization with a clear chain of command, and within this structure, there are two primary categories of personnel: officers and enlisted. While both groups play critical roles in the success of the military, there are significant differences between them in terms of their responsibilities, training, and career paths.
The distinction between officers and enlisted personnel is not unique to the military, as similar divisions exist in other organizations, such as law enforcement and firefighting. However, the military's unique culture and mission require a specialized understanding of the differences between these two groups.
In this article, we will explore the top 5 differences between military officers and enlisted personnel, highlighting the key distinctions in their roles, responsibilities, and career paths.
Difference 1: Education and Training

One of the most significant differences between officers and enlisted personnel is the level of education and training required for each group. Officers typically require a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution, while enlisted personnel may enter the military with a high school diploma or equivalent.
Officer candidates undergo rigorous training at a service academy, such as West Point or the Naval Academy, or through a Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) program. These programs provide a comprehensive education in leadership, tactics, and military history, as well as training in specific skills relevant to their chosen branch of service.
In contrast, enlisted personnel typically attend Basic Training, also known as boot camp, which provides an introduction to military life and teaches fundamental skills such as first aid, combat techniques, and military protocol. Enlisted personnel may also attend specialized training programs, known as Advanced Individual Training (AIT), which focus on specific skills such as mechanics, communications, or healthcare.
Difference 2: Leadership Roles
Leadership Responsibilities

Another key difference between officers and enlisted personnel is the level of leadership responsibility. Officers are trained to lead and manage teams, making strategic decisions and providing guidance to their subordinates. They are responsible for planning, coordinating, and executing missions, as well as evaluating the performance of their teams.
Enlisted personnel, on the other hand, are typically responsible for executing the plans and orders of their superiors. While they may have some leadership responsibilities, their primary focus is on performing specific tasks and duties within their unit.
Difference 3: Career Paths
Career Advancement Opportunities

The career paths of officers and enlisted personnel differ significantly. Officers typically follow a more linear career progression, with clear opportunities for advancement and promotion. They may serve in a variety of roles, including command positions, staff roles, and specialized assignments such as intelligence or logistics.
Enlisted personnel, on the other hand, may follow a more specialized career path, with opportunities for advancement within their specific Military Occupational Specialty (MOS). They may also have opportunities to become non-commissioned officers (NCOs), which provide additional leadership responsibilities and career advancement opportunities.
Difference 4: Compensation and Benefits
Pay and Benefits
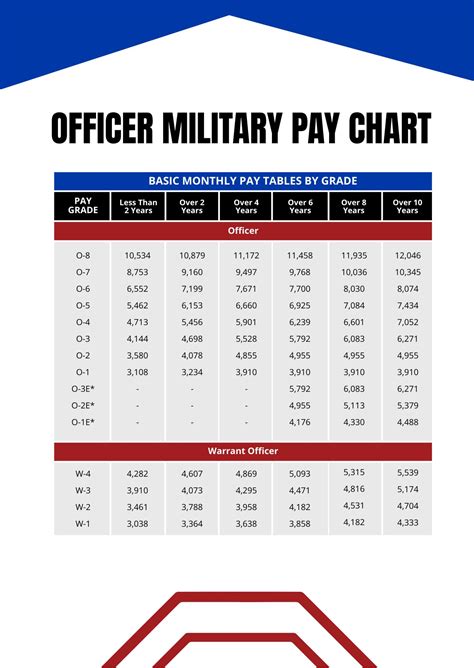
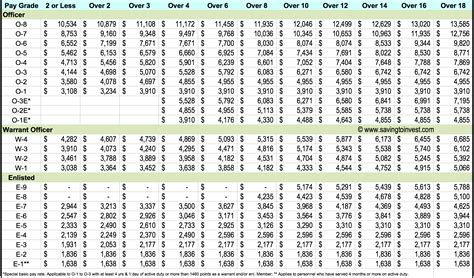
The compensation and benefits packages for officers and enlisted personnel differ significantly. Officers typically receive higher pay and allowances, as well as additional benefits such as housing and food stipends.
Enlisted personnel also receive a comprehensive benefits package, including pay, allowances, and access to military healthcare and education benefits. However, their compensation and benefits packages are generally less generous than those of officers.
Difference 5: Social Status and Perks
Military Protocol and Privileges

Finally, there are significant differences in the social status and perks associated with being an officer versus an enlisted personnel. Officers are typically accorded greater respect and deference within the military, and are often expected to adhere to a higher standard of behavior and protocol.
Enlisted personnel, on the other hand, may have more relaxed standards of behavior and protocol, although they are still expected to maintain a high level of professionalism and discipline.
In conclusion, while both officers and enlisted personnel play critical roles in the military, there are significant differences between them in terms of their responsibilities, training, and career paths. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone considering a career in the military, as well as for those seeking to appreciate the unique challenges and opportunities faced by military personnel.
Military Officer and Enlisted Gallery








We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on the differences between military officers and enlisted personnel. Have you served in the military, or do you have a family member or friend who has? Share your stories and insights in the comments below.
