Naming a range in VBA is a fundamental skill that can significantly enhance your productivity and the clarity of your code. When working with Excel, naming ranges can simplify your code, making it easier to understand and maintain. In this article, we will explore five different ways to name a range in VBA, covering various scenarios and techniques to suit different needs.
Understanding Range Naming in VBA
Before diving into the methods, it's essential to understand the basics of range naming in VBA. Range names are used to refer to a range of cells in a workbook, making it easier to perform operations on those cells without having to specify the exact cell addresses. Range names can be used in formulas, VBA code, and even in Excel's built-in functions.
Method 1: Using the Name Manager
One of the most straightforward ways to name a range in VBA is by using the Name Manager. This approach involves directly interacting with Excel's interface.
To use the Name Manager:
- Open the workbook in which you want to name a range.
- Press
Ctrl + F3to open the Name Manager dialog box. - Click
Newto create a new range name. - Enter a name for your range in the
Namefield. - Specify the range of cells you want to name in the
Refers tofield. - Click
OKto create the range name.
While this method is intuitive and visual, it requires direct interaction with Excel's interface, which might not be suitable for automating tasks or working within VBA exclusively.
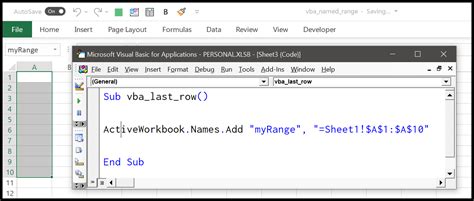
Method 2: Using VBA to Create a Named Range
This method involves writing VBA code to create a named range. This approach is more suitable for automation or when you want to create named ranges dynamically.
To create a named range using VBA:
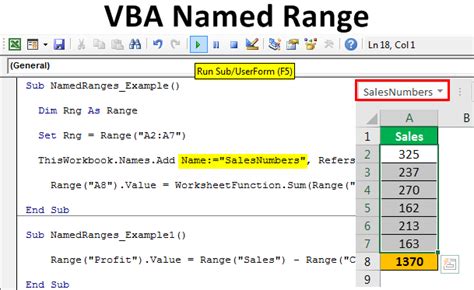
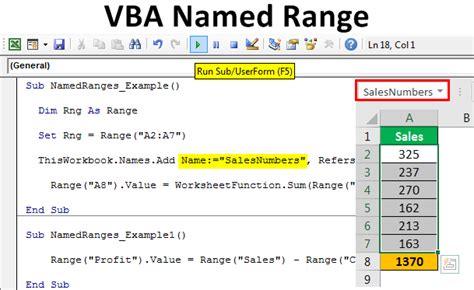
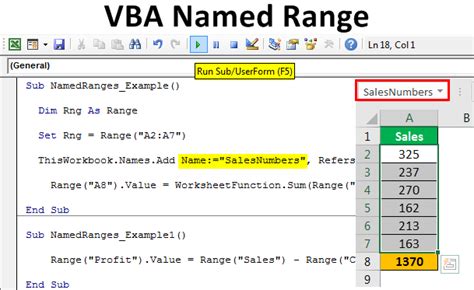
Sub CreateNamedRange()
' Declare the variables
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rng As Range
Dim strName As String
' Set the worksheet and range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Set rng = ws.Range("A1:B10")
' Specify the name for the range
strName = "MyNamedRange"
' Check if the range name already exists and delete it if it does
On Error Resume Next
ws.Names(strName).Delete
On Error GoTo 0
' Create the named range
rng.Name = strName
' Optional: Create a named range with a scope
' ThisWorkbook.Names.Add strName, rng
End Sub
This method allows for greater control and flexibility, especially when automating tasks or creating named ranges based on dynamic conditions.
Method 3: Using the `Define Name` Dialog
Another method to name a range involves using the Define Name dialog, which can be accessed through the Excel interface.
To use the Define Name dialog:
- Select the range of cells you want to name.
- Go to the
Formulastab in the ribbon. - Click on
Define Namein theDefined Namesgroup. - In the
New Namedialog, enter a name for your range in theNamefield. - Click
OKto create the range name.
This method is similar to using the Name Manager but is accessed through a different route.

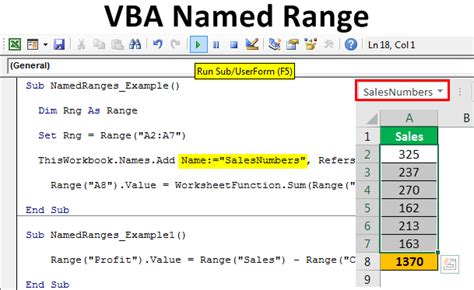
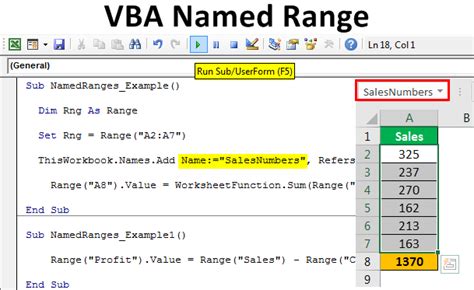
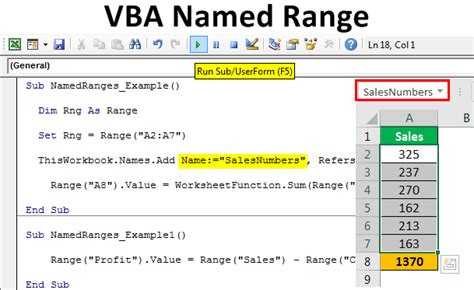
Method 4: Creating a Named Range with a Formula
Sometimes, you might want to create a named range that is defined by a formula rather than a static range of cells.
To create a named range with a formula using VBA:
Sub CreateNamedRangeWithFormula()
' Declare the variables
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim strName As String
Dim strFormula As String
' Set the worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
' Specify the name and formula for the range
strName = "MyNamedRangeFormula"
strFormula = "=OFFSET(A1,0,0,COUNT(A:A),1)"
' Check if the range name already exists and delete it if it does
On Error Resume Next
ws.Names(strName).Delete
On Error GoTo 0
' Create the named range with a formula
ThisWorkbook.Names.Add strName, strFormula
End Sub
This method allows for dynamic range definitions based on formulas, which can be particularly useful for data analysis and reporting.
Method 5: Creating a Named Range for a Table
If you're working with tables in Excel, you might want to create named ranges for them.
To create a named range for a table using VBA:
Sub CreateNamedRangeForTable()
' Declare the variables
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim tbl As ListObject
Dim strName As String
' Set the worksheet and table
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Set tbl = ws.ListObjects("MyTable")
' Specify the name for the range
strName = "MyTableName"
' Check if the range name already exists and delete it if it does
On Error Resume Next
ws.Names(strName).Delete
On Error GoTo 0
' Create the named range for the table
tbl.Range.Name = strName
End Sub
This method is particularly useful for managing data within tables and referencing them in formulas or VBA code.
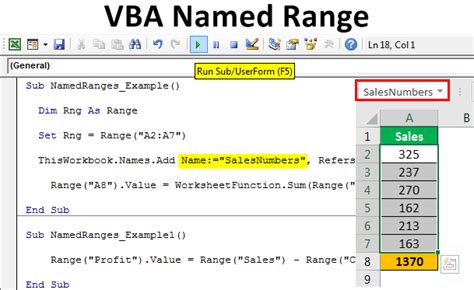
Gallery of VBA Range Naming
VBA Range Naming Image Gallery
In conclusion, naming ranges in VBA is a powerful tool for simplifying your code and enhancing productivity. By understanding the different methods for creating named ranges, you can better manage your data and create more robust Excel applications. Whether you're automating tasks, analyzing data, or simply seeking to organize your code more effectively, mastering range naming in VBA can make a significant difference.
Take the first step today by experimenting with the methods outlined above. As you explore the capabilities of VBA range naming, remember to share your experiences and insights with others, and don't hesitate to reach out with any questions or topics you'd like to discuss further.
