Intro
Explore the 5 key differences between National Guard and Army Reserve, including service commitment, deployment, training, and benefits. Discover how these two Reserve Components of the US Armed Forces differ in terms of military service, duty, and civilian life. Learn which path is right for you and make an informed decision.
Serving in the military is a significant commitment, and for those who want to balance their civilian life with military service, the National Guard and Army Reserve are two popular options. While both organizations are part of the US military, there are key differences between them. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals who are considering joining one of these organizations. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between the National Guard and Army Reserve.
Understanding the Basics
Before we dive into the differences, it's essential to understand the basics of both organizations. The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces that consists of citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to serve in both state and federal capacities. The Army Reserve, on the other hand, is a federal force that consists of soldiers who can be called upon to support the active-duty army in times of war or national emergency.
Difference 1: Mission and Purpose

The primary mission of the National Guard is to provide support to state and local authorities during natural disasters, civil unrest, and other emergencies. In addition to their state mission, National Guard units can also be deployed overseas to support federal missions. The Army Reserve, on the other hand, has a more narrow focus on supporting the active-duty army in times of war or national emergency. Army Reserve soldiers are trained to deploy alongside active-duty soldiers to provide additional support and capabilities.
Difference 2: Training and Deployment
National Guard soldiers typically drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training period. They may also be called upon to deploy overseas to support federal missions. Army Reserve soldiers, on the other hand, typically drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training period. However, Army Reserve soldiers are more likely to deploy overseas than National Guard soldiers, as their primary mission is to support the active-duty army.
Difference 3: Service Requirements
The service requirements for National Guard and Army Reserve soldiers differ. National Guard soldiers typically serve 6-8 years, while Army Reserve soldiers serve 6-8 years as well. However, National Guard soldiers are required to attend drill weekends and annual training periods, as well as participate in state emergencies. Army Reserve soldiers, on the other hand, are required to attend drill weekends and annual training periods, but may not be required to participate in state emergencies.
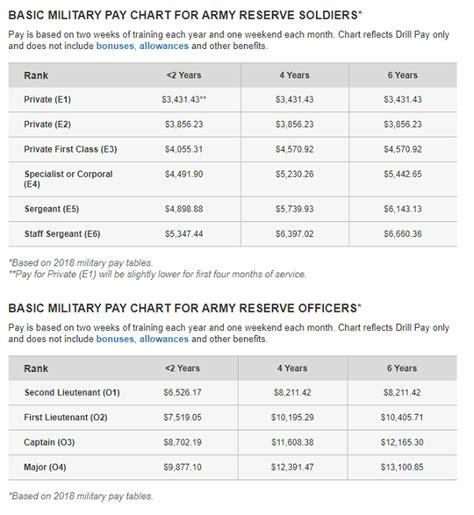
Difference 4: Benefits and Pay
Both National Guard and Army Reserve soldiers are eligible for a range of benefits, including education assistance, medical insurance, and retirement plans. However, the pay and benefits for National Guard soldiers may differ depending on their state of service. Army Reserve soldiers, on the other hand, are paid a set amount for drill weekends and annual training periods, as well as for deployments.
Difference 5: State vs. Federal Service
One of the most significant differences between the National Guard and Army Reserve is the type of service they provide. National Guard soldiers serve both state and federal governments, while Army Reserve soldiers serve only the federal government. This means that National Guard soldiers may be called upon to respond to state emergencies, such as natural disasters or civil unrest, while Army Reserve soldiers are more likely to deploy overseas.
Gallery of National Guard and Army Reserve Images








Call to Action
If you're considering joining the National Guard or Army Reserve, it's essential to understand the differences between these two organizations. By understanding their unique missions, training requirements, and benefits, you can make an informed decision about which path is right for you. Whether you're looking to serve your state or country, or simply want to be part of a proud tradition of military service, the National Guard and Army Reserve offer a range of opportunities for individuals who want to serve their country.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between the National Guard and Army Reserve? The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces that consists of citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to serve in both state and federal capacities. The Army Reserve, on the other hand, is a federal force that consists of soldiers who can be called upon to support the active-duty army in times of war or national emergency.
- How long do National Guard and Army Reserve soldiers serve? National Guard soldiers typically serve 6-8 years, while Army Reserve soldiers serve 6-8 years as well.
- What are the benefits of joining the National Guard or Army Reserve? Both National Guard and Army Reserve soldiers are eligible for a range of benefits, including education assistance, medical insurance, and retirement plans.
- Can National Guard soldiers be deployed overseas? Yes, National Guard soldiers can be deployed overseas to support federal missions.
- Can Army Reserve soldiers be called upon to respond to state emergencies? No, Army Reserve soldiers are not typically called upon to respond to state emergencies.
