Discover the hierarchical structure of the National Guard ranks in order, from lowest to highest. Learn about the 9 ranks, including Private, Specialist, Sergeant, and more. Understand the roles, responsibilities, and requirements for advancement in the National Guard, and explore the different levels of leadership and expertise.
The National Guard is a unique branch of the US military that operates under the dual authority of both the federal and state governments. With a rich history dating back to 1636, the National Guard has played a vital role in protecting the country and its communities. Understanding the National Guard ranks is essential to appreciate the organization's structure and the responsibilities of its members. In this article, we will delve into the 9 National Guard ranks in order, providing an in-depth look at each rank's insignia, responsibilities, and requirements.
Understanding the National Guard Ranks

The National Guard ranks are divided into two main categories: enlisted and officer. Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the force, while officers hold leadership positions. The ranks are further subdivided into different pay grades, which reflect the individual's level of experience, training, and responsibility.
Enlisted Ranks
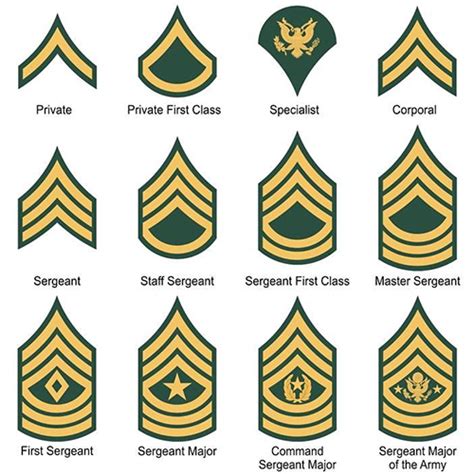
The enlisted ranks in the National Guard are the backbone of the organization. These individuals are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations. The enlisted ranks are further divided into three main categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior NCOs.
1. Private (PVT) - E-1
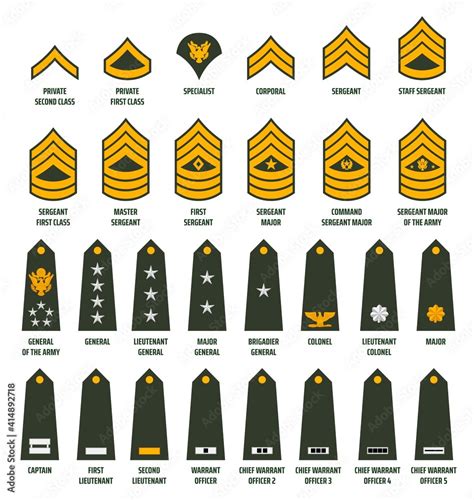

The Private (PVT) is the lowest rank in the National Guard. Privates are entry-level soldiers who have just joined the force. They are responsible for learning the basics of military life, including drill and ceremony, first aid, and combat skills.
2. Private First Class (PFC) - E-2

The Private First Class (PFC) rank is the second-lowest rank in the National Guard. PFCs have gained some experience and have demonstrated a basic level of competence. They are responsible for leading small teams and assisting NCOs with tasks.
3. Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) - E-4

The Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) rank is the first NCO rank in the National Guard. SPCs/CPLs have gained significant experience and have demonstrated leadership potential. They are responsible for leading teams, providing guidance, and mentoring junior soldiers.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks
The NCO ranks in the National Guard are responsible for leading and mentoring enlisted personnel. These individuals have gained significant experience and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills.
4. Sergeant (SGT) - E-5

The Sergeant (SGT) rank is the first senior NCO rank in the National Guard. SGTs have gained significant experience and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills. They are responsible for leading teams, providing guidance, and mentoring junior NCOs.
5. Staff Sergeant (SSG) - E-6

The Staff Sergeant (SSG) rank is the second senior NCO rank in the National Guard. SSGs have gained significant experience and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills. They are responsible for leading teams, providing guidance, and mentoring junior NCOs.
Officer Ranks
The officer ranks in the National Guard are responsible for leading and commanding units. These individuals have gained significant experience and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills.
6. Second Lieutenant (2LT) - O-1

The Second Lieutenant (2LT) rank is the lowest officer rank in the National Guard. 2LTs are responsible for leading platoons and assisting company-grade officers with tasks.
7. First Lieutenant (1LT) - O-2

The First Lieutenant (1LT) rank is the second-lowest officer rank in the National Guard. 1LTs are responsible for leading platoons and assisting company-grade officers with tasks.
8. Captain (CPT) - O-3
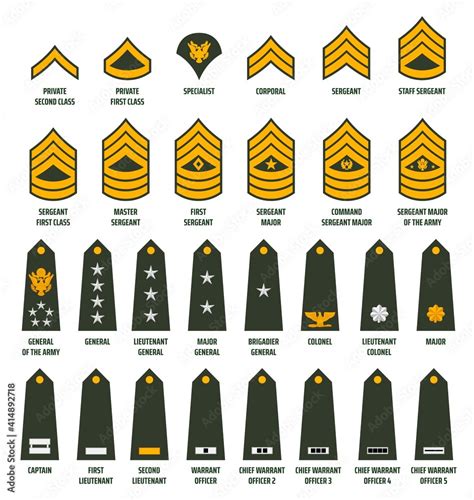

The Captain (CPT) rank is the company-grade officer rank in the National Guard. CPTs are responsible for leading companies and assisting field-grade officers with tasks.
9. Major (MAJ) - O-4
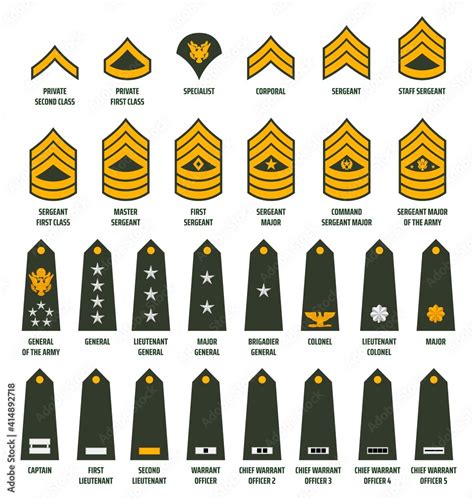

The Major (MAJ) rank is the field-grade officer rank in the National Guard. MAJs are responsible for leading battalions and assisting senior officers with tasks.
National Guard Ranks Gallery
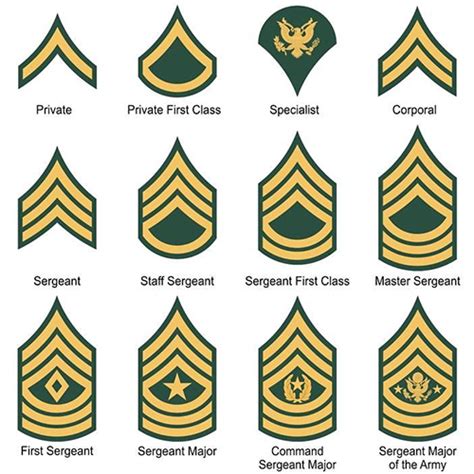




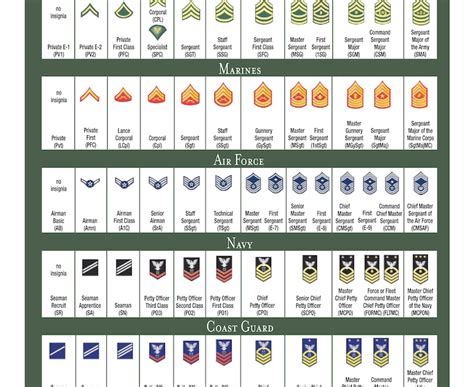



In conclusion, the National Guard ranks are an essential part of the organization's structure and hierarchy. Understanding the different ranks and their responsibilities is crucial for anyone looking to join the National Guard or advance in their career. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the National Guard ranks and the opportunities available to them.
We hope you found this article informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
