Intro
Serve your country with pride and purpose. Learn how to join the National Guard, including eligibility requirements, enlistment process, and benefits. Discover a career with leadership opportunities, education assistance, and camaraderie. Take the first step to a fulfilling military career and become a citizen-soldier, defending America and your community.
Joining the National Guard can be a life-changing decision, offering a unique blend of military service, education benefits, and civilian career opportunities. If you're considering signing up to serve your country, here's what you need to know.
The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces, comprising citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to support both state and federal missions. As a Guardsman, you'll have the opportunity to serve your community, develop valuable skills, and receive comprehensive benefits. Whether you're looking for a new challenge, want to give back to your country, or need help paying for college, the National Guard may be the perfect fit.
Benefits of Joining the National Guard

Joining the National Guard offers a wide range of benefits, including:
- Education Benefits: The National Guard offers various education assistance programs, including the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Army National Guard's State Tuition Reimbursement Program.
- Career Opportunities: The National Guard offers training in over 150 Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), from infantry and artillery to engineering and healthcare.
- Leadership Development: As a Guardsman, you'll have the opportunity to develop valuable leadership skills, including problem-solving, decision-making, and communication.
- Camaraderie: The National Guard is a tight-knit community, offering a sense of belonging and camaraderie that's hard to find in other careers.
How to Join the National Guard

Joining the National Guard is a straightforward process that involves several steps:
- Meet the Eligibility Requirements: To join the National Guard, you must be a US citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 35, and meet certain physical and moral standards.
- Choose Your Military Occupational Specialty (MOS): The National Guard offers over 150 different MOS, so you'll need to choose the one that best fits your skills and interests.
- Take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) Test: The ASVAB test measures your aptitude in various subjects, including math, reading, and technical skills.
- Complete Basic Combat Training (BCT): BCT is a 10-week training program that teaches you the basics of soldiering, including first aid, combat techniques, and military protocol.
- Attend Advanced Individual Training (AIT): AIT is specialized training that teaches you the skills you need for your specific MOS.
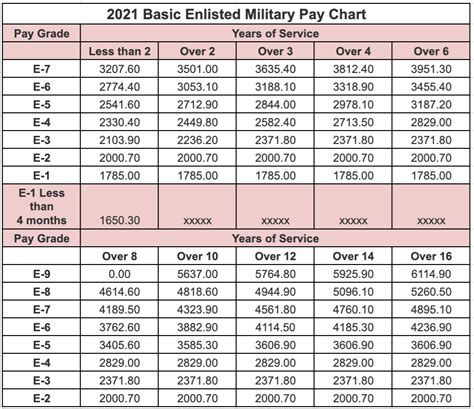
National Guard Pay and Allowances

As a Guardsman, you'll receive a competitive salary and benefits package, including:
- Basic Pay: Your basic pay will depend on your rank and time in service.
- Drill Pay: You'll receive drill pay for each drill period, which can be used to supplement your income.
- Allowances: You may be eligible for various allowances, including Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) and Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS).
National Guard Deployment and Training

As a Guardsman, you'll be required to deploy and train regularly, including:
- Annual Training (AT): You'll attend annual training for 2-3 weeks, where you'll receive specialized training and participate in exercises.
- Drill Periods: You'll attend drill periods one weekend a month, where you'll receive training and participate in unit activities.
- Deployment: You may be deployed in support of state or federal missions, which can include disaster relief, homeland security, and combat operations.
National Guard Ranks and Promotion

The National Guard uses a rank structure similar to the active duty Army, with the following ranks:
- Private (PVT): The lowest rank in the National Guard, private is the entry-level rank for new recruits.
- Private First Class (PFC): The second-lowest rank, private first class is a junior enlisted rank.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): The first non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank, specialist/corporal is a leadership position.
- Sergeant (SGT): A senior NCO rank, sergeant is a leadership position that requires experience and technical expertise.
National Guard FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the National Guard:
- Q: What is the National Guard? A: The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces, comprising citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to support both state and federal missions.
- Q: How do I join the National Guard? A: To join the National Guard, you must meet the eligibility requirements, choose your MOS, take the ASVAB test, complete BCT and AIT, and attend drill periods.
- Q: What are the benefits of joining the National Guard? A: The National Guard offers various benefits, including education assistance, career opportunities, leadership development, and camaraderie.
Gallery of National Guard Images
National Guard Image Gallery








We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the National Guard and what it takes to join. If you're considering signing up to serve your country, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with friends and family who may be interested. Thank you for your interest in the National Guard!
