Discover Nematoda key features, including parasitic behaviors, roundworm characteristics, and phylum-specific traits, to understand these microscopic organisms and their role in ecosystems, ecology, and biology.
The phylum Nematoda, commonly known as roundworms, is a diverse group of organisms that can be found in a wide range of environments, from the freezing cold Antarctic to the hottest deserts. These organisms have been on the planet for over a billion years and have evolved to occupy almost every conceivable ecological niche. Despite their ubiquity, nematodes remain poorly understood by the general public, and their importance in ecosystems is often overlooked. However, nematodes play a vital role in many ecosystems, and their unique characteristics make them fascinating creatures. In this article, we will delve into the key features of nematodes, exploring their morphology, physiology, and behavior, as well as their importance in ecosystems and their potential applications in various fields.
Nematodes are incredibly diverse, with over 20,000 known species, ranging in size from a few millimeters to several meters in length. They can be found in almost every environment, from the deep sea to the highest mountains, and from the freezing tundra to the hottest deserts. This diversity is reflected in their morphology, with different species having adapted to their specific environments in unique ways. For example, some nematodes have evolved to live in extreme environments, such as the high-temperature vents on the ocean floor, while others have adapted to live in the low-oxygen environments of the deep sea.
Nematode Morphology
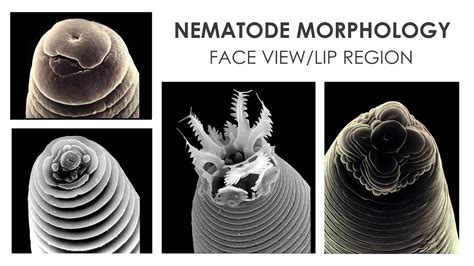
Nematode Physiology
Nematodes have a number of unique physiological features that allow them to thrive in a wide range of environments. One of the most important of these features is their ability to regulate their body temperature, allowing them to survive in environments with extreme temperatures. Nematodes also have a highly efficient nervous system, which allows them to respond quickly to changes in their environment. This is particularly important for nematodes that live in environments with high levels of predation, where the ability to respond quickly to threats can be a matter of life and death.Nematode Behavior

Nematode Importance in Ecosystems
Nematodes play a vital role in many ecosystems, serving as both predators and prey for other organisms. They are an important food source for many animals, from insects to fish, and are also important decomposers, helping to break down organic matter and recycle nutrients. Nematodes also have a number of indirect effects on ecosystems, such as influencing the structure of soil and the cycling of nutrients. For example, some nematodes help to break down organic matter, while others help to fix nitrogen in the soil.Nematode Applications

Nematode Research
Research on nematodes is ongoing, with scientists studying their morphology, physiology, and behavior in order to better understand these fascinating creatures. One area of research that is currently receiving a lot of attention is the study of nematode genetics, which is providing new insights into the evolution and development of these organisms. Scientists are also studying the interactions between nematodes and their environments, in order to better understand the complex relationships between these organisms and their ecosystems.Nematode Classification

Nematode Evolution
The evolution of nematodes is not well understood, but it is thought to have occurred over a billion years ago. The earliest known nematodes were likely simple, worm-like organisms that lived in the ocean. Over time, these organisms evolved to occupy a wide range of environments, from the deep sea to the highest mountains. Today, nematodes can be found in almost every environment on Earth, and are one of the most diverse groups of organisms on the planet.Nematode Conservation

Nematode Ecology
Nematodes play a vital role in many ecosystems, serving as both predators and prey for other organisms. They are an important food source for many animals, from insects to fish, and are also important decomposers, helping to break down organic matter and recycle nutrients. Nematodes also have a number of indirect effects on ecosystems, such as influencing the structure of soil and the cycling of nutrients.Nematode Image Gallery
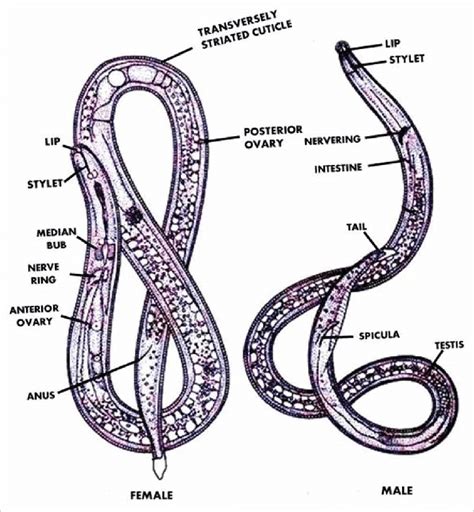
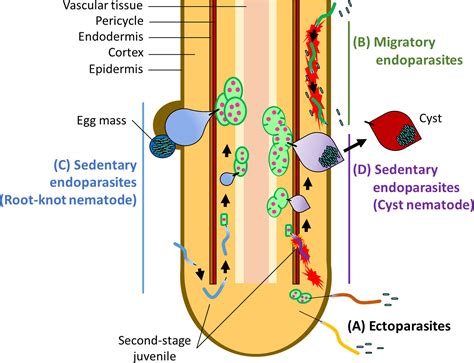



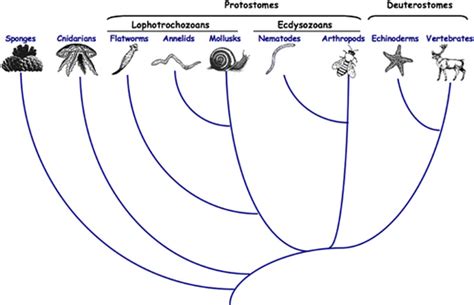

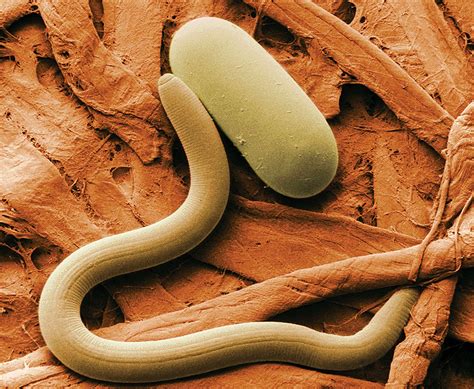
In conclusion, nematodes are fascinating creatures that play a vital role in many ecosystems. Their unique characteristics, such as their morphology, physiology, and behavior, make them an important part of the natural world. By studying nematodes, we can gain a better understanding of the complex relationships between organisms and their environments, and can develop new insights into the evolution and development of life on Earth. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of nematodes and their importance in ecosystems. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We would be happy to hear from you and to continue the conversation about these fascinating creatures.
