Intro
Ensure cybersecurity compliance with the NIST 800-171 POAM template. Learn the 5 crucial steps to achieve compliance, including risk assessment, vulnerability remediation, and ongoing monitoring. Streamline your Plan of Action and Milestones (POAM) process to meet NIST 800-171 requirements and protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
Implementing a Plan of Action and Milestones (POAM) template is a crucial step in achieving NIST 800-171 compliance. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-171 provides guidelines for protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) in non-federal systems and organizations. A POAM template helps organizations identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities, ensuring the secure handling of sensitive information. In this article, we will guide you through the five essential steps to achieve NIST 800-171 POAM template compliance.
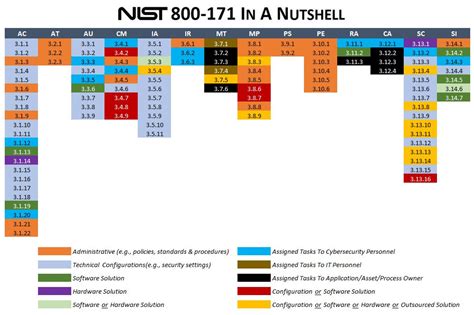
Understanding NIST 800-171 Requirements
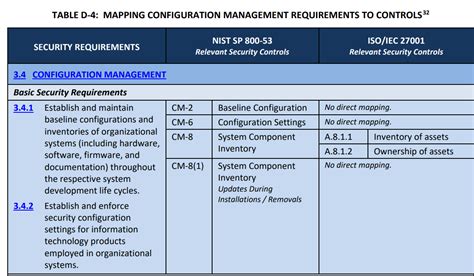
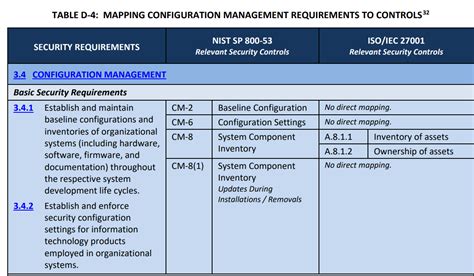
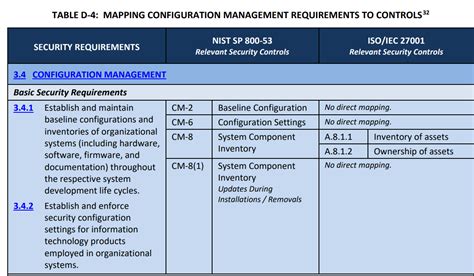
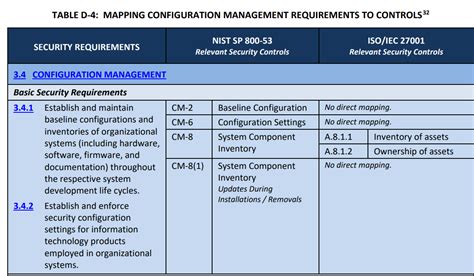
Before diving into the POAM template, it's essential to understand the NIST 800-171 requirements. The publication outlines 110 security controls, divided into 14 families, to safeguard CUI. These controls cover various aspects, including access control, awareness and training, audit and accountability, configuration management, and incident response.
Step 1: Conduct a Risk Assessment
The first step in creating a POAM template is to conduct a risk assessment to identify potential security vulnerabilities. This involves evaluating your organization's systems, networks, and data to determine the likelihood and impact of a security breach. The risk assessment should consider the following factors:
- Identification of sensitive data and systems
- Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing
- Analysis of threat intelligence and incident response
- Evaluation of existing security controls and countermeasures
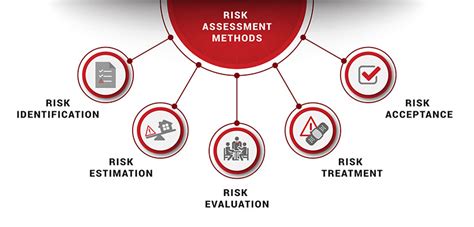
Risk Assessment Methodologies
There are several risk assessment methodologies, including:
- NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
- ISO 27005
- OCTAVE (Operationally Critical Threat, Asset, and Vulnerability Evaluation)
Choose a methodology that aligns with your organization's needs and security posture.
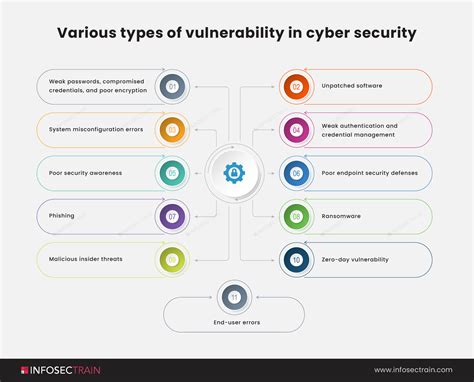
Step 2: Identify and Prioritize Vulnerabilities
Based on the risk assessment, identify and prioritize vulnerabilities that need to be addressed. This involves categorizing vulnerabilities into high, medium, and low-risk categories, considering factors such as:
- Severity of the vulnerability
- Potential impact on the organization
- Likelihood of exploitation
- Existing security controls and countermeasures
Vulnerability Categorization
Use the following categories to prioritize vulnerabilities:
- High-risk: Critical vulnerabilities that require immediate attention
- Medium-risk: Vulnerabilities that need to be addressed within a reasonable timeframe
- Low-risk: Vulnerabilities that can be addressed at a lower priority
Step 3: Develop a POAM Template
Create a POAM template to document and track the remediation efforts. The template should include the following elements:
- Vulnerability description
- Risk level (high, medium, low)
- Remediation actions
- Responsible personnel
- Target completion date
- Status updates
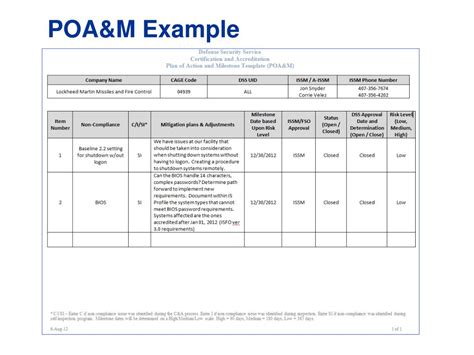
POAM Template Example
| Vulnerability | Risk Level | Remediation Actions | Responsible Personnel | Target Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak password policy | High | Implement multi-factor authentication | IT Department | 2023-02-28 | In progress |
Step 4: Implement Remediation Actions
Implement the remediation actions outlined in the POAM template. This involves:
- Assigning tasks to responsible personnel
- Tracking progress and status updates
- Providing necessary resources and support
- Conducting regular reviews and assessments
Remediation Action Examples
- Implementing a multi-factor authentication solution
- Conducting security awareness training for employees
- Deploying a vulnerability scanning tool

Step 5: Monitor and Review Progress
Regularly monitor and review progress to ensure remediation actions are being implemented effectively. This involves:
- Tracking status updates and completion dates
- Conducting regular reviews and assessments
- Identifying and addressing new vulnerabilities
- Updating the POAM template as necessary
Progress Monitoring and Review
- Schedule regular review meetings to discuss progress and address concerns
- Use metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress
- Identify and address new vulnerabilities that may arise during the remediation process

By following these five steps, organizations can create a POAM template that helps them achieve NIST 800-171 compliance. Remember to regularly review and update the POAM template to ensure ongoing compliance and security posture.
NIST 800-171 POAM Template Compliance Gallery

We hope this article has provided valuable insights into achieving NIST 800-171 POAM template compliance. If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences, please leave a comment below.
