Intro
Create a comprehensive non-profit budget template in 7 essential steps. Learn how to allocate resources, manage finances, and achieve fiscal transparency. Discover the importance of budgeting for grants, donations, and fundraising events, and ensure long-term sustainability for your organization with a well-structured budget plan.
Creating a non-profit budget template is a crucial step in managing the financial resources of a non-profit organization. A well-crafted budget template helps non-profits track income and expenses, make informed decisions, and ensure sustainability. In this article, we will guide you through the 7 essential steps to create a non-profit budget template.
Understanding the Importance of a Non-Profit Budget Template
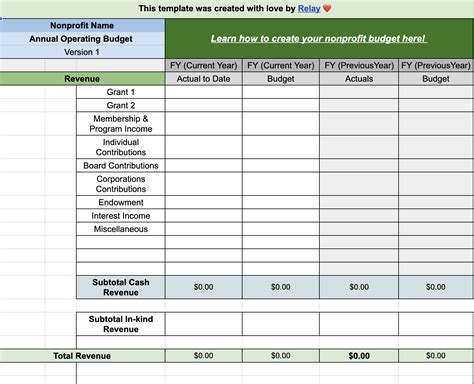
A non-profit budget template serves as a roadmap for financial management. It helps non-profits allocate resources effectively, prioritize spending, and achieve their mission. Without a budget template, non-profits may struggle to manage their finances, leading to financial instability and decreased effectiveness.
Benefits of a Non-Profit Budget Template
A non-profit budget template offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved financial management and planning
- Enhanced transparency and accountability
- Better decision-making and resource allocation
- Increased donor trust and confidence
- Reduced financial risk and uncertainty
Step 1: Identify Income Sources

The first step in creating a non-profit budget template is to identify all income sources. This includes:
- Donations and grants
- Fundraising events and campaigns
- Membership fees and dues
- Sales of goods and services
- Interest income and investments
Types of Income Sources
Non-profits may have various types of income sources, including:
- Unrestricted income: available for general use
- Restricted income: designated for specific purposes or programs
- Temporary income: one-time or short-term funding
Step 2: Categorize Expenses

The second step is to categorize expenses into different categories. This includes:
- Program expenses: direct costs related to programs and services
- Administrative expenses: indirect costs related to management and operations
- Fundraising expenses: costs associated with fundraising events and campaigns
- Capital expenses: costs related to assets and infrastructure
Expense Categories
Non-profits may have various expense categories, including:
- Salaries and benefits
- Rent and utilities
- Travel and training
- Marketing and advertising
- Equipment and supplies
Step 3: Determine Budget Period
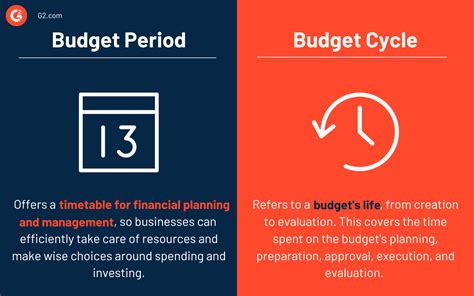
The third step is to determine the budget period, which is the timeframe for the budget. This can be:
- Annual budget: covers a 12-month period
- Quarterly budget: covers a 3-month period
- Monthly budget: covers a 1-month period
Budget Period Considerations
When determining the budget period, consider:
- Funding cycles and grant periods
- Program and project timelines
- Financial reporting requirements
Step 4: Establish Budget Assumptions

The fourth step is to establish budget assumptions, which are the underlying assumptions that guide the budgeting process. This includes:
- Economic assumptions: inflation rates, interest rates, and market trends
- Program assumptions: program growth, participation rates, and service delivery
- Funding assumptions: funding levels, grant awards, and donor support
Budget Assumption Considerations
When establishing budget assumptions, consider:
- Historical data and trends
- Industry benchmarks and best practices
- Stakeholder input and feedback
Step 5: Create Budget Line Items
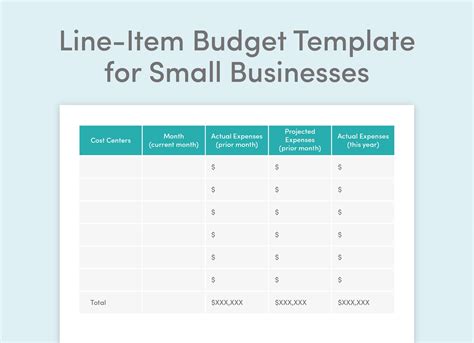
The fifth step is to create budget line items, which are the specific budget categories and accounts. This includes:
- Income line items: donations, grants, and fundraising revenue
- Expense line items: salaries, rent, and program expenses
Budget Line Item Considerations
When creating budget line items, consider:
- Account structure and coding
- Budget categorization and classification
- Financial reporting requirements
Step 6: Assign Budget Amounts

The sixth step is to assign budget amounts to each line item. This involves:
- Allocating income and expenses to specific budget categories
- Establishing budget targets and goals
- Identifying budget variances and adjustments
Budget Amount Considerations
When assigning budget amounts, consider:
- Historical data and trends
- Program and project requirements
- Funding levels and grant awards
Step 7: Review and Revise Budget Template
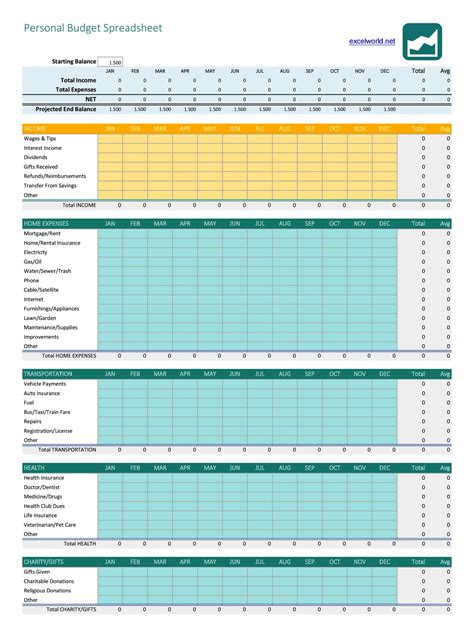
The seventh and final step is to review and revise the budget template. This involves:
- Reviewing budget assumptions and line items
- Revising budget amounts and targets
- Ensuring budget accuracy and completeness
Budget Template Review Considerations
When reviewing and revising the budget template, consider:
- Stakeholder input and feedback
- Financial reporting requirements
- Budgeting best practices and industry standards
Non-Profit Budget Template Gallery



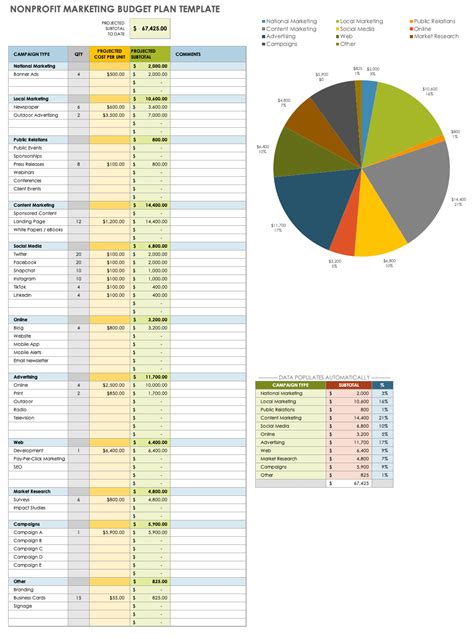
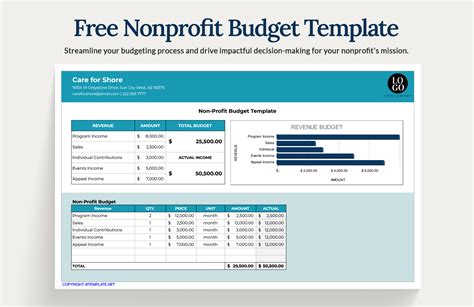



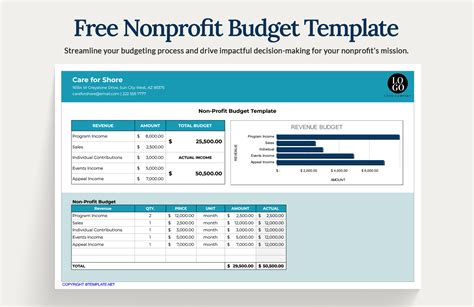
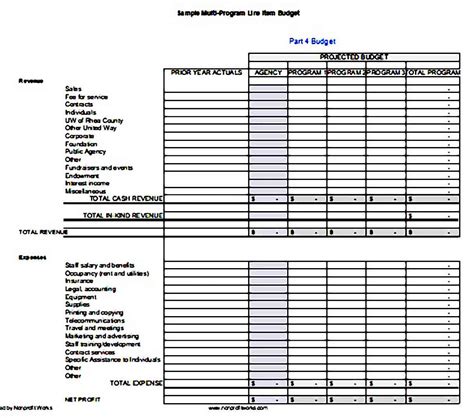
By following these 7 essential steps, non-profits can create a comprehensive and effective budget template that helps them manage their finances, achieve their mission, and make a positive impact in their communities.
