Intro
Discover the crucial 5 key roles of a nuclear power plant operator, ensuring safe and efficient energy production. From monitoring reactor performance to maintaining equipment, learn about the critical responsibilities and LSI-related tasks, including radiation safety, plant security, and regulatory compliance, that nuclear operators undertake to prevent accidents.
Nuclear power plants play a crucial role in meeting the world's increasing energy demands while minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. These plants rely on highly trained and skilled professionals to ensure safe and efficient operation. Among the most critical positions in a nuclear power plant is the operator, responsible for overseeing the entire facility and making real-time decisions to maintain safety and performance. Here, we will delve into the 5 key roles of a nuclear power plant operator, highlighting their importance and the skills required to excel in this demanding profession.
1. Monitoring and Controlling the Plant
Nuclear power plant operators are responsible for monitoring the facility's systems and equipment, ensuring they operate within predetermined parameters. This involves tracking temperature, pressure, radiation levels, and other critical indicators to identify potential issues before they become major problems. Operators must respond quickly and effectively to changes in plant conditions, making adjustments as needed to maintain safety and optimize performance.
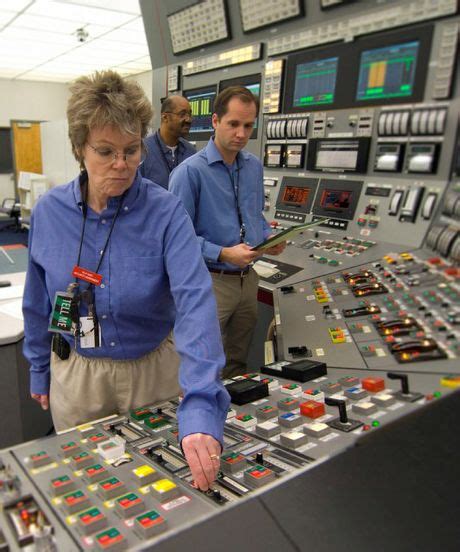
Main Control Room Operations
Operators spend most of their time in the main control room, where they monitor the plant's systems and make decisions in real-time. This involves:
- Observing and interpreting data from various sensors and instruments
- Identifying and responding to alarms and alerts
- Adjusting control settings to maintain optimal plant performance
- Coordinating with other teams, such as maintenance and engineering, to resolve issues
2. Performing Routine Maintenance and Testing

Nuclear power plant operators play a critical role in maintaining the facility's equipment and systems. This involves performing routine tests and inspections to ensure everything is functioning properly. Operators must also identify and report any issues or concerns to the maintenance team, ensuring prompt resolution and minimizing downtime.
Types of Maintenance and Testing
Operators perform various types of maintenance and testing, including:
- Scheduled maintenance: Regularly scheduled activities, such as filter changes and valve replacements
- Predictive maintenance: Using data and analytics to predict potential issues and perform maintenance before they occur
- Corrective maintenance: Responding to and resolving issues that have already occurred
3. Ensuring Radiation Safety

Radiation safety is a top priority in nuclear power plants, and operators play a critical role in ensuring the facility is safe for workers and the surrounding community. This involves monitoring radiation levels, enforcing safety protocols, and responding to radiation-related incidents.
Radiation Safety Measures
Operators implement various radiation safety measures, including:
- Monitoring radiation levels: Using instruments to track radiation levels in the plant and surrounding areas
- Enforcing safety protocols: Ensuring workers follow established safety procedures when working with radioactive materials
- Responding to incidents: Quickly and effectively responding to radiation-related incidents to minimize exposure and prevent accidents
4. Managing Emergencies and Incidents
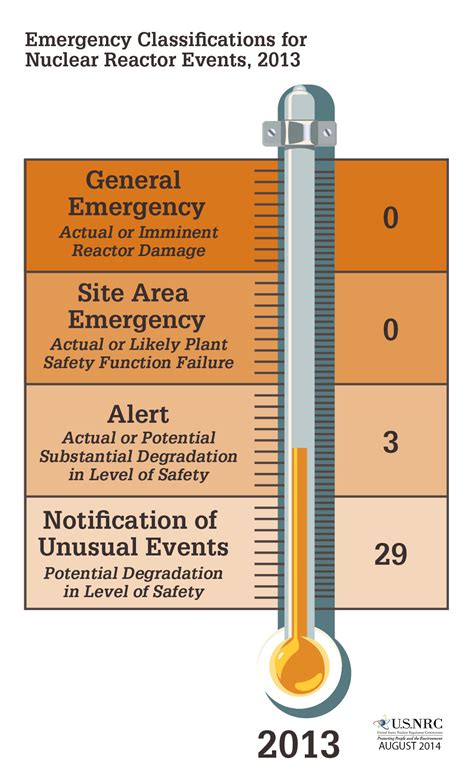
Nuclear power plant operators must be prepared to respond to emergencies and incidents, such as natural disasters, equipment failures, or radiation releases. This involves activating emergency response plans, coordinating with other teams, and making quick decisions to minimize risks and prevent accidents.
Emergency Response Procedures
Operators follow established emergency response procedures, including:
- Activating emergency response plans: Quickly initiating response plans in the event of an emergency
- Coordinating with other teams: Working with other teams, such as maintenance and engineering, to respond to incidents
- Making quick decisions: Making timely and informed decisions to minimize risks and prevent accidents
5. Complying with Regulations and Standards

Nuclear power plant operators must comply with strict regulations and standards, ensuring the facility operates safely and efficiently. This involves staying up-to-date with changing regulations, implementing new procedures, and maintaining accurate records.
Regulatory Compliance
Operators ensure regulatory compliance by:
- Staying informed: Keeping up-to-date with changing regulations and standards
- Implementing new procedures: Putting new procedures in place to ensure compliance with changing regulations
- Maintaining accurate records: Keeping accurate records of plant operations, maintenance, and incidents
Nuclear Power Plant Operations Gallery








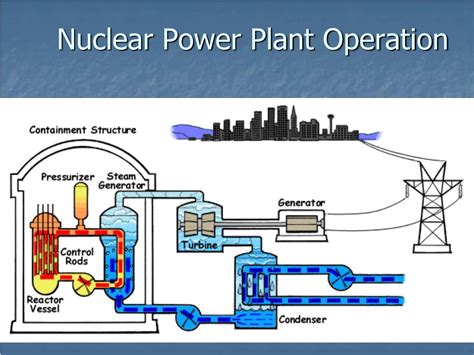

We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the critical roles and responsibilities of nuclear power plant operators. These dedicated professionals play a vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of nuclear power plants, which are essential for meeting our increasing energy demands while minimizing environmental impact.
