Delve into the inner workings of the Office of Military Commissions, a critical component of the US military justice system. Learn about its role in prosecuting Guantanamo Bay detainees, the military commission process, and the controversy surrounding it. Understand the intersection of national security, terrorism, and due process in this in-depth exploration.
The Office of Military Commissions (OMC) is a critical component of the United States' military justice system, responsible for prosecuting individuals suspected of war crimes and other offenses related to terrorism. Established in 2001, the OMC plays a vital role in upholding the rule of law and ensuring that those who commit atrocities are held accountable for their actions.
In the aftermath of the 9/11 attacks, the United States government recognized the need for a specialized tribunal to prosecute individuals captured in the war on terror. The OMC was created to fill this gap, drawing on the expertise of military lawyers, judges, and other professionals to try cases involving complex national security issues.
Overview of the Office of Military Commissions

The OMC is headquartered at the Pentagon, with a secondary office located at the Naval Station Guantanamo Bay, Cuba. The office is led by a Chief Prosecutor, who is responsible for overseeing the prosecution of cases before the Military Commissions. The Chief Prosecutor is supported by a team of experienced prosecutors, investigators, and other staff members.
Jurisdiction and Authority
The OMC has jurisdiction over individuals who are not U.S. citizens and are suspected of committing war crimes, including terrorism-related offenses. The office also has authority to prosecute individuals who are deemed to be "unlawful enemy combatants," a designation that applies to those who engage in hostilities against the United States or its allies.
Structure of Military Commissions
A Military Commission is a tribunal consisting of a military judge and a panel of military officers. The Commission is responsible for hearing evidence, evaluating the credibility of witnesses, and determining the guilt or innocence of the accused. Military Commissions are governed by the Manual for Military Commissions (MMC), which provides detailed guidance on procedures, evidence, and sentencing.
Benefits of Military Commissions
Military Commissions offer several benefits, including:
- Speed and Efficiency: Military Commissions can try cases more quickly than traditional federal courts, which is critical in national security cases where timely justice is essential.
- Specialized Expertise: Military Commissions bring together experienced military lawyers, judges, and other professionals who have expertise in national security law and the complexities of war crimes prosecutions.
- Flexibility: Military Commissions can try cases in a variety of locations, including Guantanamo Bay, which is critical for cases involving detainees held at the facility.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its benefits, the OMC has faced several challenges and controversies over the years. Some of these challenges include:
- Detainee Treatment: There have been concerns raised about the treatment of detainees at Guantanamo Bay, including allegations of torture and abuse.
- Transparency: The OMC has faced criticism for a lack of transparency in its proceedings, including restrictions on access to hearings and documents.
- Legitimacy: Some have questioned the legitimacy of Military Commissions, arguing that they lack the due process protections and other safeguards that are present in traditional federal courts.
Key Players in the Office of Military Commissions
- Chief Prosecutor: The Chief Prosecutor is the head of the OMC and is responsible for overseeing the prosecution of cases.
- Military Judge: The Military Judge is responsible for presiding over the Military Commission and ensuring that the proceedings are fair and impartial.
- Defense Counsel: Defense Counsel represent the accused and are responsible for defending their clients against the charges brought by the prosecution.
Notable Cases
Some notable cases tried by the OMC include:
- United States v. Khalid Sheikh Mohammed: Khalid Sheikh Mohammed, one of the alleged masterminds of the 9/11 attacks, was tried by a Military Commission in 2012.
- United States v. Abd al-Rahim al-Nashiri: Abd al-Rahim al-Nashiri, a Saudi Arabian national, was tried by a Military Commission in 2014 for his alleged role in the USS Cole bombing.
Gallery of Military Commissions
Military Commissions Image Gallery
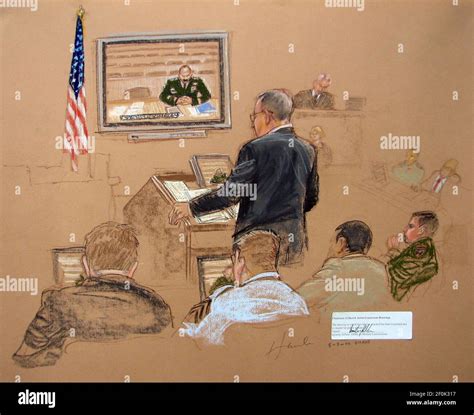









Conclusion
In conclusion, the Office of Military Commissions plays a critical role in upholding the rule of law and ensuring that those who commit war crimes and other offenses related to terrorism are held accountable. While the OMC has faced challenges and controversies, it remains an important tool for the United States government in its efforts to combat terrorism and protect national security.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and opinions on the Office of Military Commissions and its role in the war on terror. What are your concerns about the use of Military Commissions? Do you believe that they are an effective tool for trying individuals suspected of war crimes? Let us know in the comments below.
