Intro
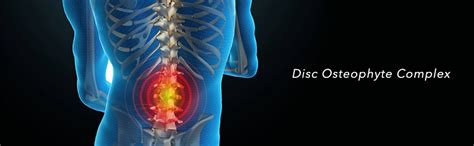
Discover the Osteophyte Disk Complex, a condition where bone spurs and disc issues intersect, causing spinal problems, joint pain, and limited mobility, requiring orthopedic treatment and management.
The human spine is a complex and intricate system, made up of numerous components that work together to provide support, flexibility, and movement. One of the key components of the spine is the intervertebral disk, which acts as a cushion between the vertebrae, absorbing shock and allowing for smooth movement. However, over time, the intervertebral disk can become damaged or degenerate, leading to the formation of osteophytes, also known as bone spurs. In this article, we will delve into the world of osteophyte disk complex, exploring what it is, how it forms, and the implications it has on our overall health.
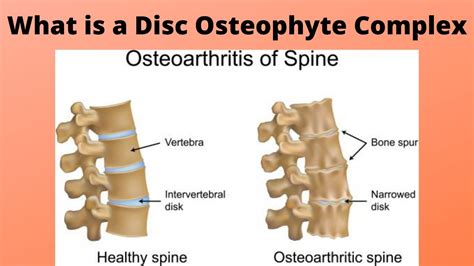
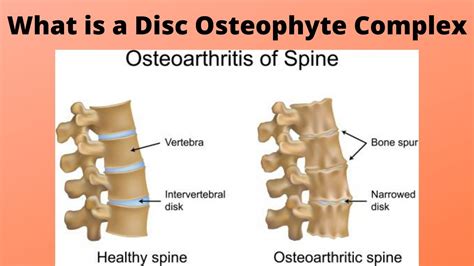
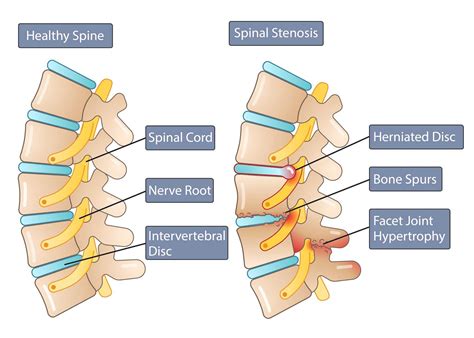
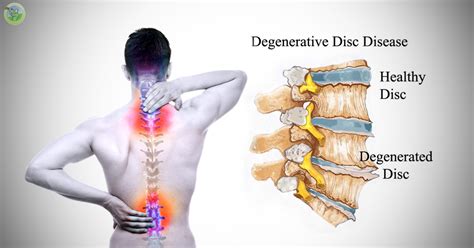
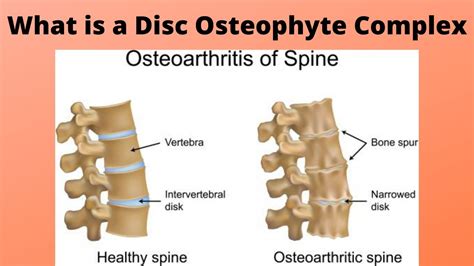
The intervertebral disk is a remarkable structure, consisting of a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus, and a soft, gel-like center called the nucleus pulposus. The disk works by absorbing shock and distributing pressure evenly throughout the spine, allowing us to move freely and comfortably. However, as we age, the disk can begin to degenerate, leading to a range of problems, including herniation, bulging, and osteophyte formation. Osteophytes are bony growths that form on the edges of the vertebrae, and can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
The formation of osteophytes is a complex process, involving a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. As the intervertebral disk degenerates, the body attempts to repair itself by growing new bone tissue. This can lead to the formation of osteophytes, which can put pressure on surrounding nerves and tissues, causing pain and discomfort. In some cases, osteophytes can also lead to the narrowing of the spinal canal, a condition known as spinal stenosis, which can cause numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs.
What is Osteophyte Disk Complex?

Causes of Osteophyte Disk Complex
The causes of osteophyte disk complex are multifaceted and can include a range of factors, such as: * Aging: As we age, the intervertebral disk can degenerate, leading to the formation of osteophytes. * Genetics: Some people may be more prone to osteophyte formation due to their genetic makeup. * Lifestyle: A sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and excessive weight can all contribute to osteophyte formation. * Injury: Trauma to the spine, such as a herniated disk or spinal fracture, can lead to osteophyte formation. * Poor posture: Poor posture can put strain on the spine, leading to osteophyte formation.Diagnosis of Osteophyte Disk Complex
Treatment Options for Osteophyte Disk Complex
Treatment for osteophyte disk complex depends on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. Conservative treatment options may include: * Physical therapy: To improve mobility and strength. * Pain management: To manage pain and discomfort. * Lifestyle modifications: To reduce strain on the spine and promote healing. * Medications: To manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the osteophytes and repair any damaged tissue.Prevention of Osteophyte Disk Complex
Complications of Osteophyte Disk Complex
If left untreated, osteophyte disk complex can lead to a range of complications, including: * Chronic pain: Osteophytes can cause ongoing pain and discomfort. * Limited mobility: Osteophytes can limit mobility and flexibility. * Nerve damage: Osteophytes can put pressure on surrounding nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and weakness. * Spinal stenosis: Osteophytes can lead to the narrowing of the spinal canal, causing numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs.Gallery of Osteophyte Disk Complex
Osteophyte Disk Complex Image Gallery
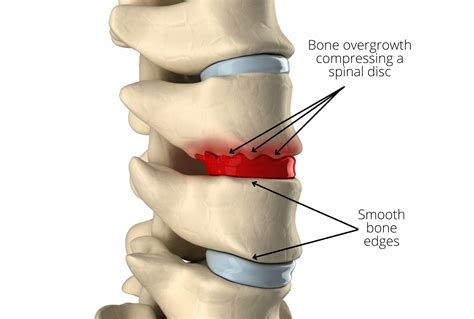
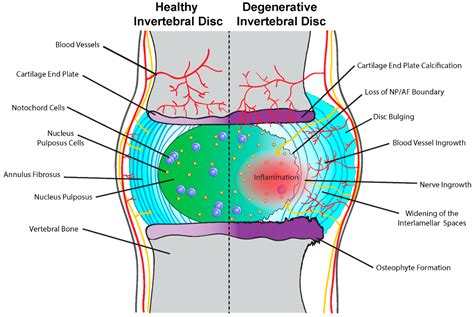



In conclusion, osteophyte disk complex is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent long-term damage to the spine. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with osteophyte disk complex in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of this complex condition and develop effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
