Intro
Uncover the legendary P-38 Lightning, a WWII fighter plane that revolutionized aerial combat. Discover its innovative design, exceptional speed, and impressive firepower. Learn about its significant role in World War II, its variants, and the aces who flew it. Explore the Lightnings impact on aviation history and its enduring legacy.
The P-38 Lightning is one of the most recognizable and iconic fighter planes of World War II. Its distinctive twin-boom design and powerful engines made it a formidable opponent in the skies, and its contributions to the Allied war effort cannot be overstated. In this article, we'll delve into the history of the P-38 Lightning, its design and development, and its impact on the outcome of World War II.
The Birth of a Legend

The P-38 Lightning was the brainchild of Lockheed's chief engineer, Hall Hibbard, and his team of designers. In 1937, the US Army Air Corps (USAAC) issued a request for proposals for a new fighter plane that could reach speeds of over 360 mph and climb to 20,000 feet in just six minutes. Lockheed's response was the XP-38, a revolutionary design that featured two boom-mounted engines and a central cockpit.
Design and Development
The XP-38 first took to the skies in January 1939, and the results were impressive. The plane's twin engines, Allison V-1710s, produced a combined 2,200 horsepower, making the P-38 one of the fastest fighter planes of its time. The plane's distinctive design also provided excellent visibility for the pilot, with a bubble canopy offering an unobstructed view of the surroundings.
However, the early P-38s were not without their problems. The plane's complex design and systems made it prone to mechanical failures, and the US Army Air Forces (USAAF) initially struggled to find a suitable role for the plane. It wasn't until the USAAF began to focus on long-range escort duties that the P-38 truly came into its own.
Combat Debut and Early Successes

The P-38 made its combat debut in the North African theater in 1942, where it quickly proved itself to be a valuable asset. The plane's long range and endurance made it ideal for escort duties, and its firepower and maneuverability made it a formidable opponent in dogfighting.
One of the P-38's earliest successes came in June 1942, when a squadron of P-38s intercepted a group of German Ju 88 bombers over the Mediterranean. The P-38s shot down several of the bombers, marking the plane's first major victory.
Breakthroughs and Innovations
Throughout the war, the P-38 continued to evolve and improve. The USAAF introduced new variants, such as the P-38J and P-38L, which featured improved engines and radar systems. The plane also played a key role in the development of drop tanks, which extended its range and endurance even further.
In 1943, the USAAF began to use the P-38 as a night fighter, equipping the plane with radar systems and moonlight-reflecting paint to make it almost invisible in the dark skies. This innovation proved to be a game-changer, allowing the P-38 to intercept and destroy enemy bombers under the cover of darkness.
Impact on the War Effort

The P-38 Lightning played a significant role in the Allied victory in World War II. Its range, endurance, and firepower made it a valuable asset in escort duties, and its innovative design and systems paved the way for future generations of fighter planes.
According to USAAF records, the P-38 accounted for over 1,800 enemy aircraft destroyed during the war, making it one of the top-scoring fighter planes of the conflict. The plane also played a key role in several major campaigns, including the North African and Italian campaigns, and the Battle of the Bulge.
Legacy and Retirement
After the war, the P-38 was gradually phased out of service, replaced by newer, more advanced fighter planes. However, the plane's legacy lived on, inspiring a new generation of aircraft designers and engineers.
Today, the P-38 Lightning is remembered as one of the most iconic and influential fighter planes of World War II. Its innovative design and systems paved the way for future generations of fighter planes, and its contributions to the Allied war effort will never be forgotten.
Specifications and Variants
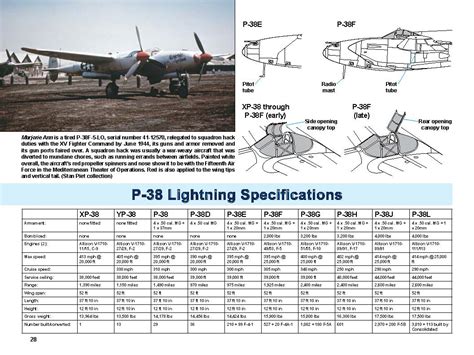
- Length: 37 ft 10 in (11.53 m)
- Wingspan: 52 ft 0 in (15.85 m)
- Height: 9 ft 10 in (3.00 m)
- Empty weight: 12,400 lb (5,623 kg)
- Gross weight: 21,600 lb (9,807 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Allison V-1710-111/113 V-12 piston engines
- Maximum speed: 443 mph (713 km/h)
- Range: 1,300 mi (2,100 km)
- Service ceiling: 44,000 ft (13,410 m)
Variants:
- P-38D: First production variant
- P-38E: Improved variant with self-sealing fuel tanks
- P-38F: Variant with uprated engines and improved performance
- P-38G: Variant with further improved performance and range
- P-38H: Variant with improved radar systems and night fighting capabilities
- P-38J: Variant with improved performance and range
- P-38L: Final production variant with uprated engines and improved performance
P-38 Lightning Image Gallery
P-38 Lightning Image Gallery










We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the P-38 Lightning, one of the most iconic and influential fighter planes of World War II. Its innovative design, impressive performance, and significant contributions to the Allied war effort make it a truly legendary aircraft.
