Intro
Discover how Canadas parliamentary system functions, from the monarch to the prime minister. Learn about the role of the House of Commons, Senate, and provincial governments. Understand the complexities of Canadas democratic system, including parliamentary supremacy, responsible government, and the rule of law, and how they impact Canadian politics.
The Canadian parliamentary system is a cornerstone of the country's governance, shaping the way decisions are made and policies are implemented. As the second-largest country in the world, Canada's system of government is designed to balance power, ensure representation, and provide stability. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Canada's parliamentary system, exploring its key components, how it works, and its significance in Canadian politics.
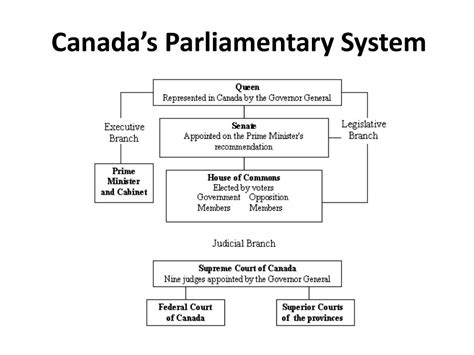
The Basics of the Canadian Parliamentary System
The Canadian parliamentary system is based on the British Westminster model, with some modifications to suit the country's unique needs. The system consists of three main branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial. The legislative branch, also known as Parliament, is composed of three elements: the Senate, the House of Commons, and the monarch (represented by the Governor General).
**The Legislative Branch: The Heart of Canadian Democracy**
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws, approving government spending, and holding the government accountable for its actions. The House of Commons, composed of 338 members of parliament (MPs) elected by Canadians, is the most powerful component of the legislative branch. MPs are elected for a maximum term of four years, although the Prime Minister can request an election at any time.

The Senate: A Chamber of Review
The Senate, composed of 105 appointed senators, serves as a chamber of review, providing a second opinion on legislation passed by the House of Commons. Senators are appointed by the Governor General, on the advice of the Prime Minister, and typically serve until the age of 75. While the Senate has the power to delay or amend legislation, it cannot initiate or veto bills.
**The Executive Branch: The Government in Action**
The executive branch is headed by the Prime Minister, who is the leader of the party with the most seats in the House of Commons. The Prime Minister is responsible for advising the Governor General, setting the government's agenda, and overseeing the administration of government departments and agencies. The Prime Minister is also supported by a cabinet of ministers, each responsible for a specific portfolio, such as finance, defense, or education.

The Judicial Branch: Ensuring the Rule of Law
The judicial branch, composed of the Supreme Court of Canada and lower courts, is responsible for interpreting laws and ensuring that they are consistent with the Constitution. The Supreme Court, composed of nine justices, has the final say on matters of law and the Constitution.
**How the Parliamentary System Works**
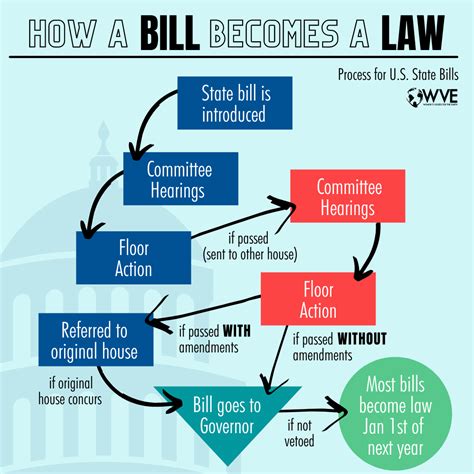
The parliamentary system is designed to facilitate the passage of legislation and ensure accountability. Here is a step-by-step overview of how the system works:
- Introduction of a Bill: A member of parliament introduces a bill in the House of Commons.
- Debate and Voting: The bill is debated, and MPs vote on whether to proceed with the bill.
- Committee Review: The bill is referred to a committee, which reviews and amends the bill.
- Second Reading: The bill is debated again in the House of Commons, and MPs vote on whether to proceed with the bill.
- Third Reading: The bill is debated for a final time, and MPs vote on whether to pass the bill.
- Senate Review: The bill is sent to the Senate, where it is reviewed and amended.
- Royal Assent: The bill is sent to the Governor General, who signs the bill into law.
The Benefits of the Parliamentary System
The parliamentary system offers several benefits, including:
- Stability: The system provides stability, as the government can maintain power for a maximum term of four years.
- Accountability: The system ensures accountability, as the government is responsible to the House of Commons.
- Representation: The system provides representation, as MPs are elected to represent the interests of their constituents.
**Challenges Facing the Parliamentary System**
Despite its benefits, the parliamentary system faces several challenges, including:
- Partisan Politics: The system can be dominated by partisan politics, leading to gridlock and polarization.
- Unelected Senate: The appointed Senate can be seen as undemocratic, leading to calls for reform.
- Disconnection from Citizens: The system can be seen as disconnected from citizens, leading to disillusionment and disengagement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Canadian parliamentary system is a complex and multifaceted system that has evolved over time. While it provides stability, accountability, and representation, it also faces challenges, such as partisan politics, an unelected Senate, and disconnection from citizens. As Canada continues to grow and evolve, it is essential that the parliamentary system adapts to meet the changing needs of its citizens.
Gallery of Canadian Parliament
Canadian Parliament Image Gallery









FAQ
Q: What is the Canadian parliamentary system? A: The Canadian parliamentary system is a system of government based on the British Westminster model, with a legislative, executive, and judicial branch.
Q: Who is the head of the Canadian government? A: The Prime Minister is the head of the Canadian government.
Q: How are members of parliament elected? A: Members of parliament are elected by Canadians through a general election.
Q: What is the role of the Senate? A: The Senate serves as a chamber of review, providing a second opinion on legislation passed by the House of Commons.
Q: Can the Senate veto legislation? A: No, the Senate cannot veto legislation, but it can delay or amend bills.
Q: What is the role of the Governor General? A: The Governor General represents the monarch and signs bills into law.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the Canadian parliamentary system. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more, please let us know in the comments below. Share this article with others to help them understand the complexities of the Canadian parliamentary system.
