Intro
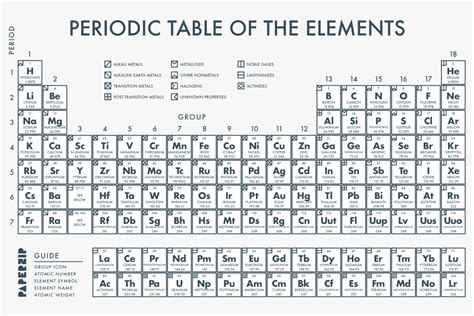
Unlock the secrets of the elements with our Periodic Table Black and White Printable Version. A comprehensive guide to the periodic table, featuring a downloadable printable chart, element symbols, atomic numbers, and groups. Perfect for students, teachers, and chemistry enthusiasts, this black and white periodic table is easy to read and print.
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, helping us organize and understand the properties of elements. While colorful periodic tables can be visually appealing, a black and white printable version can be just as useful and beneficial. In this article, we'll explore the importance of having a printable periodic table, its benefits, and provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to use it.
Why Do You Need a Printable Periodic Table?
Having a printable periodic table can be incredibly useful for students, teachers, and professionals in the field of chemistry. Here are a few reasons why:
- Convenience: A printable periodic table allows you to have a physical copy of the table that you can refer to whenever you need it. You can hang it on your wall, keep it in your binder, or even laminate it for future use.
- Cost-effective: Printing your own periodic table can be more cost-effective than purchasing a pre-made one. You can print it on regular paper or cardstock, depending on your preference.
- Customization: With a printable periodic table, you can customize it to suit your needs. You can add notes, highlight important elements, or even create a personalized key.
Benefits of Using a Black and White Periodic Table
While colorful periodic tables can be visually appealing, a black and white version has its own set of benefits:
- Easy to read: A black and white periodic table can be easier to read, especially for those with visual impairments. The lack of color can reduce distractions and make it simpler to focus on the information.
- Simplistic design: A black and white periodic table often features a more simplistic design, which can make it easier to navigate and understand.
- Better for note-taking: A black and white periodic table provides a clean and minimalist background, making it ideal for note-taking and adding annotations.
How to Use a Periodic Table
Using a periodic table can seem overwhelming at first, but once you understand the basics, it becomes an invaluable tool. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use a periodic table:
- Start with the elements: The periodic table is organized by elements, which are listed in order of their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus).
- Understand the rows and columns: The periodic table is arranged in rows (periods) and columns (groups). Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties.
- Identify the blocks: The periodic table is divided into blocks, which are determined by the electron configuration of the elements.
- Look for trends: The periodic table shows trends in element properties, such as atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy.
Periodic Table Blocks
The periodic table is divided into four main blocks:
- s-block: Elements in the s-block have their outermost electrons in the s-orbital.
- p-block: Elements in the p-block have their outermost electrons in the p-orbital.
- d-block: Elements in the d-block have their outermost electrons in the d-orbital.
- f-block: Elements in the f-block have their outermost electrons in the f-orbital.

Periodic Table Symbols and Notations
The periodic table uses a variety of symbols and notations to convey information about the elements. Here are some common ones to look out for:
- Element symbols: Each element has a unique symbol, which is usually a one- or two-letter abbreviation of its name.
- Atomic number: The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Atomic mass: The atomic mass is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
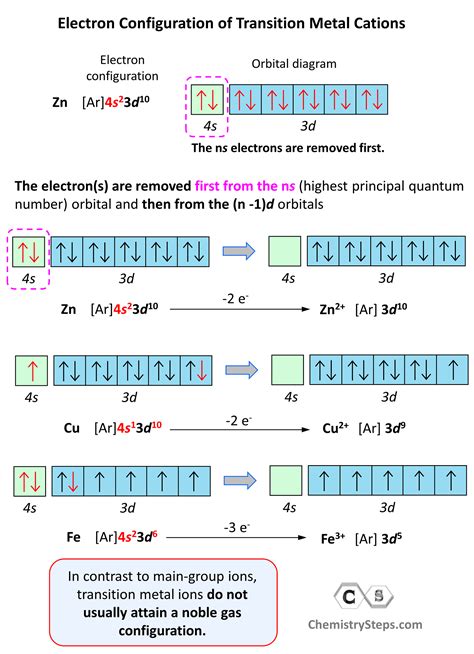
- Electron configuration: The electron configuration shows the arrangement of electrons in an atom.
Electron Configuration Notations
Electron configuration notations can be written in different ways, but the most common one is the Aufbau notation. This notation shows the energy levels and orbitals that electrons occupy.
- Aufbau notation: The Aufbau notation shows the energy levels and orbitals that electrons occupy, from lowest to highest energy.
Periodic Table Trends
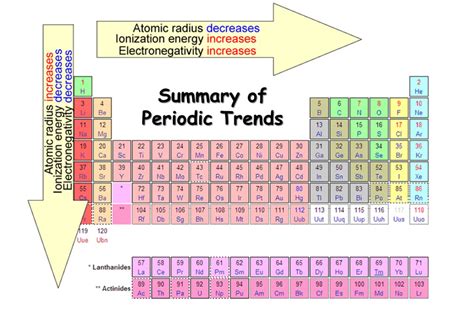
The periodic table shows trends in element properties, which can be useful for predicting the behavior of elements. Here are some common trends to look out for:
- Atomic radius: The atomic radius decreases from left to right across a period and increases from top to bottom down a group.
- Electronegativity: Electronegativity increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom down a group.
- Ionization energy: Ionization energy increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom down a group.
Periodic Table Trend Exceptions
While the periodic table shows trends, there are some exceptions to these trends. Here are a few examples:
- Noble gases: The noble gases (Group 18) have a full outer energy level, which makes them unreactive.
- Hydrogen: Hydrogen is a unique element that doesn't fit into any group or block.
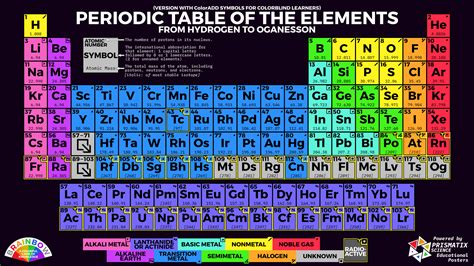
Gallery of Periodic Table Images
Periodic Table Image Gallery
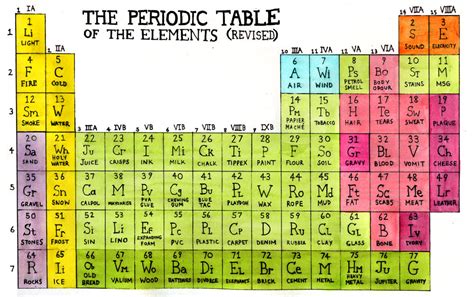
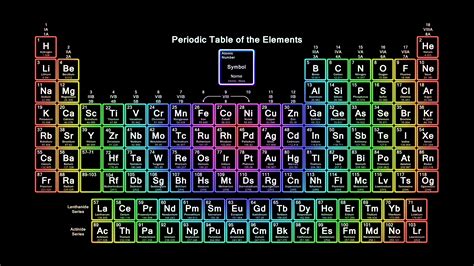
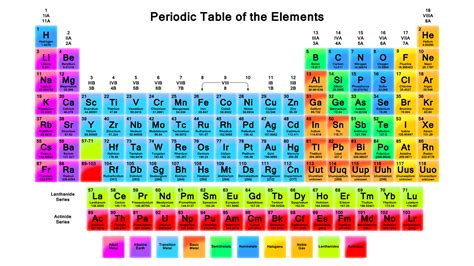
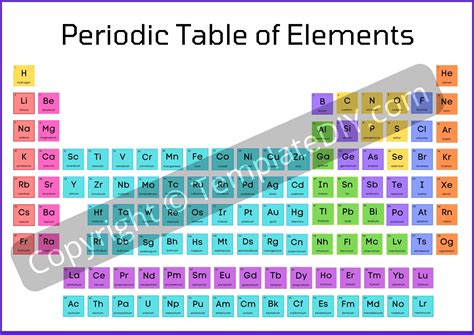

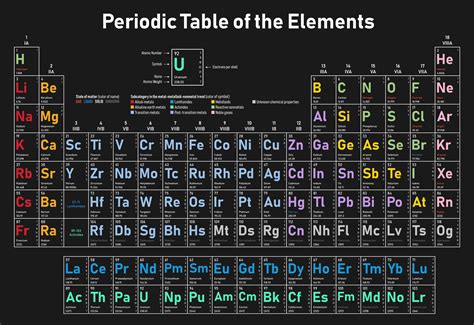
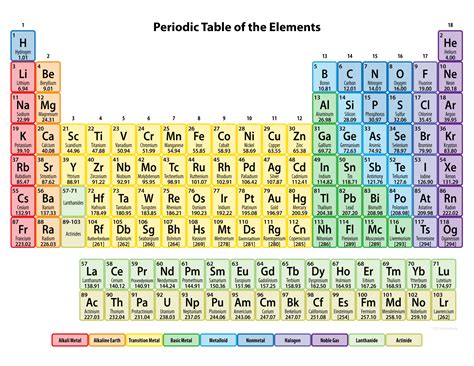
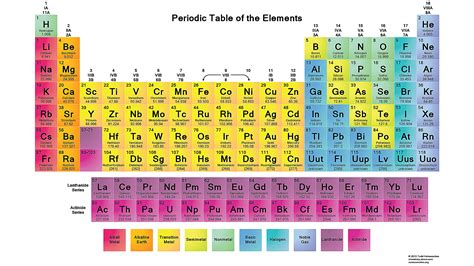
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the periodic table used for? A: The periodic table is used to organize and understand the properties of elements.
Q: How do I read the periodic table? A: The periodic table is read from left to right and top to bottom, with elements organized by their atomic number.
Q: What are the blocks of the periodic table? A: The periodic table is divided into four main blocks: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
Call to Action
We hope this article has helped you understand the importance of having a printable periodic table. Whether you're a student, teacher, or professional, a periodic table is an essential tool for anyone working with chemistry. Share this article with your friends and colleagues, and don't forget to print out your own periodic table for future reference.
