Intro
Mastering pivot tables is an essential skill for any Excel user, and adding VBA tricks to your toolkit can take your data analysis to the next level. Pivot tables are a powerful feature in Excel that allows you to summarize and analyze large datasets with ease. By combining pivot tables with VBA, you can automate repetitive tasks, create dynamic reports, and gain deeper insights into your data.
In this article, we will explore five essential VBA tricks to help you master pivot tables and take your data analysis to new heights.
Trick #1: Automate Pivot Table Creation with VBA
One of the most time-consuming tasks when working with pivot tables is creating them from scratch. With VBA, you can automate this process and create pivot tables with just a few lines of code. This trick is especially useful when working with large datasets or creating multiple pivot tables.
To create a pivot table using VBA, you can use the following code:
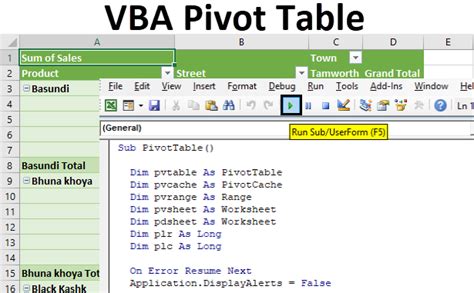
Sub CreatePivotTable()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim pc As PivotCache
Dim pt As PivotTable
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Data")
Set pc = ThisWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=ws.Range("A1:E1000"))
Set pt = pc.CreatePivotTable(TableDestination:=ws.Range("G1"), TableName:="PivotTable1")
End Sub
This code creates a new pivot table named "PivotTable1" in the worksheet "Data" using the data range A1:E1000.
Trick #2: Refresh Pivot Tables with VBA
When working with large datasets, pivot tables can become outdated quickly. With VBA, you can refresh pivot tables automatically, ensuring that your data is always up-to-date. This trick is especially useful when working with dynamic data sources.
To refresh a pivot table using VBA, you can use the following code:
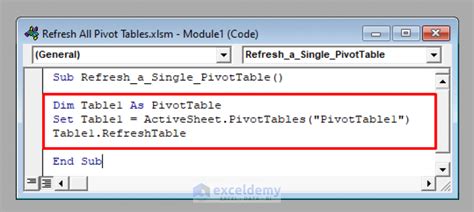
Sub RefreshPivotTable()
Dim pt As PivotTable
Set pt = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Data").PivotTables("PivotTable1")
pt.RefreshTable
End Sub
This code refreshes the pivot table named "PivotTable1" in the worksheet "Data".
Optimizing Pivot Table Refresh with VBA
While refreshing pivot tables with VBA is a useful trick, it can also be optimized for better performance. By using the PivotCache object, you can refresh the pivot cache instead of the entire pivot table. This can significantly improve performance, especially when working with large datasets.
To optimize pivot table refresh with VBA, you can use the following code:
Sub RefreshPivotCache()
Dim pc As PivotCache
Set pc = ThisWorkbook.PivotCaches("PivotCache1")
pc.Refresh
End Sub
This code refreshes the pivot cache named "PivotCache1" instead of the entire pivot table.
Trick #3: Create Dynamic Pivot Tables with VBA
Creating dynamic pivot tables with VBA allows you to create pivot tables that adjust to changing data sources. This trick is especially useful when working with dynamic data sources or creating reports that need to adapt to changing data.
To create a dynamic pivot table using VBA, you can use the following code:
Sub CreateDynamicPivotTable()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim pc As PivotCache
Dim pt As PivotTable
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Data")
Set pc = ThisWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=ws.Range("A1:E1000"))
Set pt = pc.CreatePivotTable(TableDestination:=ws.Range("G1"), TableName:="PivotTable1")
' Add dynamic fields to the pivot table
pt.PivotFields("Field1").Orientation = xlRowField
pt.PivotFields("Field2").Orientation = xlColumnField
End Sub
This code creates a dynamic pivot table named "PivotTable1" in the worksheet "Data" using the data range A1:E1000. The pivot table is then adjusted to include dynamic fields.

Trick #4: Hide and Show Pivot Table Fields with VBA
Hiding and showing pivot table fields with VBA allows you to control the visibility of fields in your pivot table. This trick is especially useful when creating reports that need to adapt to changing data or when working with sensitive data.
To hide and show pivot table fields using VBA, you can use the following code:
Sub HidePivotTableFields()
Dim pt As PivotTable
Set pt = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Data").PivotTables("PivotTable1")
pt.PivotFields("Field1").Visible = False
pt.PivotFields("Field2").Visible = True
End Sub
This code hides the field "Field1" and shows the field "Field2" in the pivot table named "PivotTable1".
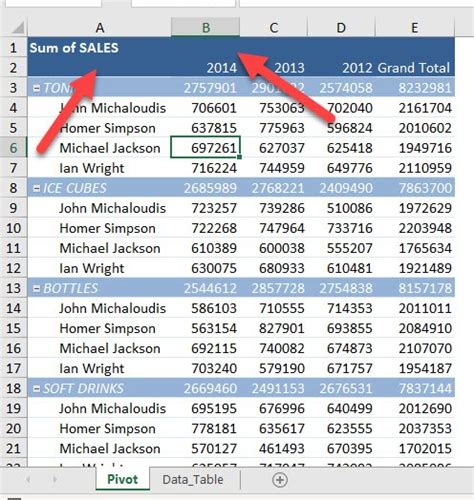
Trick #5: Automate Pivot Table Formatting with VBA
Automating pivot table formatting with VBA allows you to control the appearance of your pivot table. This trick is especially useful when creating reports that need to conform to specific formatting guidelines.
To automate pivot table formatting using VBA, you can use the following code:
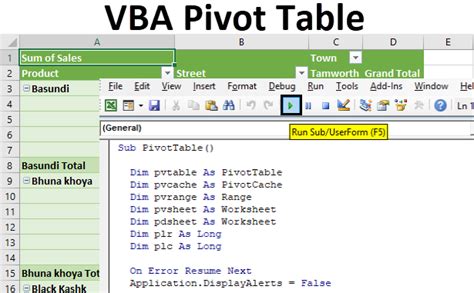
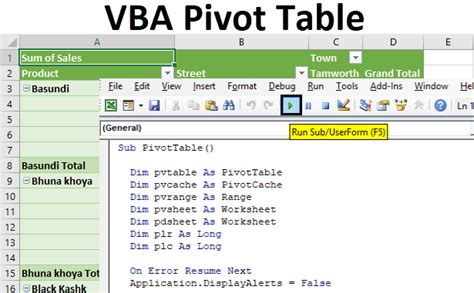
Sub FormatPivotTable()
Dim pt As PivotTable
Set pt = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Data").PivotTables("PivotTable1")
pt.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
pt.LayoutForm = xlOutline
End Sub
This code applies the "PivotStyleMedium9" table style and sets the layout to "xlOutline" for the pivot table named "PivotTable1".
Pivot Tables and VBA Tricks Gallery
We hope you found these five essential VBA tricks for mastering pivot tables helpful in taking your data analysis to the next level. With these tricks, you can automate repetitive tasks, create dynamic reports, and gain deeper insights into your data. Remember to practice and experiment with different VBA code to become proficient in using pivot tables with VBA. Happy coding!
