Porter Five Forces Analysis Template Guide Summary
Unlock strategic insights with our Porter Five Forces Analysis Template Guide. Learn how to apply Michael Porters framework to assess industry competition, identify market opportunities, and develop a competitive advantage. Discover the five forces driving industry rivalry, including buyer power, supplier power, threat of substitution, threat of new entry, and competitive rivalry.
Understanding the competitive landscape of an industry is crucial for businesses to develop effective strategies and make informed decisions. The Porter Five Forces Analysis is a widely used framework that helps organizations analyze the competitive forces that shape their industry. In this article, we will delve into the Porter Five Forces Analysis template, its components, and how to apply it to your business.
What is Porter Five Forces Analysis?
Developed by Michael Porter in 1979, the Porter Five Forces Analysis is a strategic management tool that examines the competitive forces within an industry. It helps businesses identify the strengths and weaknesses of their position within the market, as well as the opportunities and threats that they face. By understanding these forces, organizations can develop strategies to improve their competitiveness and achieve their goals.
The Five Forces of Porter's Model
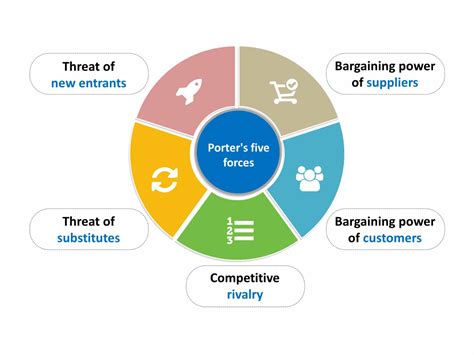
The Porter Five Forces Analysis consists of five key components:
Threat of New Entrants

The threat of new entrants refers to the likelihood of new competitors entering the market. This force is influenced by factors such as:
- Barriers to entry: High startup costs, regulatory requirements, and patent protection can deter new entrants.
- Economies of scale: Existing companies may have a cost advantage due to their larger size and scale.
- Brand loyalty: Strong brand loyalty can make it difficult for new entrants to attract customers.
Factors Affecting Threat of New Entrants
- Capital requirements
- Switching costs
- Access to distribution channels
- Government policies and regulations
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers refers to the ability of suppliers to influence the prices and terms of the products or services they provide. This force is influenced by factors such as:
- Concentration of suppliers: A small number of suppliers can increase their bargaining power.
- Differentiation of products: Suppliers of unique or specialized products may have more bargaining power.
- Switching costs: High switching costs can make it difficult for companies to change suppliers.
Factors Affecting Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Concentration of suppliers
- Differentiation of products
- Switching costs
- Presence of substitute products
Bargaining Power of Buyers

The bargaining power of buyers refers to the ability of customers to influence the prices and terms of the products or services they purchase. This force is influenced by factors such as:
- Concentration of buyers: A small number of buyers can increase their bargaining power.
- Differentiation of products: Buyers of unique or specialized products may have more bargaining power.
- Switching costs: High switching costs can make it difficult for buyers to change suppliers.
Factors Affecting Bargaining Power of Buyers
- Concentration of buyers
- Differentiation of products
- Switching costs
- Presence of substitute products
Threat of Substitute Products

The threat of substitute products refers to the likelihood of customers switching to alternative products or services. This force is influenced by factors such as:
- Availability of substitutes: The presence of substitute products can increase the threat of substitution.
- Switching costs: High switching costs can make it difficult for customers to switch to substitutes.
- Price and performance: Substitutes that offer better price and performance may attract customers.
Factors Affecting Threat of Substitute Products
- Availability of substitutes
- Switching costs
- Price and performance
- Marketing and advertising
Competitive Rivalry Among Existing Competitors

The competitive rivalry among existing competitors refers to the intensity of competition among existing companies in the market. This force is influenced by factors such as:
- Number of competitors: A large number of competitors can increase the intensity of competition.
- Differentiation of products: Companies that offer unique or differentiated products may have a competitive advantage.
- Advertising and marketing: Aggressive advertising and marketing can increase competition.
Factors Affecting Competitive Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
- Number of competitors
- Differentiation of products
- Advertising and marketing
- Price competition
Gallery of Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Image Gallery






Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Porter Five Forces Analysis is a powerful tool that helps businesses understand the competitive landscape of their industry. By analyzing the five forces of competition, businesses can identify the strengths and weaknesses of their position within the market, as well as the opportunities and threats that they face. By applying the Porter Five Forces Analysis template, businesses can develop effective strategies to improve their competitiveness and achieve their goals.
