Intro
Unlock the secrets of competitive analysis with Porters Five Forces. Discover how to assess industry rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. Boost your business strategy with actionable insights and stay ahead of the competition.
Analyzing competition is a crucial aspect of business strategy, and one of the most effective frameworks for doing so is Porter's Five Forces. Developed by Michael Porter in 1979, this model provides a comprehensive approach to understanding the competitive landscape of an industry. By examining the five forces that shape competition, businesses can gain valuable insights into their industry's dynamics and develop strategies to stay ahead of the competition.
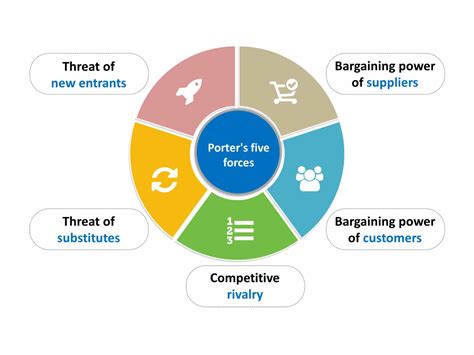
Understanding Porter's Five Forces
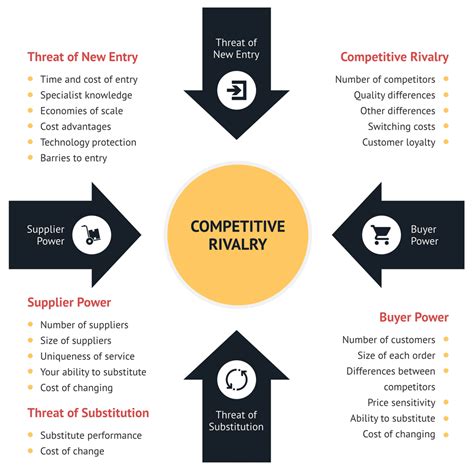
Porter's Five Forces model is based on the idea that competition in an industry is influenced by five key factors: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitute products, and rivalry among existing competitors. By analyzing these forces, businesses can identify opportunities and threats in their industry and develop strategies to improve their competitive position.
Force 1: Threat of New Entrants
The threat of new entrants is a critical force in Porter's model, as it can disrupt the existing competitive landscape and create new challenges for established businesses. To analyze this force, businesses should consider factors such as:
- Barriers to entry: How easy or difficult is it for new businesses to enter the industry?
- Economies of scale: Can new entrants take advantage of economies of scale to reduce costs and improve efficiency?
- Differentiation: How differentiated are the products or services offered by established businesses, and can new entrants easily replicate them?

Force 2: Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is another key force in Porter's model, as it can impact the cost structure and profitability of businesses. To analyze this force, businesses should consider factors such as:
- Concentration of suppliers: How concentrated is the supply base, and can suppliers exert significant influence over prices and terms?
- Differentiation of products: How differentiated are the products or services offered by suppliers, and can businesses easily switch to alternative suppliers?
- Switching costs: How easy or difficult is it for businesses to switch to alternative suppliers?
Force 3: Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of buyers is a critical force in Porter's model, as it can impact the pricing and profitability of businesses. To analyze this force, businesses should consider factors such as:
- Concentration of buyers: How concentrated is the buyer base, and can buyers exert significant influence over prices and terms?
- Differentiation of products: How differentiated are the products or services offered by businesses, and can buyers easily switch to alternative products?
- Switching costs: How easy or difficult is it for buyers to switch to alternative products?
Force 4: Threat of Substitute Products
The threat of substitute products is a key force in Porter's model, as it can impact the demand for businesses' products or services. To analyze this force, businesses should consider factors such as:
- Availability of substitutes: How available are substitute products, and can they meet the needs of buyers?
- Switching costs: How easy or difficult is it for buyers to switch to substitute products?
- Differentiation: How differentiated are the products or services offered by businesses, and can substitutes easily replicate them?

Force 5: Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
The rivalry among existing competitors is a critical force in Porter's model, as it can impact the competitive landscape and profitability of businesses. To analyze this force, businesses should consider factors such as:
- Number of competitors: How many competitors are in the industry, and how intense is the competition?
- Differentiation: How differentiated are the products or services offered by competitors, and can businesses easily replicate them?
- Switching costs: How easy or difficult is it for buyers to switch to alternative products?
Applying Porter's Five Forces
By analyzing the five forces that shape competition, businesses can gain valuable insights into their industry's dynamics and develop strategies to improve their competitive position. Here are five ways to apply Porter's Five Forces:
- Identify opportunities and threats: By analyzing the five forces, businesses can identify opportunities and threats in their industry and develop strategies to capitalize on them.
- Develop a competitive strategy: By understanding the competitive landscape, businesses can develop a competitive strategy that takes into account the five forces and improves their competitive position.
- Improve operational efficiency: By analyzing the five forces, businesses can identify areas for operational improvement and develop strategies to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Enhance differentiation: By understanding the five forces, businesses can develop strategies to enhance differentiation and improve their competitive position.
- Monitor industry trends: By analyzing the five forces, businesses can monitor industry trends and develop strategies to stay ahead of the competition.
Porter's Five Forces Image Gallery






We hope this article has provided valuable insights into Porter's Five Forces and how to apply them to improve your business's competitive position. By analyzing the five forces that shape competition, businesses can develop strategies to stay ahead of the competition and achieve long-term success. Share your thoughts and experiences with Porter's Five Forces in the comments section below!
