Intro
Learn effective strategies for managing postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), a life-threatening condition that can occur after childbirth. Discover the causes, symptoms, and 5 crucial ways to prevent and treat PPH, including uterine massage, medical interventions, and fluid resuscitation. Ensure a safe postpartum recovery with these essential tips.
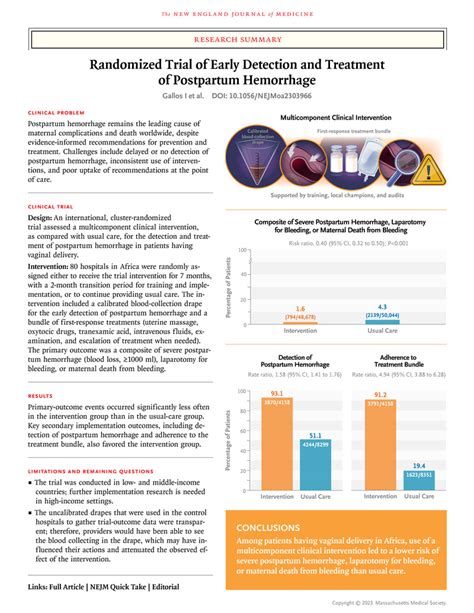
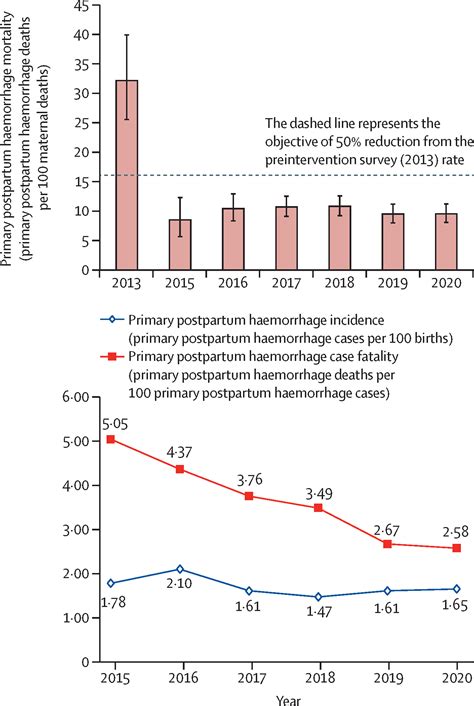
As a new mother, the arrival of your baby is a momentous occasion, filled with joy, excitement, and a mix of emotions. However, the postpartum period can be a challenging time for many women, especially when it comes to managing postpartum hemorrhage (PPH). PPH is a serious condition that can occur after childbirth, characterized by excessive bleeding that can lead to shock, organ failure, and even death if left untreated. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), PPH is one of the leading causes of maternal mortality worldwide. In this article, we will explore five ways to manage postpartum hemorrhage, highlighting the importance of prompt recognition, effective treatment, and prevention strategies.
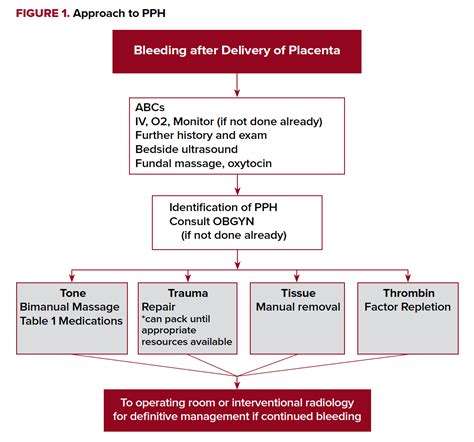
Understanding Postpartum Hemorrhage
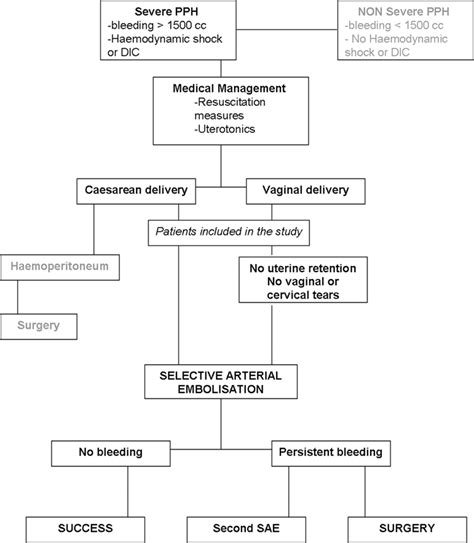
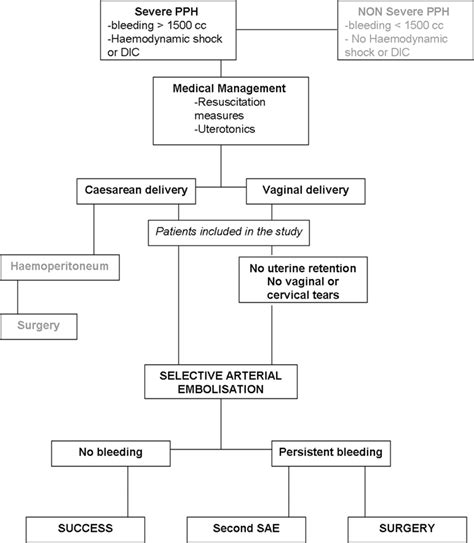
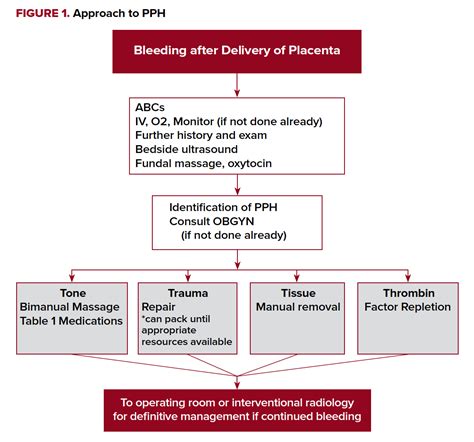
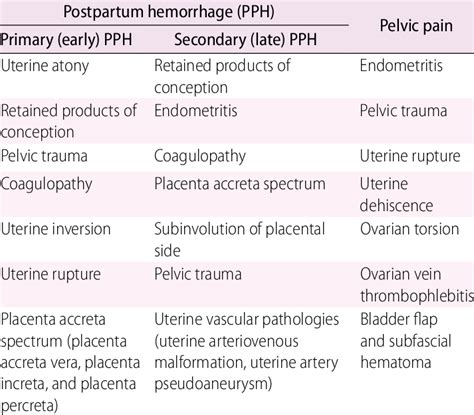
PPH is defined as the loss of more than 500 ml of blood after a vaginal delivery or more than 1000 ml after a cesarean section. The condition can be caused by various factors, including uterine atony, retained placental tissue, and lacerations or tears. PPH can be classified into three stages: mild, moderate, and severe. Mild PPH is characterized by blood loss of 500-1000 ml, while moderate PPH involves blood loss of 1000-2000 ml. Severe PPH is defined as blood loss exceeding 2000 ml, which can lead to shock and organ failure.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing PPH, including:
- Uterine atony: This is the most common cause of PPH, accounting for approximately 80% of cases.
- Retained placental tissue: Failure to remove the placenta completely after delivery can lead to PPH.
- Lacerations or tears: Vaginal or cervical lacerations can cause significant blood loss.
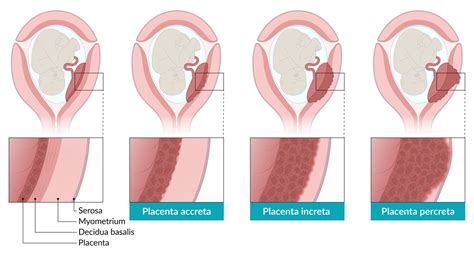
- Placenta previa: This condition occurs when the placenta covers the cervix, increasing the risk of bleeding during delivery.
- Placental abruption: Premature separation of the placenta from the uterus can cause PPH.
5 Ways to Manage Postpartum Hemorrhage
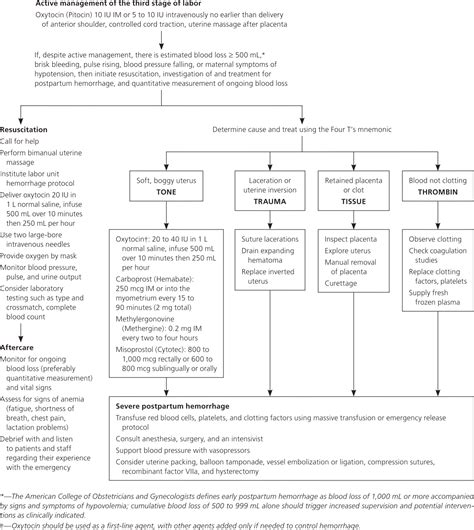
1. Active Management of the Third Stage of Labor (AMTSL)
AMTSL is a critical step in preventing PPH. This involves administering oxytocin or other uterotonic agents to stimulate uterine contractions and help the uterus expel the placenta. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends AMTSL as a standard practice for all vaginal deliveries.
2. Uterine Massage and Compression
Uterine massage and compression can help control bleeding by stimulating uterine contractions. This technique involves massaging the uterus to help it contract and reduce bleeding. Uterine compression can also be used to apply pressure to the uterus and help control bleeding.
3. Fluid Resuscitation and Blood Transfusion
Fluid resuscitation and blood transfusion are essential in managing PPH. Administering fluids and blood products can help restore blood volume, prevent shock, and ensure adequate oxygen delivery to vital organs.
4. Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions, such as administering uterotonic agents, can help manage PPH. Oxytocin, ergot alkaloids, and prostaglandins are commonly used to stimulate uterine contractions and reduce bleeding.
5. Surgical Interventions
In severe cases of PPH, surgical interventions may be necessary. This can include procedures such as uterine artery ligation, hysterectomy, or the use of intrauterine balloons to control bleeding.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing PPH is crucial in reducing maternal morbidity and mortality. The following prevention strategies can be implemented:
- Ensure adequate antenatal care and monitor for risk factors
- Implement AMTSL for all vaginal deliveries
- Use uterotonic agents to stimulate uterine contractions
- Monitor for bleeding and take prompt action if PPH occurs
- Ensure adequate training for healthcare providers in managing PPH
Postpartum Hemorrhage Image Gallery

Conclusion
Postpartum hemorrhage is a serious condition that requires prompt recognition and effective management. Implementing prevention strategies, such as AMTSL and uterotonic agents, can help reduce the risk of PPH. Understanding the causes and risk factors of PPH is essential in identifying women who are at high risk of developing the condition. By providing adequate training for healthcare providers and promoting awareness about PPH, we can work towards reducing maternal morbidity and mortality worldwide.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on managing postpartum hemorrhage. Your input can help us improve our understanding of this critical condition and develop more effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
