Unlock the power of potential energy with our expert guide. Discover 5 innovative ways to harness energy from force, exploring concepts like kinetic energy conversion, elastic potential energy, and gravitational potential energy. Learn how to optimize energy storage, kinetic energy recovery, and more to revolutionize industries and daily life.
Harnessing potential energy from force is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, with numerous applications in our daily lives. Potential energy, by definition, is the energy that an object possesses due to its position or state. When a force is applied to an object, it can convert this potential energy into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. In this article, we will explore five ways to harness potential energy from force.
Understanding Potential Energy and Force
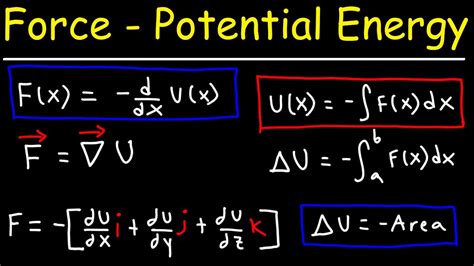
Before we dive into the ways to harness potential energy, it's essential to understand the relationship between potential energy and force. Potential energy is a result of the position or state of an object, while force is a push or pull that causes an object to change its motion. When a force is applied to an object, it can increase or decrease its potential energy, depending on the direction and magnitude of the force.
Types of Potential Energy
There are several types of potential energy, including:
- Gravitational potential energy: the energy an object possesses due to its height or position in a gravitational field.
- Elastic potential energy: the energy stored in an object that is stretched or compressed.
- Electric potential energy: the energy an object possesses due to its electric charge and position in an electric field.
- Chemical potential energy: the energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules.
1. Hydroelectric Power Plants

Hydroelectric power plants harness potential energy from the force of water flowing from a higher elevation to a lower elevation. The water is channeled through a turbine, which converts the kinetic energy of the water into electrical energy. Hydroelectric power plants are a clean and renewable source of energy, producing no greenhouse gas emissions or pollution.
How Hydroelectric Power Plants Work
Hydroelectric power plants work by:
- Channeling water from a higher elevation to a lower elevation through a penstock.
- Using the force of the water to drive a turbine.
- Converting the kinetic energy of the turbine into electrical energy through a generator.
2. Wind Turbines
Wind turbines harness potential energy from the force of wind. As wind flows over the blades of a turbine, it creates a force that drives the turbine to rotate. The rotation of the turbine is converted into electrical energy through a generator. Wind turbines are a clean and renewable source of energy, producing no greenhouse gas emissions or pollution.
How Wind Turbines Work
Wind turbines work by:
- Using the force of wind to drive the blades of a turbine.
- Converting the rotation of the turbine into electrical energy through a generator.
3. Pumps and Compressors
Pumps and compressors harness potential energy from the force of fluid flow. When a fluid is compressed or pumped, it stores potential energy that can be converted into kinetic energy. Pumps and compressors are used in a wide range of applications, including hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems, and refrigeration systems.
How Pumps and Compressors Work
Pumps and compressors work by:
- Using the force of fluid flow to compress or pump a fluid.
- Storing potential energy in the compressed or pumped fluid.
- Converting the potential energy into kinetic energy through a turbine or engine.
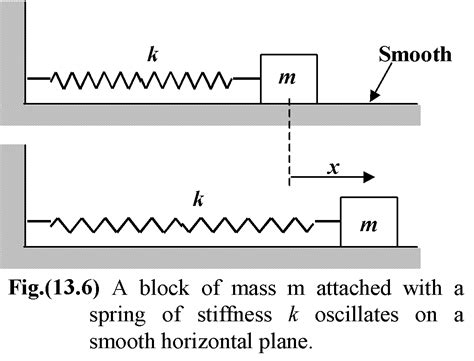
4. Springs and Elastic Systems

Springs and elastic systems harness potential energy from the force of deformation. When a spring or elastic material is stretched or compressed, it stores potential energy that can be converted into kinetic energy. Springs and elastic systems are used in a wide range of applications, including mechanical systems, electrical systems, and biomedical devices.
How Springs and Elastic Systems Work
Springs and elastic systems work by:
- Using the force of deformation to store potential energy.
- Converting the potential energy into kinetic energy through a release of the stored energy.
5. Tidal Power Plants

Tidal power plants harness potential energy from the force of ocean tides. As the tide rises and falls, it creates a force that drives a turbine. The rotation of the turbine is converted into electrical energy through a generator. Tidal power plants are a clean and renewable source of energy, producing no greenhouse gas emissions or pollution.
How Tidal Power Plants Work
Tidal power plants work by:
- Using the force of ocean tides to drive a turbine.
- Converting the rotation of the turbine into electrical energy through a generator.
Potential Energy from Force Image Gallery









We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the ways to harness potential energy from force. From hydroelectric power plants to tidal power plants, there are numerous ways to convert potential energy into kinetic energy. We encourage you to share your thoughts and ideas on this topic and explore the various applications of potential energy in our daily lives.
