Intro
Learn effective strategies for managing pressure injury wounds with our expert guide. Discover 7 ways to prevent and treat pressure ulcers, including wound care techniques, nutrition and positioning tips, and product recommendations. Reduce risk, promote healing, and improve patient outcomes with our comprehensive advice on pressure injury management.
Pressure injuries, also known as pressure ulcers or bed sores, are a significant concern for individuals who are bedridden, wheelchair-bound, or have limited mobility. These injuries can be painful, debilitating, and even life-threatening if left untreated or managed improperly. Effective management of pressure injury wounds is crucial to prevent complications, promote healing, and improve the overall quality of life for those affected.
Pressure injuries occur when prolonged pressure on the skin and underlying tissues restricts blood flow, leading to tissue damage and eventual breakdown. The most common areas prone to pressure injuries are the skin over bony prominences, such as the hips, heels, and tailbone. Understanding the risk factors, prevention strategies, and treatment options is essential for managing pressure injury wounds effectively.
Understanding Pressure Injury Wounds
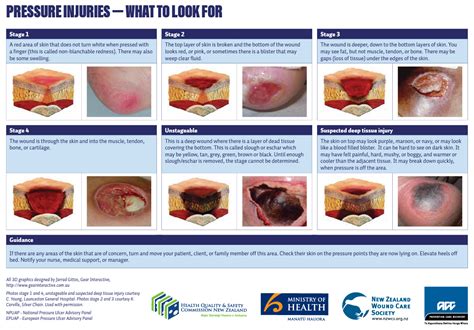
Pressure injury wounds are classified into four stages, each representing a different level of tissue damage and severity. Stage 1 pressure injuries are the least severe, characterized by non-blanchable erythema (redness that does not fade when pressed). Stage 2 pressure injuries involve partial-thickness skin loss, while Stage 3 pressure injuries are characterized by full-thickness skin loss. Stage 4 pressure injuries are the most severe, with exposed bone, tendon, or muscle.
Risk Factors for Pressure Injury Wounds
Several factors contribute to the development of pressure injury wounds, including:
- Prolonged immobility or bed rest
- Limited mobility or wheelchair use
- Poor nutrition and hydration
- Skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis
- Diabetes or peripheral artery disease
- Obesity or being underweight
- Smoking or tobacco use
Prevention Strategies for Pressure Injury Wounds
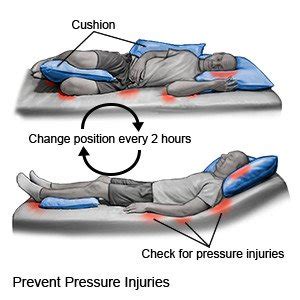
Preventing pressure injury wounds is crucial to avoid the discomfort, pain, and complications associated with these injuries. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Regular turning and repositioning (every 2-3 hours)
- Using pressure-redistributing mattresses and seat cushions
- Maintaining good nutrition and hydration
- Encouraging mobility and exercise
- Protecting vulnerable areas with padding and dressings
- Monitoring skin integrity and reporting any concerns to healthcare professionals
Assessment and Treatment of Pressure Injury Wounds
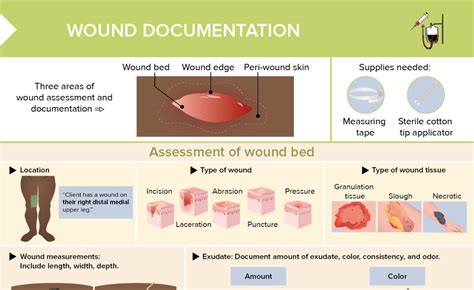
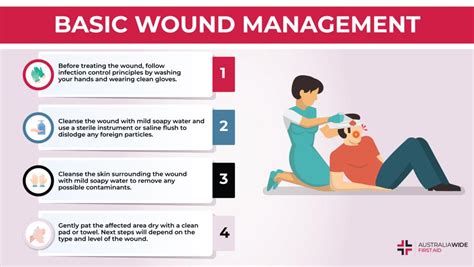
Assessing pressure injury wounds involves evaluating the stage, size, and severity of the injury, as well as the individual's overall health and medical history. Treatment options vary depending on the stage and severity of the injury but may include:
- Debridement (removing dead tissue and debris)
- Dressing and bandaging
- Topical treatments (e.g., antibiotics, creams)
- Pressure-redistributing devices (e.g., mattresses, seat cushions)
- Nutritional support and supplements
- Pain management and wound care education
Managing Pressure Injury Wounds Effectively
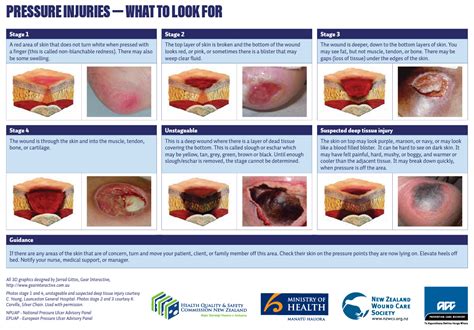
Effective management of pressure injury wounds requires a comprehensive approach, including:
- Regular wound assessment and documentation: Monitoring the wound's progress and documenting changes is crucial for adjusting treatment plans and preventing complications.
- Individualized care plans: Tailoring care plans to the individual's specific needs and medical history ensures effective management and promotes healing.
- Multidisciplinary team approach: Collaborating with healthcare professionals, including wound care specialists, nutritionists, and physical therapists, ensures a comprehensive approach to wound management.
- Patient and caregiver education: Educating patients and caregivers on wound care, prevention strategies, and nutrition promotes empowerment and self-management.
- Pain management and comfort measures: Addressing pain and discomfort is essential for improving the individual's quality of life and promoting wound healing.
- Nutritional support and supplements: Ensuring adequate nutrition and hydration is crucial for wound healing and overall health.
- Pressure-redistributing devices and equipment: Using pressure-redistributing devices and equipment, such as mattresses and seat cushions, helps prevent further tissue damage and promotes healing.
Conclusion
Managing pressure injury wounds effectively requires a comprehensive approach that addresses prevention, assessment, treatment, and ongoing care. By understanding the risk factors, prevention strategies, and treatment options, individuals and healthcare professionals can work together to promote healing, prevent complications, and improve the overall quality of life for those affected.
Pressure Injury Wound Management Gallery
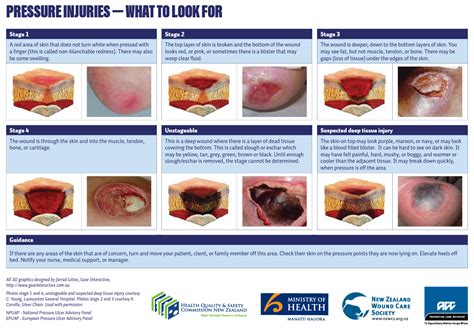





We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the effective management of pressure injury wounds. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to us.
