Intro
Learn how to diagnose and manage preterm labor with our comprehensive system disorder template guide. Understand the causes, risk factors, and symptoms of preterm labor, and discover the latest treatment options and interventions. Get expert insights on prevention, diagnosis, and management of preterm labor, preterm birth, and associated complications.
Preterm labor is a serious medical condition that affects millions of pregnant women worldwide. It is a leading cause of infant mortality and morbidity, and can have significant emotional and financial impacts on families. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for preterm labor is crucial for expectant mothers and healthcare providers. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the preterm labor system disorder, its effects on pregnancy, and the various ways to manage and prevent it.
What is Preterm Labor?
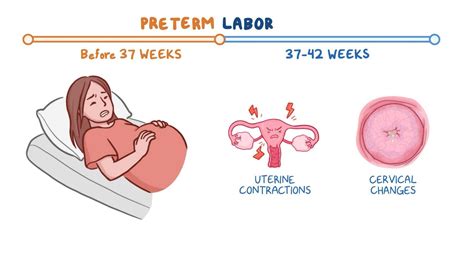
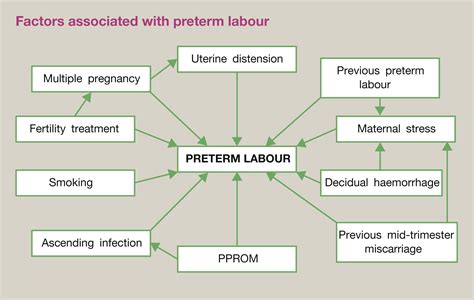
Preterm labor is defined as labor that occurs before 37 weeks of gestation. It is also known as premature labor or early labor. Preterm labor can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, cervical insufficiency, and placental abruption. Women who experience preterm labor are at risk of delivering their baby prematurely, which can lead to serious health complications for the infant.
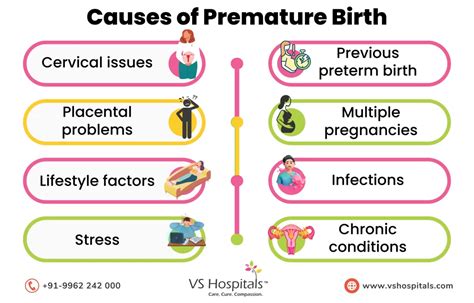
Causes of Preterm Labor
Preterm labor can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Infections: Bacterial vaginosis, urinary tract infections, and group B strep infections can all increase the risk of preterm labor.
- Cervical Insufficiency: Women with a weakened cervix are at higher risk of preterm labor.
- Placental Abruption: A condition in which the placenta separates from the uterus, placental abruption can cause preterm labor.
- Multiple Gestations: Carrying twins or other multiples increases the risk of preterm labor.
- Previous Preterm Birth: Women who have had a previous preterm birth are at higher risk of preterm labor in subsequent pregnancies.
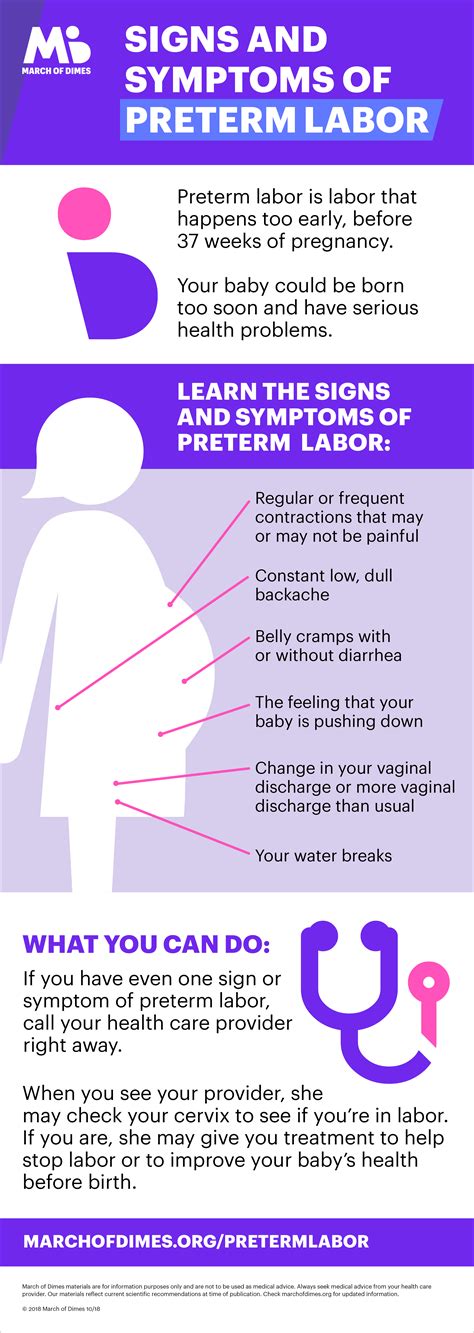
Symptoms of Preterm Labor
The symptoms of preterm labor can be similar to those of regular labor, but may include:
- Contractions: Women may experience contractions that feel like menstrual cramps or a tightening sensation in the abdomen.
- Back Pain: Back pain can be a symptom of preterm labor, especially if it radiates to the abdomen.
- Vaginal Discharge: Women may experience a change in vaginal discharge or bleeding.
- Abdominal Cramping: Abdominal cramping can be a symptom of preterm labor.
Diagnosing Preterm Labor
Diagnosing preterm labor typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may use the following tests to diagnose preterm labor:
- Uterine Contractions: Healthcare providers may use a fetal monitor to measure uterine contractions.
- Cervical Exam: A cervical exam can help determine if the cervix is dilated or effaced.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound can help determine the gestational age of the fetus and check for any signs of fetal distress.
Managing Preterm Labor
Managing preterm labor typically involves a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle changes. Healthcare providers may recommend the following treatments:
- Bed Rest: Bed rest can help reduce the risk of preterm labor.
- Tocolytics: Medications such as tocolytics can help slow down uterine contractions.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids can help promote fetal lung maturity.
- Progesterone: Progesterone can help reduce the risk of preterm labor.
Preventing Preterm Labor
Preventing preterm labor requires a combination of medical care and lifestyle changes. Women can reduce their risk of preterm labor by:
- Getting Regular Prenatal Care: Regular prenatal care can help healthcare providers monitor the pregnancy and detect any potential complications.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support the pregnancy.
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help reduce the risk of preterm labor.
- Avoiding Stress: Stress can increase the risk of preterm labor, so finding ways to manage stress is crucial.
Complications of Preterm Labor
Preterm labor can lead to a range of complications for both the mother and the baby. Some of the potential complications include:
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Babies born prematurely may experience respiratory distress syndrome, a condition in which the lungs are not fully developed.
- Infections: Premature babies are at higher risk of infections, which can be serious and even life-threatening.
- Developmental Delays: Premature babies may experience developmental delays, including delays in cognitive, motor, and language development.
Gallery of Preterm Labor Images
Preterm Labor Image Gallery






Conclusion
Preterm labor is a serious medical condition that affects millions of pregnant women worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for preterm labor is crucial for expectant mothers and healthcare providers. By following the guidelines outlined in this comprehensive guide, women can reduce their risk of preterm labor and ensure a healthy pregnancy. If you or someone you know is experiencing preterm labor, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. With proper care and support, women can have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.
