12 Lead Ekg Interpretation Cheat Sheet Made Easy Summary
Master 12 lead EKG interpretation with our easy-to-use cheat sheet. Learn to identify arrhythmias, myocardial infarctions, and other cardiac conditions with confidence. Our comprehensive guide covers lead placement, waveform analysis, and key findings, making EKG interpretation a breeze for medical professionals and students alike.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) interpretation is a crucial skill for healthcare professionals, as it helps diagnose and manage various heart conditions. However, mastering 12-lead EKG interpretation can be a daunting task, especially for those new to the field. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive cheat sheet to make 12-lead EKG interpretation easier to understand and apply.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the cheat sheet, it's essential to understand the basics of ECG interpretation. A 12-lead EKG provides a comprehensive view of the heart's electrical activity from 12 different angles. Each lead represents a specific view of the heart, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis.
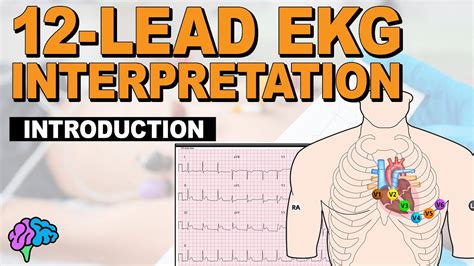
The 12-Lead EKG Cheat Sheet
To make 12-lead EKG interpretation easier, we've broken down the process into a simple, step-by-step guide.
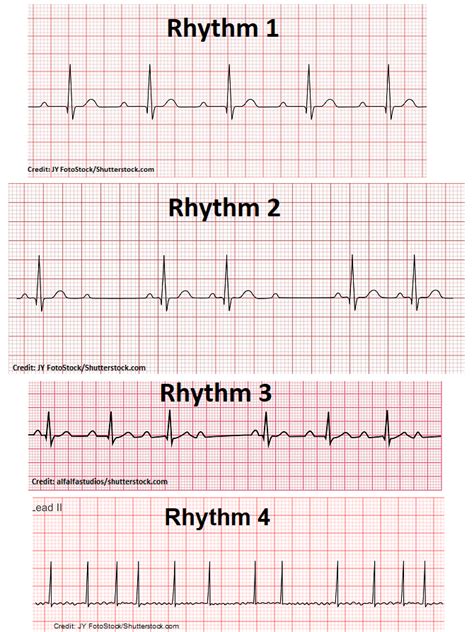
Step 1: Identify the Rhythm
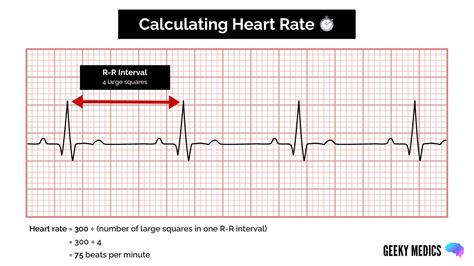
- Determine the heart rate: Measure the time between two consecutive R-waves to calculate the heart rate.
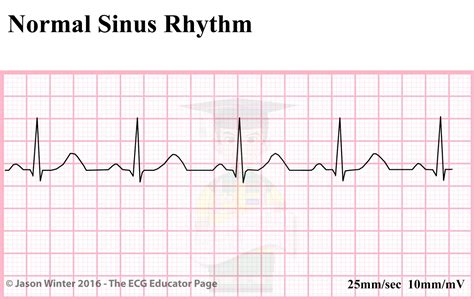
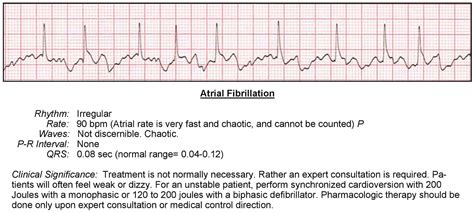
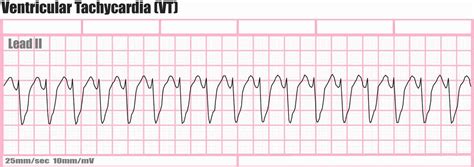
- Identify the rhythm: Look for patterns in the R-waves to determine the heart rhythm (e.g., normal sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia).
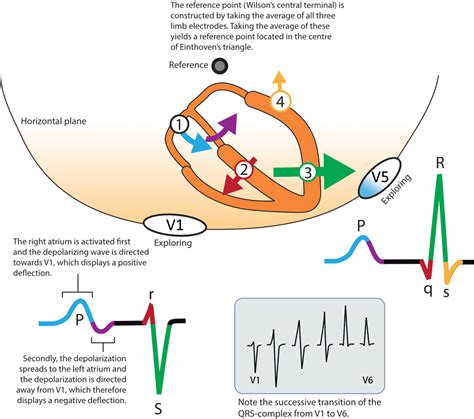
Step 2: Analyze the P-Wave
- Look for P-waves: Identify the P-waves in leads II, III, and aVF.
- Measure the P-wave duration: Measure the time between the beginning and end of the P-wave.
- Check for P-wave abnormalities: Look for signs of atrial enlargement or abnormal P-wave morphology.
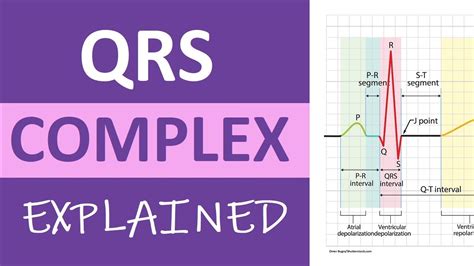
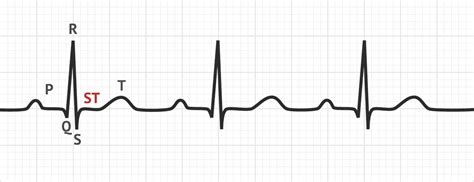
Step 3: Evaluate the QRS Complex
- Measure the QRS duration: Measure the time between the beginning and end of the QRS complex.
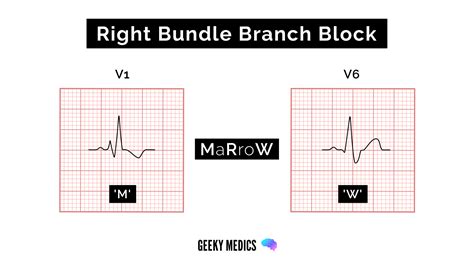
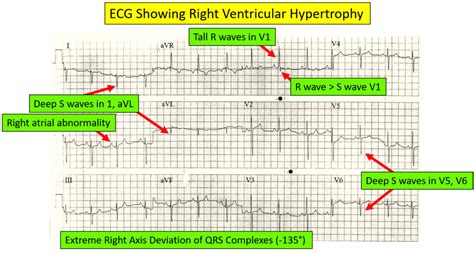
- Check for QRS abnormalities: Look for signs of bundle branch block, ventricular hypertrophy, or other QRS complex abnormalities.
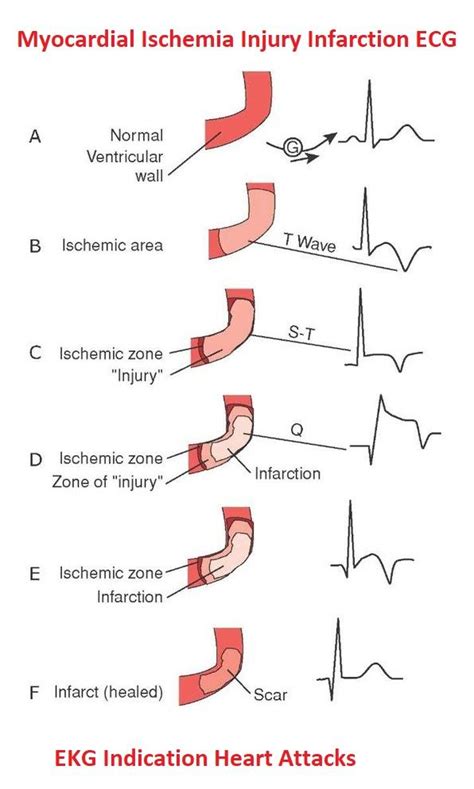
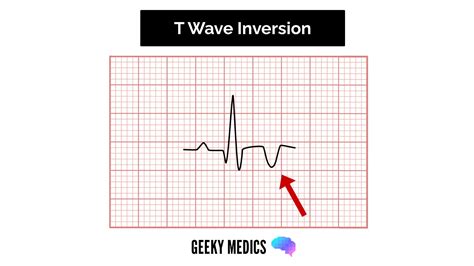
Step 4: Analyze the T-Wave
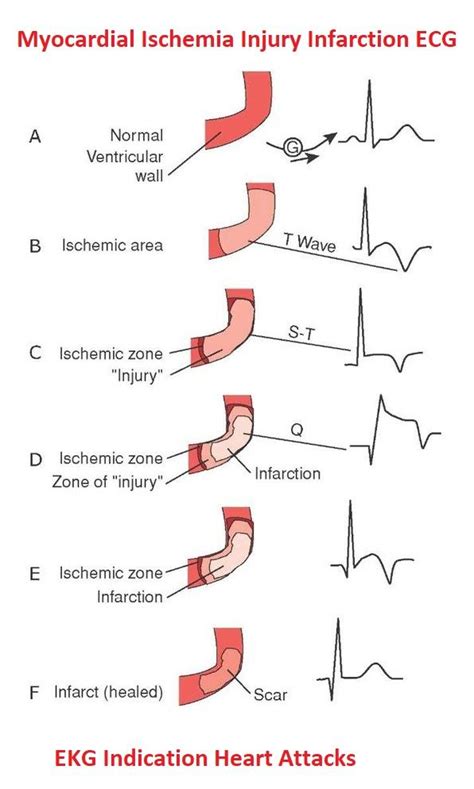
- Evaluate T-wave morphology: Look for signs of ischemia, infarction, or ventricular hypertrophy.
- Check for T-wave abnormalities: Look for signs of T-wave inversion, flattening, or other abnormalities.
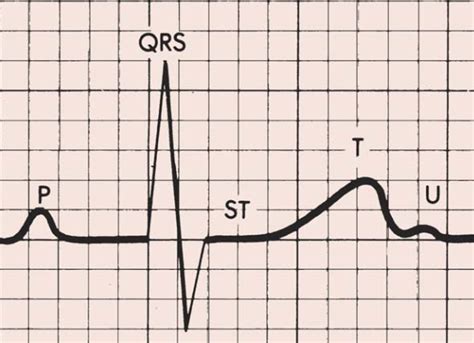
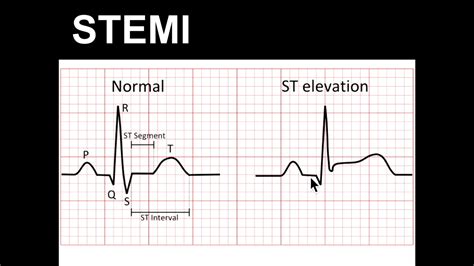
Step 5: Evaluate the ST Segment
- Measure the ST segment elevation: Measure the distance between the J-point and the beginning of the T-wave.
- Check for ST segment abnormalities: Look for signs of ischemia, infarction, or other ST segment abnormalities.
Putting it all Together
By following these steps and using the cheat sheet provided, you can improve your 12-lead EKG interpretation skills. Remember to always consider the patient's clinical presentation and medical history when interpreting the EKG.
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Image Gallery
Final Thoughts
Mastering 12-lead EKG interpretation takes time and practice. By using this cheat sheet and continuing to practice, you can improve your skills and become more confident in your ability to interpret EKGs. Remember to always consider the patient's clinical presentation and medical history when interpreting the EKG, and don't hesitate to seek guidance from more experienced healthcare professionals.
We hope this article has been helpful in making 12-lead EKG interpretation easier to understand and apply. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
