Intro
Master EKG interpretation with our comprehensive cheat sheet for nurses and medical students. Learn to identify normal and abnormal heart rhythms, including arrhythmias, blocks, and ischemia. Get instant access to a concise guide covering P wave, QRS complex, and T wave analysis, plus tips for accurate EKG reading and diagnosis.
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG) is a crucial diagnostic tool in the field of medicine, providing valuable information about the heart's electrical activity. As a nurse or medical student, having a solid understanding of ECG interpretation is essential for delivering high-quality patient care. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of ECGs, exploring the basics, types of ECGs, and providing a detailed ECG cheat sheet for nurses and medical students.
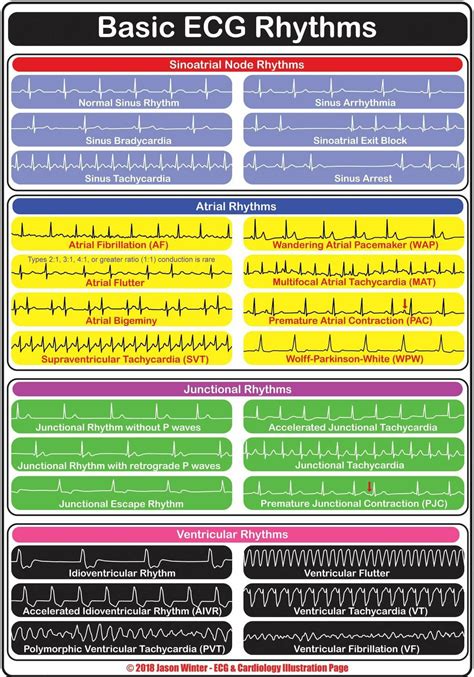
Understanding the Basics of ECG
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of ECG interpretation, it's essential to understand the basics. An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart, which is generated by the movement of ions across the cardiac cell membrane. This activity is recorded using electrodes placed on the skin, resulting in a graph that represents the heart's electrical signals.
Types of ECGs
There are several types of ECGs, including:
- Resting ECG: A standard ECG performed while the patient is at rest.
- Exercise Stress Test ECG: An ECG performed during physical activity, usually on a treadmill.
- Holter Monitor ECG: A 24-hour ECG recording that monitors the heart's activity over an extended period.
- Event Monitor ECG: A portable device that records the heart's activity over a shorter period, usually 30 days.
ECG Cheat Sheet for Nurses and Medical Students
Here is a comprehensive ECG cheat sheet to help you improve your ECG interpretation skills:
ECG Components
- P Wave: The first upward deflection of the ECG, representing atrial depolarization.
- PR Interval: The time between the P wave and the QRS complex, representing the delay between atrial and ventricular depolarization.
- QRS Complex: The group of waves representing ventricular depolarization.
- ST Segment: The flat section between the QRS complex and the T wave, representing the period of ventricular repolarization.
- T Wave: The upward deflection following the ST segment, representing ventricular repolarization.
- QT Interval: The time between the QRS complex and the T wave, representing the period of ventricular repolarization.
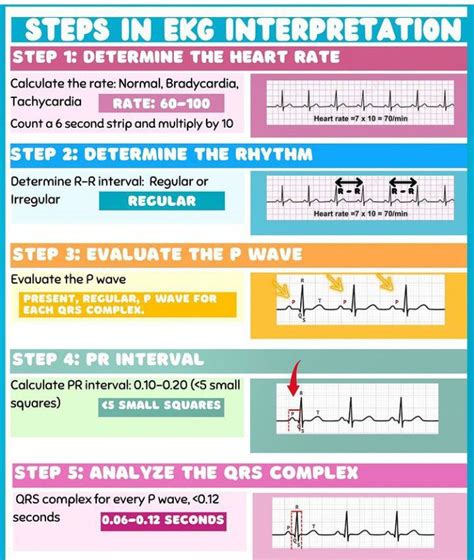
ECG Interpretation Steps
- Determine the heart rate: Calculate the heart rate by dividing 300 by the number of large squares between two R waves.
- Identify the rhythm: Determine if the rhythm is regular or irregular, and if it's a normal sinus rhythm or an abnormal rhythm.
- Measure the PR interval: Measure the time between the P wave and the QRS complex.
- Measure the QT interval: Measure the time between the QRS complex and the T wave.
- Assess the ST segment: Evaluate the ST segment for any elevations or depressions.
- Evaluate the T wave: Evaluate the T wave for any abnormalities.
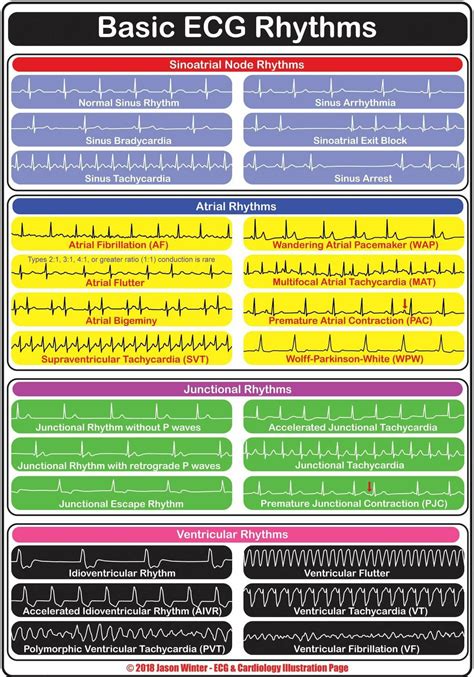
Common ECG Abnormalities
- Atrial Fibrillation: Characterized by an irregularly irregular rhythm, with no discernible P waves.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: Characterized by a rapid heart rate (>100 bpm), with a wide QRS complex.
- Myocardial Infarction: Characterized by ST segment elevation or depression, with or without Q waves.
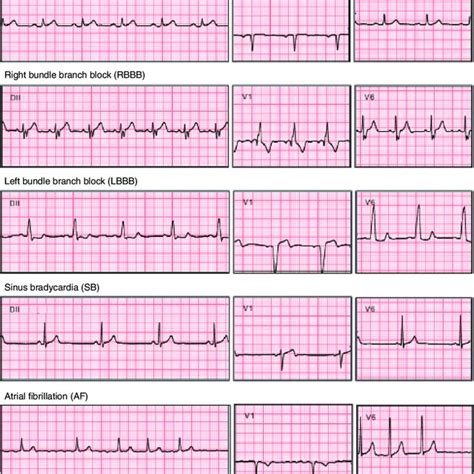
ECG Leads
- Lead I: Records the difference in electrical potential between the left and right arms.
- Lead II: Records the difference in electrical potential between the left leg and the right arm.
- Lead III: Records the difference in electrical potential between the left leg and the left arm.
- Lead aVR: Records the difference in electrical potential between the right arm and the average of the left arm and left leg.
- Lead aVL: Records the difference in electrical potential between the left arm and the average of the right arm and left leg.
- Lead aVF: Records the difference in electrical potential between the left leg and the average of the right arm and left arm.
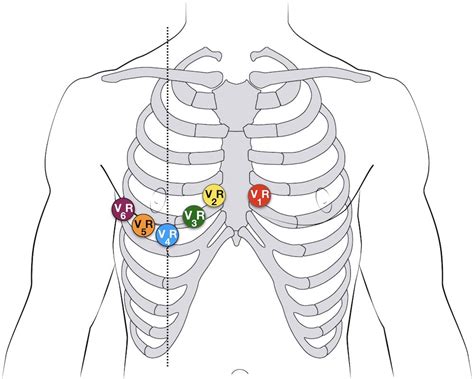
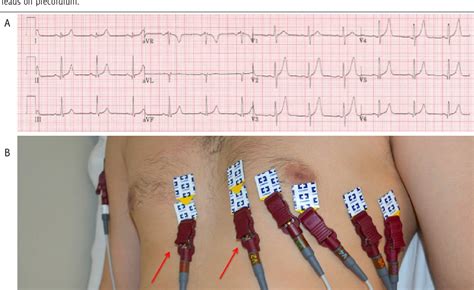
ECG Lead Placement
- Chest leads: Placed on the chest, with V1-V6 leads recording the heart's activity from different angles.
- Limb leads: Placed on the arms and legs, with I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF leads recording the heart's activity from different angles.
ECG Interpretation Pitfalls
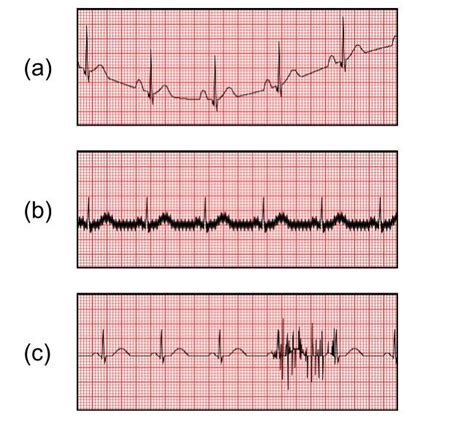
- Artifact: Electrical interference that can mimic ECG abnormalities.
- Lead placement errors: Incorrect lead placement can result in inaccurate ECG readings.
- Patient movement: Patient movement can cause electrical interference and inaccurate ECG readings.

Gallery of ECG-Related Images
ECG Image Gallery
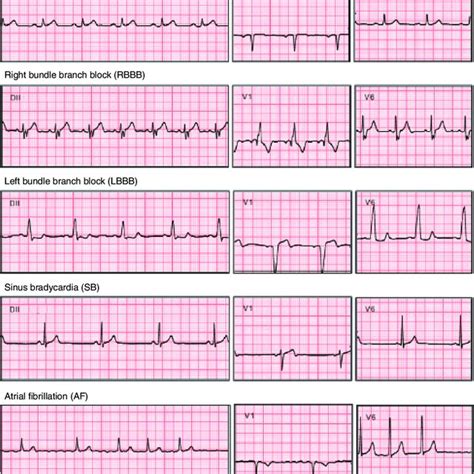



By mastering the basics of ECG interpretation and following the steps outlined in this cheat sheet, you'll be well on your way to becoming proficient in ECG interpretation. Remember to practice regularly, and don't hesitate to seek guidance from experienced professionals if you're unsure about any aspect of ECG interpretation. Happy learning!
We hope you found this ECG cheat sheet for nurses and medical students helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Don't forget to share this article with your colleagues and friends who may benefit from this comprehensive guide.
