Phlebotomy is a crucial medical procedure that involves collecting blood samples from patients for laboratory testing. The phlebotomy order of draw is a critical step in this process, as it ensures that the samples are collected in the correct order to prevent contamination and ensure accurate test results. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to the phlebotomy order of draw, including a printable guide that you can use as a reference.
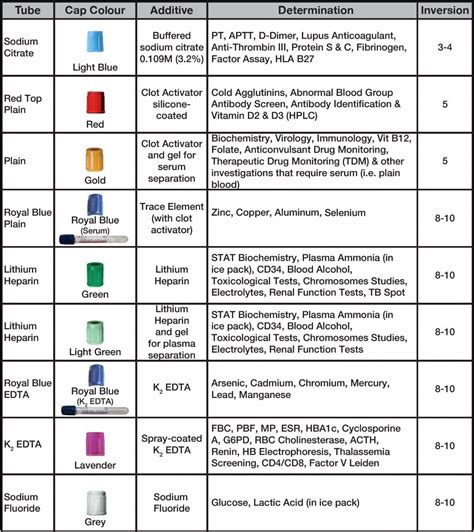
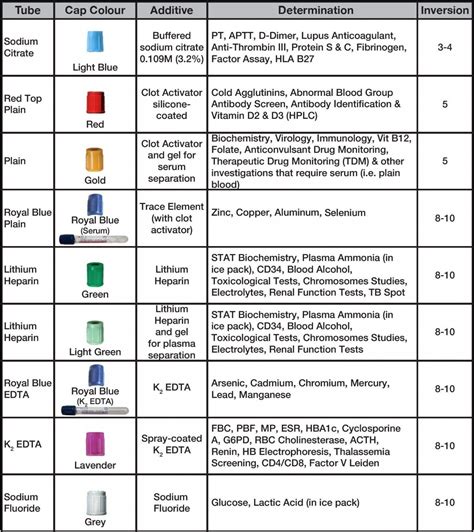
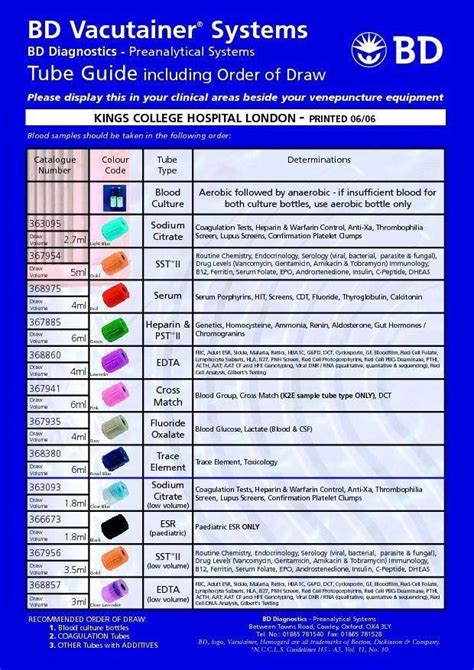
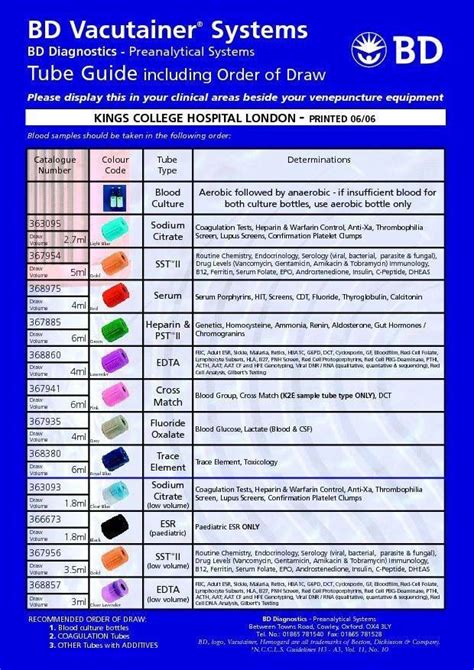
The phlebotomy order of draw is a standardized procedure that outlines the order in which blood samples should be collected. This order is based on the type of additive or anticoagulant used in the collection tube, as well as the type of test being performed. The order of draw is crucial, as it prevents cross-contamination of samples and ensures that the test results are accurate.
Understanding the Phlebotomy Order of Draw
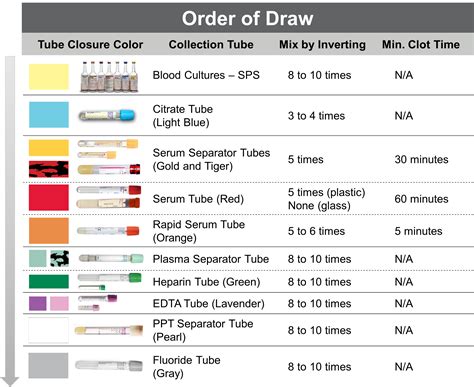
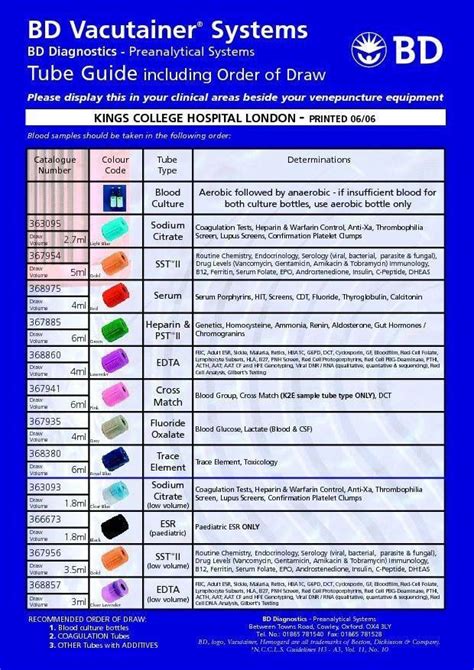
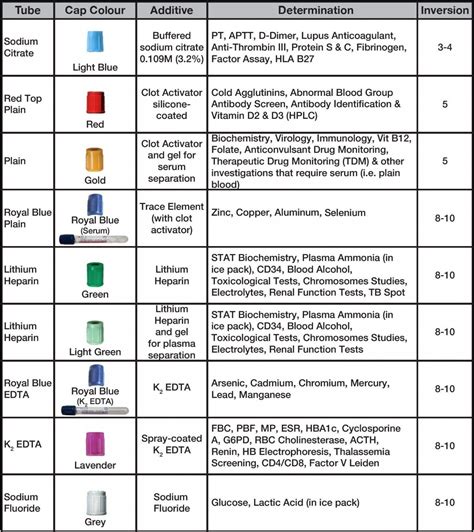
The phlebotomy order of draw is based on the following principles:
- Blood cultures should be collected first, as they require a sterile environment to prevent contamination.
- Tubes with additives or anticoagulants should be collected next, in the following order:
- Blood collection tubes with clot activators (e.g., serum separator tubes)
- Blood collection tubes with heparin or EDTA
- Blood collection tubes with citrate
- Blood collection tubes with oxalate or fluoride
- Tubes without additives or anticoagulants should be collected last.
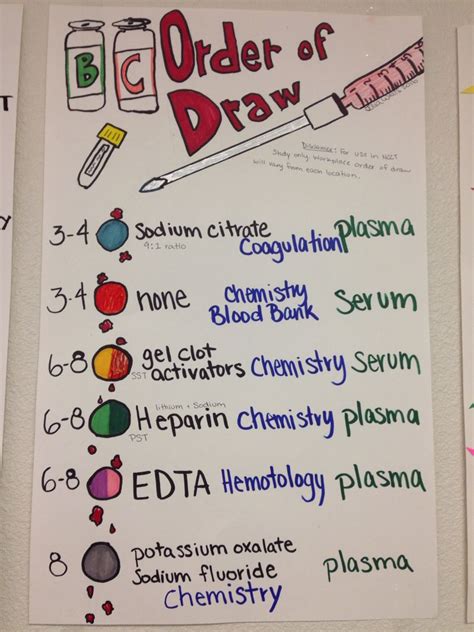
Phlebotomy Order of Draw: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here is a step-by-step guide to the phlebotomy order of draw:
- Blood Cultures: Collect blood cultures first, using a sterile needle and syringe.
- Serum Separator Tubes: Collect serum separator tubes next, which contain clot activators.
- Heparin or EDTA Tubes: Collect heparin or EDTA tubes next, which contain anticoagulants.
- Citrate Tubes: Collect citrate tubes next, which contain anticoagulants.
- Oxalate or Fluoride Tubes: Collect oxalate or fluoride tubes next, which contain anticoagulants.
- Tubes without Additives: Collect tubes without additives or anticoagulants last.

Printable Phlebotomy Order of Draw Guide
Here is a printable guide to the phlebotomy order of draw:
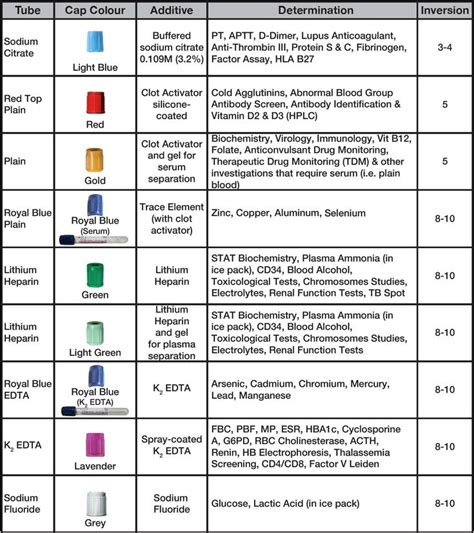
Phlebotomy Order of Draw Guide
- Blood Cultures
- Serum Separator Tubes
- Heparin or EDTA Tubes
- Citrate Tubes
- Oxalate or Fluoride Tubes
- Tubes without Additives
Importance of Following the Phlebotomy Order of Draw
Following the phlebotomy order of draw is crucial to ensure accurate test results and prevent contamination. Failure to follow the order of draw can result in:
- Inaccurate test results
- Contamination of samples
- Delayed or cancelled testing
- Patient harm
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Phlebotomy Order of Draw
Here are some common mistakes to avoid in phlebotomy order of draw:
- Collecting tubes out of order
- Failing to use a sterile needle and syringe for blood cultures
- Not using the correct additive or anticoagulant for the type of test being performed
- Not labeling tubes correctly
- Not storing tubes properly
Best Practices for Phlebotomy Order of Draw
Here are some best practices for phlebotomy order of draw:
- Always follow the standardized phlebotomy order of draw
- Use a sterile needle and syringe for blood cultures
- Use the correct additive or anticoagulant for the type of test being performed
- Label tubes correctly
- Store tubes properly
Phlebotomy Order of Draw Image Gallery
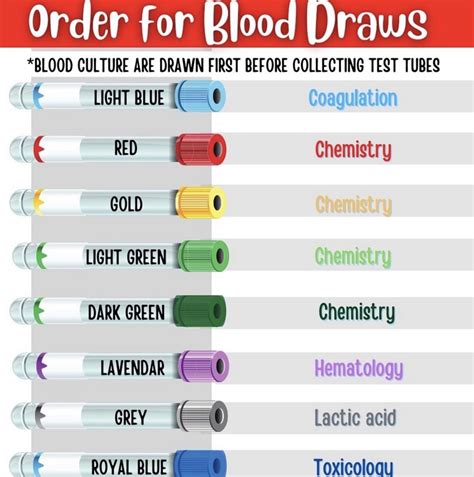

We hope this comprehensive guide to the phlebotomy order of draw has been helpful. Remember to always follow the standardized phlebotomy order of draw to ensure accurate test results and prevent contamination. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your phlebotomy skills are up-to-date and effective.
