Intro
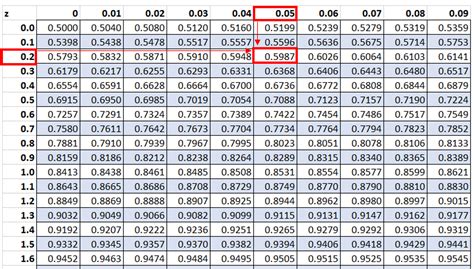
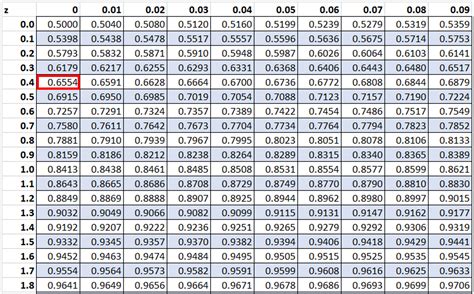
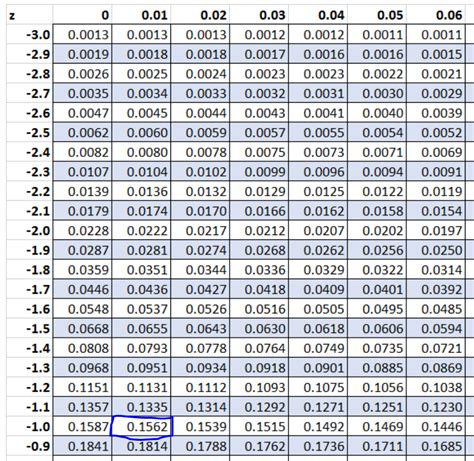
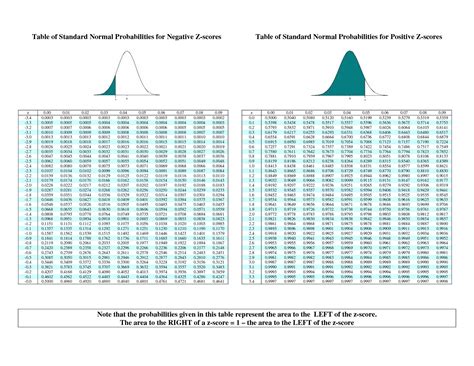
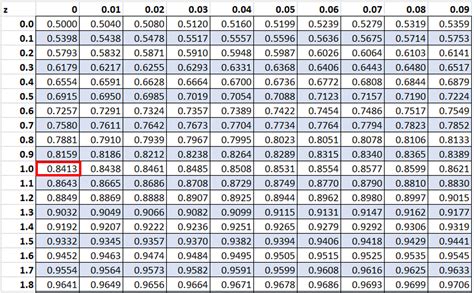
The Z-table, also known as the standard normal distribution table, is a statistical tool used to find the probability of a value falling within a certain range in a normal distribution. A printable Z-table can be a valuable resource for students, researchers, and professionals who work with statistical data. Here, we will explore 7 ways to use a printable Z-table.
Understanding the Z-Table
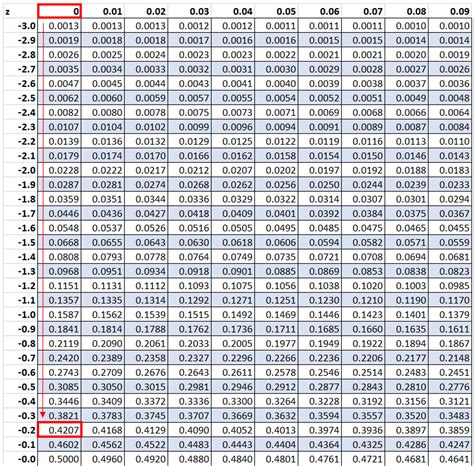
The Z-table is a table of values that shows the area under the standard normal curve to the left of a given Z-score. The Z-score is a measure of how many standard deviations an observation is away from the mean of the distribution. The Z-table is used to find the probability of a value falling within a certain range in a normal distribution.
How to Read the Z-Table
To use the Z-table, you need to know how to read it. The table is organized with Z-scores on the left-hand side and the corresponding probabilities on the right-hand side. The probabilities are listed in rows and columns, with the Z-score on the left and the probability on the right.
7 Ways to Use a Printable Z-Table
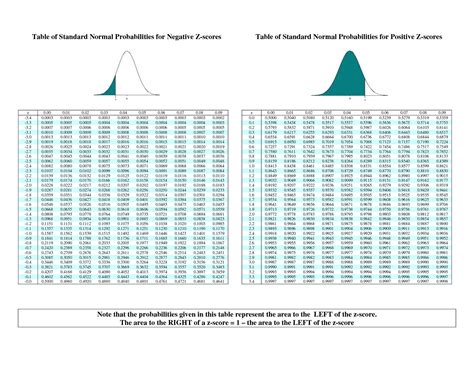
- Finding Probabilities
One of the most common uses of the Z-table is to find the probability of a value falling within a certain range in a normal distribution. For example, if you want to find the probability of a value being less than 1.5 standard deviations above the mean, you would look up the Z-score of 1.5 in the table and find the corresponding probability.
Example
Suppose you want to find the probability of a value being less than 2.5 standard deviations above the mean. You would look up the Z-score of 2.5 in the table and find the corresponding probability.
- Finding Z-Scores
Another use of the Z-table is to find the Z-score corresponding to a given probability. For example, if you want to find the Z-score that corresponds to a probability of 0.05, you would look up the probability in the table and find the corresponding Z-score.
Example
Suppose you want to find the Z-score that corresponds to a probability of 0.01. You would look up the probability in the table and find the corresponding Z-score.
- Comparing Probabilities
The Z-table can also be used to compare probabilities. For example, you can use the table to compare the probability of a value falling within a certain range in a normal distribution to the probability of a value falling within a different range.
Example
Suppose you want to compare the probability of a value being less than 1.5 standard deviations above the mean to the probability of a value being less than 2.5 standard deviations above the mean. You would look up the Z-scores of 1.5 and 2.5 in the table and compare the corresponding probabilities.
- Finding Percentiles
The Z-table can also be used to find percentiles. For example, if you want to find the 95th percentile of a normal distribution, you would look up the Z-score corresponding to a probability of 0.05 and find the corresponding value.
Example
Suppose you want to find the 99th percentile of a normal distribution. You would look up the Z-score corresponding to a probability of 0.01 and find the corresponding value.
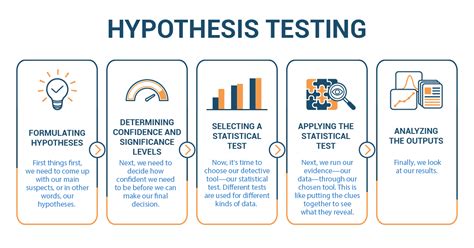
- Testing Hypotheses
The Z-table can also be used to test hypotheses. For example, if you want to test the hypothesis that a population mean is equal to a certain value, you would use the Z-table to find the probability of observing a sample mean at least as extreme as the one you observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
Example
Suppose you want to test the hypothesis that a population mean is equal to 10. You would use the Z-table to find the probability of observing a sample mean at least as extreme as the one you observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
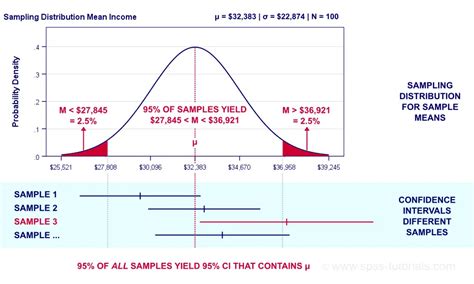
- Constructing Confidence Intervals
The Z-table can also be used to construct confidence intervals. For example, if you want to construct a 95% confidence interval for a population mean, you would use the Z-table to find the Z-scores corresponding to a probability of 0.025 and 0.975 and find the corresponding values.
Example
Suppose you want to construct a 99% confidence interval for a population mean. You would use the Z-table to find the Z-scores corresponding to a probability of 0.005 and 0.995 and find the corresponding values.
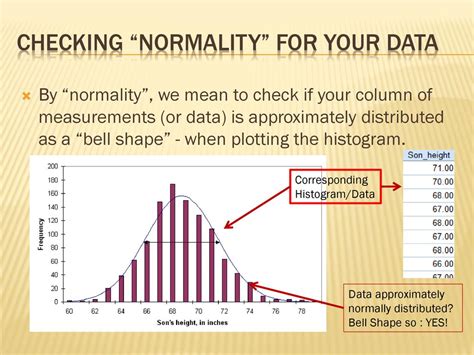
- Checking Normality
Finally, the Z-table can be used to check normality. For example, if you want to check whether a dataset is normally distributed, you would use the Z-table to find the probability of observing a value at least as extreme as the one you observed, assuming that the data is normally distributed.
Example
Suppose you want to check whether a dataset is normally distributed. You would use the Z-table to find the probability of observing a value at least as extreme as the one you observed, assuming that the data is normally distributed.
Conclusion
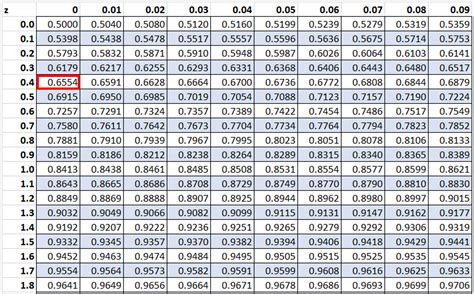
In conclusion, a printable Z-table is a valuable resource for anyone who works with statistical data. It can be used to find probabilities, Z-scores, and percentiles, as well as to test hypotheses, construct confidence intervals, and check normality.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful in understanding the uses of a printable Z-table. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
Gallery of Z-Table Images
Z-Table Image Gallery