Intro
Discover the intricacies of Pulmonary Embolism, a life-threatening disorder affecting the lungs. Learn about its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Understand the risks of blood clots, pulmonary infarction, and the importance of prompt medical attention to prevent complications like respiratory failure and cardiac arrest.
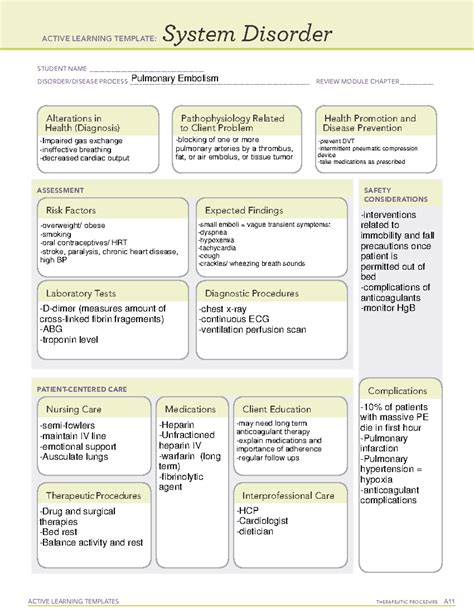
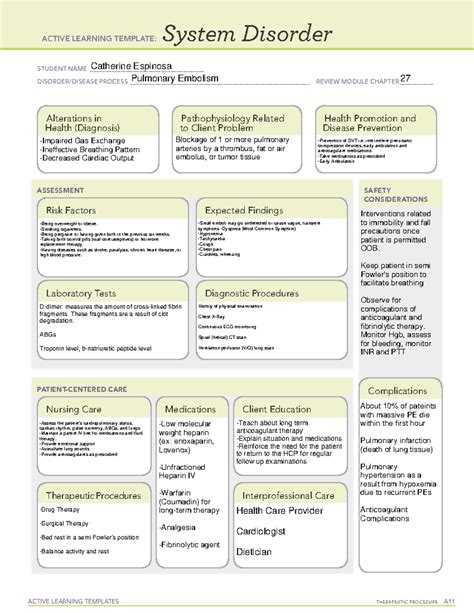
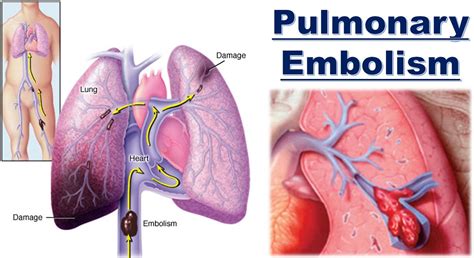
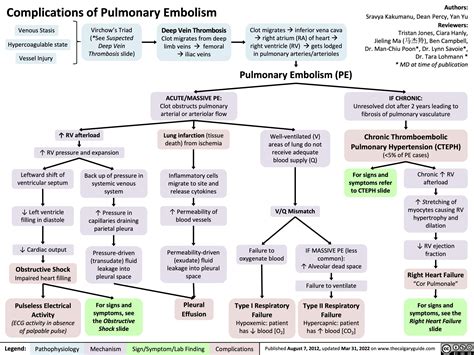
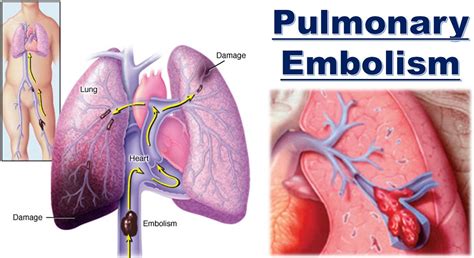
Pulmonary embolism is a serious and potentially life-threatening medical condition that occurs when one or more arteries in the lungs become blocked by a blood clot. This can cause sudden and severe symptoms, and if left untreated, can lead to serious complications, including death. In this article, we will delve into the world of pulmonary embolism system disorder, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What is Pulmonary Embolism System Disorder?
Pulmonary embolism system disorder occurs when a blood clot, also known as a thrombus, forms in a vein and breaks loose, traveling through the bloodstream to the lungs. This can cause a blockage in one or more of the pulmonary arteries, which are responsible for carrying oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. When a pulmonary embolism occurs, it can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Causes of Pulmonary Embolism System Disorder
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing pulmonary embolism system disorder. These include:
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): This is a condition in which a blood clot forms in a vein, usually in the legs.
- Blood clotting disorders: Certain conditions, such as factor V Leiden, can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Trauma: Injuries, such as a broken bone or surgery, can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Immobility: Prolonged bed rest or immobility can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Heart failure: Weakened heart muscle can increase the risk of blood clots.
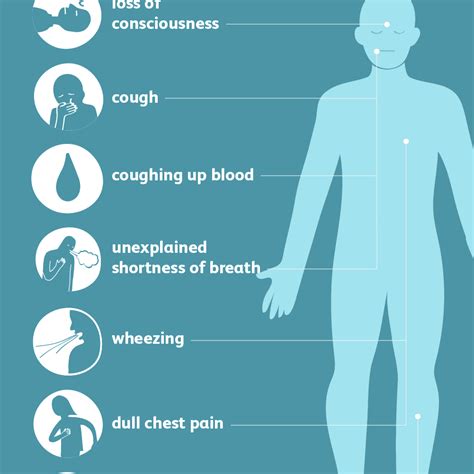
Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism System Disorder
The symptoms of pulmonary embolism system disorder can vary depending on the size and location of the blood clot. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort that worsens with deep breathing or coughing
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Rapid heart rate or palpitations
- Coughing up blood or frothy mucus
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism System Disorder
Diagnosing pulmonary embolism system disorder can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. To diagnose pulmonary embolism, doctors may use a combination of the following tests:
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: This is a specialized X-ray test that can help doctors visualize the lungs and detect any blockages.
- Ventilation-perfusion scan: This test uses a small amount of radioactive material to measure airflow and blood flow to the lungs.
- Pulmonary angiogram: This is a test that uses a special dye to visualize the pulmonary arteries.
- Blood tests: Doctors may use blood tests to check for the presence of certain proteins that can indicate the presence of a blood clot.
Treatment Options for Pulmonary Embolism System Disorder
Treatment for pulmonary embolism system disorder typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Medications may include:
- Anticoagulants: These medications can help prevent the formation of new blood clots and reduce the risk of complications.
- Thrombolytics: These medications can help dissolve existing blood clots.
- Pain relief medications: Doctors may prescribe pain relief medications to help manage symptoms.
Lifestyle changes may include:
- Rest: Doctors may recommend rest and avoidance of strenuous activities to help reduce the risk of complications.
- Compression stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help reduce the risk of blood clots in the legs.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve circulation and reduce the risk of blood clots.
Prevention Strategies for Pulmonary Embolism System Disorder
Preventing pulmonary embolism system disorder requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Strategies may include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding prolonged periods of immobility
- Wearing compression stockings
- Avoiding smoking
- Managing underlying medical conditions

Pulmonary Embolism Image Gallery
Pulmonary Embolism Image Gallery


Conclusion
Pulmonary embolism system disorder is a serious and potentially life-threatening medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and improve their overall health. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of pulmonary embolism, seek medical attention immediately.
